REVIEW OF CHLORINE-HAIR INTERACTION 363 fibers. In chlorinating wool, Valk (22) found amino acid residues in the spent chlorine reaction liquors at all Ph levels. It has been suggested that peptide bond cleavage can occur in wool at the tyrosine residue. Studies on the bromination of tyrosine peptides have indicated a probable mechanism (Figure 3) (42,43). Tyrosine peptides (I) are readily brominated in bromine water to 3,5-dibromotyrosyl residues (II). Further bromination ruptures the tyrosyl peptide bond by way of tribromodienone (III) and iminolactone (IV) intermediates, resulting in a new N-terminal peptide fragment and a dibromodienone spirolactone (V). The dibromodienone spirolactone (V) ultimately results in the C-terminal 3,5 di- (I) (11) (111) R'-CH-CONHR R'-CH-CONHR •s•,,.• • I I I HE CH 2Br CH + O• "•CH R' I 2 2 . 12 Br • I Br'" •Br Bd • •Br OH OH O Br"' •Br Br"' •Br + Hfin 3 (V) IHBr R'-CH-COOH I Br I Br OH Figure 3. Mechanism of cleavage of the tyrosyJ peptide bond with bromine water.
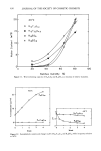
364 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS bromotyrosyl residue (VI). This reaction appears more likely to take place in the acid region than in the neutral or the alkaline regions. The reaction proposed by Gold- schmidt (44) may be the more prevalent route in the alkaline region (Figure 4). The hydrogen abstraction associated with the formation of lanthionine could also lead to peptide bond cleavage under alkaline conditions. EFFECT ON CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF KERATIN FIBERS CHEMICAL REACTIVITY The effect produced by halogens on keratin fibers has been characterized by a number of chemical tests. Alkali solubility, indicating the extent to which disulfide fission has taken place, has been found to be the greatest when the chlorination treatment was carried out in the region between pH 4 and 7 (2, 13,22,45). Urea-bisulfite solubility, indicating the extent to which both peptide and disulfide bond cleavage have taken place, has been found to be higher in the acid region, and it decreases with increase in pH of the chlorine solution (13,22,46). The base binding capacity of wool has also been found to increase greatly with chlorina- H NCHCONHCCONHCHCO H R R' R" NaOBr I .CH."CO=H NH , NaOBr Figure 4. Oxidative degradauon of peprides at the N-terminal amino acid by hypobromite.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)