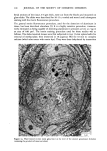
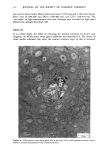
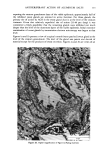
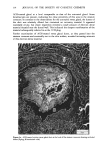
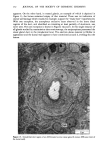
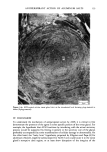
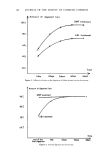
J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 32, 137-152 (May/June 1981) Isolation of melanin pigments from human hair j. c. ARNAUD and P. BOR•, L'Oreal Research Laboratories, Societe L'Oreal, 1 Avenue de Saint Germain, Boite Postale no. 22, 93601 Aulnay-sous-bois, France. Received March 17, 1980. Synopsis The isolation of melanin pigments from human hair requires the SOLUBILIZATION OF KERATIN material. The chemical reagents which have been previously used for this purpose often give rise to impure melanin pigments through side reactions. We propose a new method based on the digestion of human hair with a PROTOLYTIC ENZYME, Proteinase PSF 2019. The enzymatic reaction is carried out at 40øC and results in 90% PROTEIN DIGESTION. A preliminary hair sensitization is necessary to improve the digestion yield. Two procedures have been investigated which enhance the digestion of hair with minimum damage to peptide and disulfide bonds: (1) Treatment of hair with anhydrous dimethylformamide at 120øC and (2) Treatment of hair under reflux with an aqueous solution of lithium bromide. The method has been applied to hair of different racial types. I. INTRODUCTION The isolation of melanin pigment from human hair requires the solubilization of the keratin. In the first reported study of hair pigment, the solubilizing properties of mineral acids were employed (1). Over the years, hydrochloric and sulfuric acids (2,3,5,6) have been widely used for isolating the insoluble melanin pigment from human hair. In these methods the hair was subjected to treatments with very concentrated acids for several days at room temperature or hot acid solutions for a shorter time. Other methods for dissolution of the hair have also been proposed using alkaline solutions. Different alkalies have been tried as hydrolyrics where time, temperature, concentrations and amount are varied (7-11). The PHT method in which the hair sample is maintained at reflux for 24 h in a phenol hydrate thioglycolic acid mixture has also been used by several authors (4,8,12,13). In the present work, we propose a new enzymatic digestion procedure which allows the dissolution of about 90% of the weight of natural hair. 137
138 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS II. EXPERIMENTAL A. MATERIALS 1. Human hair. Virgin human hair collected from hairdressers was used in this study. It was cleaned by washing with 4% lauryl sulfate solution, then rinsed in deionized water and dried in an oven at 40øC (clean hair). 2. Reagents. All the reagents used were of laboratory grade. 3. Enzyme. PSF 2019 is a proteinase available from Soci•t• Oril, 26 rue Berthollet, Paris. It is obtained from a strain of $treptomyces Fradiae which differs slightly from the typical strain described by Waksman (14). PSF 2019 is the active product of Fradiase ©, commercialized by Soci•t• Oril for animal nutrition. B. METHODS 1. DMF--Sensitization of human hair One hundred grams (100 g) of clean (2-cm-long) hair was introduced into a 5-liter flask containing 2 liters of hot (120øC) DMF. The mixture was heated for 3 to 5 h at 120øC after which the hair was isolated by filtration. The hair was rinsed several times with deionized water, soaked overnight, washed with ethanol, then with diethylether and allowed to dry at room temperature. A preliminary test on 1 g of hair in 20 ml hot DMF, and subsequent digestion with the enzyme is recommended in order to choose the best time of sensitization. 2. LiBr--Sensitization of human hair. One hundred grams (100 g) of clean cut hair (2-cm-long) were treated at reflux with 2 liters of aqueous LiBr (10M/l) for 1 to 2 h. The treated hair was filtered, then washed with hot deionized water (60øC), rinsed several times with cold deionized water, ethanol and diethylether, and allowed to dry at room temperature. It is recommended to choose the best time of sensitization after a preliminary test on 1 g of hair refluxed in 20 ml LiBr solution then digested with the enzyme. 3. Digestion procedure. The enzymatic solution was prepared just before use, using following formula: --Purified lyophilised PSF 2019 (16,500 Anson units/mg) ....................................... 1.8 g --Boric acid (H3BO3) .................................................................................................... 22.5 g --NaOH (1N) ................................................................................................................ 200 ml --MgCI2 - 6 H20 ........................................................................................................... 0.03 g --Demineralized water s.q ........................................................................................ 2000 ml The pH was adjusted to 9.0. 100 g of (DMF or LiBr) sensitized cut hair was immersed in the enzymatic solution and maintained at 40øC. A double bladed propeller provided continuous stirring. The flask was closed with 2 sheets of laboratory parafilm © in order to limit the evaporation. Each day, the liquid height in the flask was checked and demineralized water added, if necessary. For the DMF-sensitized hair, the digestion was stopped after
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)