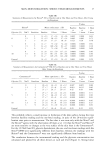
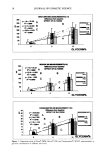
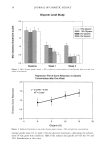
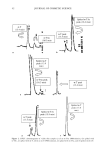
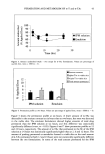
CATIONIC POLYMERS 53 and Robbins (6), involved attaching the root end of a hair fiber to a load cell of an Instron tester. The fiber was weighted at the tip end and partially wrapped around two man- drels. The mandrels were attached to the crosshead of the Instron tester, and the frictional tension was measured as the mandrels moved against the fiber. Temperature and humidity are the two main experimental variables that must be controlled in friction tests. The wrap angle of hair and the material for the mandrels have to be carefully selected to achieve utmost sensitivity. Additionally, the variability of hair fibers often impacts the data consistency. EVALUATION OF CATIONIC POLYMERS Since the invention of conditioning shampoos, shampoos containing cationic polymers have been disclosed in numerous patents. In fact, polyquaternium-10 and cationic guar have become the two most popular cationic polymers in many different commercial hair products. The generic structures of polyquaternium-10 and cationic guar are depicted in Schemes la and lb, respectively. Polyquaternium-10 is a quaternary ammonium salt of hydroxyethyl cellulose reacted with a trimethyl ammonium substituted epoxide. Guar gum is a polysaccharide consisting of linear polymannose with a galactose side chain on an alternating mannose unit. Cationic guar is produced by the same chemical deriviti- zation of hydroxyl groups. Faucher and Goddard have demonstrated that the adsorption of cationic hydroxyethyl cellulose onto hair occurs rapidly (7). The uptake is 50 times that of the uncharged polymer. It is widely believed that in the presence of surfactants, the coacervate forma- tion in conditioning shampoos, body washes, and soap bars enhances polymer adsorption to keratinous substrates. The polymer-surfactant interaction influences both the adsorp- tivity and conformation of adsorbing macromolecules (8). At low and intermediate concentrations, anionic surfactants such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) depress the polymer adsorption. However, the quantity of polymer JR adsorption is restored at higher SDS concentration (9). Even in the presence of excess anionic surfactant, cationic polymer can still deposit on hair (10). Hannah and coworkers have also shown that the coacervate complex formed from 0.1% polymer JR and 1% SDS is strongly bound to the hair (11). Cationic polymers deposit on the hair, either in the form of neat polymer or polymer/ surfactant complex. To some extent, the deposited thin layer can be regarded as a coating on hair. Therefore, the knowledge of film properties should allow one to predict the performance of the polymer on the hair. Gloss, opacity, and friction results imply OH OH CH3 CI' I Scheme la. Generic structure of polyquaternium-10.
54 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE OH CH. ,.,, _,-- o OH 0 --0 --0 0 0 b [ I • I I Jn Scheme lb. Generic structure of cationic guar. relevant connections to shine and combing properties of human hair treated with cat- ionic polymers. EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS AND FILM PREPARATIONS Polyquaternium-10 and cationic guar samples were obtained from Amerchol Corpora- tion and Rhodia, respectively. The samples used in this study are listed in Table I. The polymers from the same chemical class are categorized as H, M, and L (high, medium, and low) for both molecular weight and cationic substitution. For example, guar (L/H) denotes relative low molecular weight and high cationic charge. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was purchased from ACROS/Fisher Scientific (99%). All chemicals were used as received without further purification. Polyquaternium-10 and guar (L/H) were dissolved at 6% by weight in double de-ionized water. The only exception to this was guar (H/H), which was prepared at 1.5% because it gelled at higher concentrations. The polymer/surfactant coacervate gels were prepared by adding SDS slowly to a 1% polymer solution under agitation until the maximum viscosity was Table I Polyquaternium-10 and Cationic Guar Samples Sample Cationic reference Polymer INCI name Molecular weight substitution PQ-10 (L/H) UCARE JR125 Polyquaternium-10 Low High PQ-10 (M/H) UCARE JR400 Polyquaternium-10 Medium High PQ- 10 (M/M) UCARE LR400 Polyquaternium- 10 Medium Medium PQ- 10 (M/L) UCARE LK400 Polyquaternium- 10 Medium Low Guar (H/H) Jaguar C17 Guar hydroxytrimonium High High chloride Guar (L/H) Jaguar C2000 Hydroxypropyl guar Low High hydroxylpropyl trimonium chloride
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)