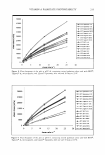
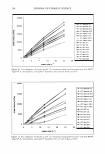
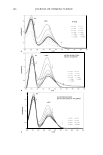
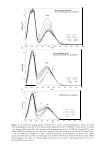
ETHOSOMAL AND LIPOSOMAL DISPERSIONS ,, .-� .,. ... �� � .... , 41 'If 01 , . ' '. " , ,, :- :-..., �·· 1"'['.• la � ·-.. \ ··:--:' '��··"/, ,, 7 1 ,�t � _' ' _:��· 1 ... ,, l ... , "'·-: -�,:cc_,'•�-:, '!;,- ,, \ � . "l ' �-- \ 1t••" .. "t' �½...' • .. � \ ' ·�-· '\, l 't � �' ' . I -., ;t'-.... 1, · .. ....:r'Y""' - • ,. I\ '.:, . �"� ! I ,, 259 Figure 1. Freeze-fracture electron micrographs of liposomal dispersion (panel A), ethosomal 20% disper sion (panel B), and ethosomal 40% dispersion (panel C). Liposomal and ethosomal dispersions were sub jected to extrusion through 200-nm-pore-size membranes. The bar equals 510 nm. After production of dispersions, free azelaic acid was not separated from the encapsulated one since azelaic acid, due to its amphiphilic nature, aims toward partitioning rapidly between the internal and external spaces of ethosomes or liposomes. During the sepa ration process, performed by gel permeation chromatography, the concentration gradi ent, due to the removal of the nonencapsulated drug, leads to leakage of azelaic acid from the ethosomes and/or liposomes, thus preventing the correct evaluation of encapsulation efficiency and finally resulting in a progressive decrease in the total azelaic acid con centration. For these reasons, the whole preparation was employed for DSC and in vitro release rate studies. DSC studies. In order to gain some information about ethosome properties, free energy measurements of the vesicle bilayers were conducted by DSC studies. It is well known that DSC measures the temperature dependence of the excess heat capacity of a system due to thermal capacity. The heat capacity curves of liposomes that undergo such transitions contain information on the enthalpy and entropy of these transitions. In particular, the main transition temperature (Tm) is the gel-to-lipid-crystal transition, which is a rather rapid transition that can be described in equilibrium thermodynamic terms during DSC experiments. Ts is a very subgel transition (Ts = Tm- 30°C) that is not very well characterized in molecular terms (14). Table III reports transition tem peratures (Tm and Ts) of empty and AA-containing vesicles, as calculated from DSC thermograms. In particular, the Tm of empty liposomes was found higher than 2.7 ° C and 5.8 ° C with respect to ETHO 20 and ETHO 40, respectively. These results are in agreement with the findings of Touitou and colleagues (5,6), suggesting that the etho- Table III Transition Temperatures of Vesicles as Determined by DSC LIPO ETHO 20 ETHO 40 Tm Empty vesicles + 11.5 ° c +8.8°C +5.7°C Tm: main thermal transition temperature. Ts: subtransition temperature. Ts/Tm Azelaic acid-containing vesicles -10.s00+11.5 ° c -10.2°C/+9.0°C -6.7 ° C/+ 7.5 ° C
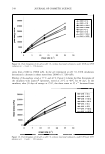
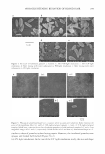
260 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE somes are in a more fluid state than vesicles in the absence of ethanol. The lower Tm displayed by ETHO 40 (5.7 ° C) with respect to ETHO 20 (8.8°C) can be ascribed to the higher ethanol concentration that provides increased vesicle malleability. Moreover, one can notice that empty vesicles display positive Tm values both for liposomes and for ethosomes, while in the case of AA-containing vesicles, thermograms show both a negative Ts and a positive Tm, indicating the presence of an endothermic as well as an esothermic peak. This result is consistent with the hypothesis that the presence of AA within the dispersions can affect vesicle structure, leading to some changes in their softness. 3500 A 3000 � 2500 0 - C) � 2000 � -0 1500 [fl Q) en / as �� Q) a 1000 cc 500 /t ,(r 0 0 5 1 0 1 5 2 0 25 square root of time (minutes) 3500 B 3000 � 2500 0 - C) 2000 � � 1500 -0 Q) � -JQ en as Q) 1000 'SJ.- a :si- cc � 500 0 0 5 1 0 1 5 20 2 5 square root of time (minutes) Figure 2. In vitro release rate kinetics of azelaic acid vehiculated in an ethanol solution (�) or in liposomal (v), ethosomal 20% (0), and ethosomal 40 % (0) dispersions. Experiments were performed by a cellulose ester membrane with 0.6-µm pore size and !PB/ethanol 70:30 (v/v) as receptor phase. The reported results represent the mean values ± SD of six independent experiments.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)