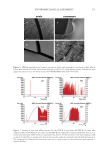
319 Microsponge Loaded Topical Gel into it under stirring to form a uniform dispersion and cooled to room temperature (28). Drug benzoyl peroxide–loaded microsponge formulation (1 g) was added and dispersed into the solution under stirring for 10–15 minutes (see Table I). Then propylene glycol and silicone oil were added and mixed finally, the weight was adjusted with purified water with continued stirring for 15 minutes (29). EVALUATION PARAMETERS FOR MICROSPONGE LOADED TOPICAL GEL Determination of pH. The pH of the formulation was determined by using a digital pH meter. The pH meter electrode was washed with distilled water and then dipped into the formulation to measure pH. This process was repeated three times (29, 30). Determination of spreadability. Glass slides with standard dimension (length of 6.0 cm) were taken. Topical gel formulation was placed on the one side of the glass slide and sandwiched with the help of another slide. We removed the adhering gel on the outer surface of the glass slides by wiping (31). Slides were fixed in a stand so that only the upper slide could slip off freely without any disturbance by force of weight (20 g) tied to it. Time taken for the movement of upper slide to the distance of 6.0 cm was measured (32). Measurement of spreadability was done in triplicate and calculated by using the following formula: Spreadability (m×l)/t, =where, S =spreadability m =weight tied to the upper slide (20 g) l =length of the glass (6.0 cm) and t =time taken in seconds. Measurement of viscosity. The viscosity of the formulated batches was determined using a Brookfield Viscometer with spindle 63 (SRIHER, Chennai, India). The formulation whose viscosity was to be determined was added to the beaker and allowed to settle down for 30 minutes at the assay temperature (25 ± 1°C 33). Drug content study. A drug content study was done to determine the amount of the drug present in the certain quantity of the formulation. One g of the formulation was taken into a 10 mL volumetric flask. Methanol was added in to make up the volume and shaken well (23). The volumetric flask was kept for 2 hours and shaken well in a shaker to mix it Table I Composition of Microsponge Loaded Topical Gel S. No. Ingredients Quantity 1. Benzoyl peroxide–loaded microsponge 1 g 2. Carbopol 934 1 g 3. Methyl paraben 0.2 g 4. Propyl paraben 0.02 g 5. Disodium edetate 0.1 g 6. Silicone oil 1 mL 7. Propylene glycol 5 mL 8. Purified water Q.S 100 mL
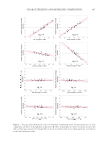
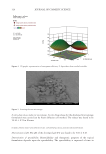
320 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE properly. The solution was passed through the filter paper and filtered with the mixer then measured absorbance by using a spectrophotometer at 235 nm (12). DRUG CONTENT SAMPLE ABSORBANCE STANDARD ABSORBANCE =×100 IN VITRO DRUG RELEASE STUDIES FOR MICROSPONGES LOADED TOPICAL GEL The dialysis membrane was used in Franz diffusion cell (19). The formulation containing benzoyl peroxide–loaded PLGA (microsponges) was applied on the dialysis membrane and then fixed in between the donor and receptor compartment of the diffusion cell. The receptor compartment contained phosphate buffer (100 mL) with a pH of 5.5. The diffusion medium temperature was thermostatically controlled at 37° ± 1° by surrounding water in jacket, and the medium was stirred at 500 rpm by a magnetic stirrer (20). The samples were withdrawn at predetermined intervals and replaced by an equal volume of fresh fluid. The samples withdrawn were spectrophotometrically estimated at 235 nm against their respective blank (21). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION DETERMINATION OF SOLUBILITY PROFILE Solubility of the benzoyl peroxide drug was found to be poorly soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetone (10). CALIBRATION CURVE Benzoyl peroxide is a topical antibiotic used in the treatment for acne vulgaris. The proposed analytical method was found to be simple and accurate for the estimation of benzoyl peroxide. The drug samples were analyzed by ultraviolet spectroscopy (235 nm) using methanol as a solvent. We concluded that the suggested method showed high linearity in organic solvent as shown in Table II and Figure 2. Moreover, this was found to be a precise and inexpensive method that can be employed for the routine quality control of benzoyl peroxide in pharmaceutical formulations (12). EVALUATION OF MICROSPONGE INCORPORATED BENZOYL PEROXIDE Experimental design and optimization of formulation. In total, 14 formulations were designed based on a CCD and characterized for entrapment efficiency and in vitro drug release. Entrapment efficiency was carried out for all the developed formulations and, based on the run, the formulation containing the highest entrapment efficiency was selected for further studies. The in vitro drug release of the developed microsponge incorporated benzoyl peroxide formulation was carried out by a diffusion method (33). Among all the developed formulations with CCD design, formulation containing PLGA and drug (benzoyl peroxide) F1 showed a sustained drug release of 50.42 in 8 hours when compared with other formulations. Entrapment efficiency (EE) and in vitro drug release (24) is shown in Table III.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)