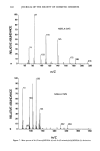
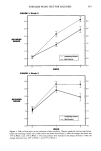
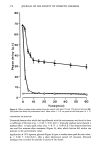
FOREARM WASH TEST FOR MILDNESS 363 Table III Effect of Test Design on Test Sensitivity* Study 5.' Base size = 115, pair test, IO-second exposure, two washes per day Clinical skin grades Product Redness Dryness Dew point Irritating control 1.43 1.97 Mild control 1.15 1.72 Difference 0.28 0.26 p-value 0.003 0.0001 27 ø F. Study 6.' Base size = 30, pair test, 90-second exposure, two washes per day Clinical skin grades Product Redness Dryness Dew point Irritating control 1.59 2.88 Mild control 1.27 2.35 Difference 0.31 0.53 p-value 0.054 0.004 27 ø F. Study 7.' Base size = 30, pair test, 90-second exposure, four washes per day Clinical skin grades Product Redness Dryness Dew point Irritating control 1.52 2.26 Mild control 0.96 1.56 Difference 0.56 0.70 p-value 0.0001 0.0001 56 ø F. * Irritating and mild control products are the same for all three studies. Studies 6 and 7 were conducted for the same two products under different dew point conditions. Study 6 used two daily washes and Study 7 used four. Significant differences were observed between the irritating and mild control products. EFFECT OF SEX AND SKIN COLOR (STUDY 8 AND STUDY 9) Data from Studies 8 and 9 were used to demonstrate differences between the males and females with regard to the clinical response to soap treatment. Table IV compares changes in skin grades for two products which are known from previous testing to differ in skin mildness. The final skin grades for the two products, the differences and the p-values from the statistical analysis, are given for both male and female subjects. The test products produce larger differences in females than in male subjects for redness, dryness, and smoothness. However, we continue to include male subjects in the test populations because their response is similar to that of females and their inclusion makes the studies more representative of the general population. The assignment of test product pairs is balanced with respect to the sexes. Skin color also affects the results of a product comparison clinical study. Trained graders
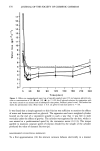
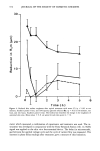
364 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table IV Effect of Sex on Clinical Test Sensitivity (Clinical Skin Grades Average Change in Two Weeks Studies 8 and 9) Class Base Product size Smoothness Redness Dryness Females Males Irritating control 68 1.26 2.64 2.64 Mild control 46 .73 1.65 1.77 Difference .53 ß 99 .87 p-value .008 .0001 .0001 Irritating control 71 1.06 2.52 2.27 Mild control 52 .67 1.92 1.60 Difference .39 .60 .67 p-value .019 .005 .0014 have noted that it is more difficult to judge redness on forearms of black subjects, and the data (not shown) support this observation, i.e., larger differences in redness are observed between control products tested on white subjects than on black subjects. There was no difference attributable to skin color in the evaluation of dryness or smoothness. CORRELATION OF SKIN CONDITION WITH TEWL AND SUBJECT SELF EVALUATIONS Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements were obtained for the ten products in Study ! (Table I). Correlations were found with redness (r = 0.80) and dryness (r = 0.80) grades. Subsequent studies have shown even stronger correlations (r = 0.89-0.97) with skin condition. The milder products produced lower TEWL values, indicating a better stratum corneum barrier function. Differences in skin condition detectable by expert skin graders have also been observed by the subjects themselves. A two-week clinical test was conducted in which several products were compared to a common control in a pair test design. Linear regression analyses demonstrate that the subjects' perceptions of their skin condition correlates well with the expert grades, i.e., soft skin with smoothness (r = 0.89), mildness with redness (r = 0.92), and skin flakiness with dryness (r = 0.90). COMPARISON WITH OTHER METHODS The mildness to the skin of two products has been assessed with both the forearm wash method and the chamber test. A comparison of the two methods, for a mild control and an irritating control (Table V), indicates that the forearm wash test demonstrates signif- Table V Comparison of Forearm Wash Test and Chamber Test Forearm wash test Chamber test Product total score Redness Dryness Irritating control 4.60•ns 1.61 • 1.82• Mild control 4.90-/ 1.28 J s 1.51 / s Difference - 0.30 0.33 0.30
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)