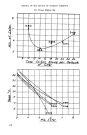
MOLECULAR INTERACTION IN BULK SOLUTION OF SODIUM DODECYL SULPHATE (SDS) AND LONG CHAIN ALCOHOLS By R. MATALON, PH.D.* -- THE MOLECULAR interaction be- tween long chain alkyl sulphates and long chain alcohols has been investi- gated at the air-water interface using the monolayer technique. The alcohol is spread on the water surface and the detergent is injected under- neath '. The interaction is then studied using various means such as Iollow•ng the pressure rise of the rnono.layer .kept at constant area = or the expansion of the monolayer kept at constant psessure. This study is limited to those alcohols which lead to a stable monolayer on the water surface. When the alcohol is water-soluble, other methods may be used. The precipitation generally observed be- tween anionic (SDS) and cationic (CTAB) compounds has been shown '• to be inhibited by the presence of polar compounds, i.e. long chain alcohols such as octyl alcohol and nonyl alcohol present in equimolecu- lar ratio with the artionic detergent. Under these conditions the long chain alcohol adlineates with the anionic detergent, producing a micelle struc- *Department of Colloid Science. University of Cambridge. 122 ture of greater fluidity and tending to inhibit the formation of a solid precipitate between the artionic and cationic compounds. The precipita- tion is also inhibited with the shorter chain alcohols C7, C6, C5, etc., provided that these alcohols are present in greater atnounts. These observati{ms suggest that the association ionic detergent-- polar compound is governed by the hydrophobic -- hydrophilic balance in the alcohol. The present work brings further evidence confirming this hypothesis. The formation of a mixed structure SDS -- alcohol should decrease the electrical repul- sion forces usually acting between the ionised polar group (--SO 4 ) and this should result in a greater stability of the structure in the adsorbed layer. Figures 1 and 2 show that the •' SDS is foa•n volume of Icc :•o• increased by the presence of alcohols. A marked stabilisation of the foam is also observed with CsOH and C,OH. This is easily demonstrated by the' stability of the laminae to drainage in the rectangular wire platinum frame 4. The results ob-
Figure 1. See caption on page 125 • ,' O-"•"- \O ' ß }oo -. .. , Figure 2. Increase in Foam Volume induced by'•lcohols 123
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)