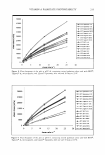
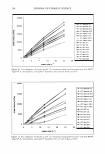
J. Cosmet. Sci., 55, 311-312 (May/June 2004) Abstracts International Journal of Cosmetic Science Vol. 26, No. 1, 2004* Objective Determination of Fatigue Development Following Sun Exposure Using Advanced Trail Making Test Toshia Horikoshi, Koji Matsue, Takumi Takahashi, Hiroaki Ishii, Ken-ichi Yamada, Shoji Hayashi, Mitsuharu Yabune, Motoko Murakami, Osami Kajimoto·. Cosmetics Laboratory, Kanebo Ltd. SOIKEN Inc. Center of Health Care, Osaka University of Foreign Studies Sun exposure during leisure activity evokes fatigue. We employed the Advanced Trail Making Test (ATMT), a recently developed objective method of evaluating brain function performance used to measure mental fatigue, for objective determination of fatigue development caused by solar exposure to the human body. First, a survey of consumer awareness was performed, and fatigue development from solar exposure was generally recognized in both summer and spring. In the field test, 15 males (26 to 41 years old) received sun exposure equivalent to 100 kJ/m2 of ultraviolet radiation 3 to 4 times each day for 3 days, during which the subjects wore a short sleeve shirt and short pants, and covered their head with a towel. A significant increase in scores for subjective sense of fatigue was observed in the evening of all 3 days following sun exposure and on the fourth day, which had no exposure, as well as in the morning of the third and fourth days, as compared with those periods during the control week, which did not have experimental solar exposure. ATMT showed a significant increase in average value in the evening of the first and second days following sun exposure, as well as in the morning of the third and fourth days. In addition, increases in body temperature and heart rate were observed during the exposure periods. Multiple regression analysis of subjective feelings results showed that fatigue caused by solar exposure was qualitatively different from that in the control week. These results suggest that brain function performance declined following solar exposure as did fatigue development. ATMT results may be useful for quantitative and objective evaluation of mental fatigue caused by sun exposure, along with development of sun care products for the prevention of solar-caused fatigue. Dry Skin and Impairment of Barrier Function Associated With Itch- New Insights Gil Y osipovitch Department of Dermatology, Wake Forest University Medical School, Winston Salem, NC 27157, USA Itch is a common symptom in dry skin related to inflammatory skin diseases, normal ageing and systemic diseases such as chronic renal failure, and HIV. However correlations between itch and objective measures of barrier function and skin dryness such as skin hydration and transepidermal water loss have been rarely found. Recent experimental evidence indicates that damage to the stratum corneum with acetone/ether and water elicits a scratching response in mice and rats. These responses correlate to the number of PGP 9.5 immunoreactive fibers in the epidermis and to FOS like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord. Other neuromediators involved in the pathogenesis of itch in dry skin are nerve growth factor (NGF), muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and opiates. Serine proteases such as tryptase and their respective proteinase activating receptor 2 (P AR2) recently found both in skin and nerves of patients with atopic eczema suggest that these molecules may have a role in itch in dry skin. This has also been exemplified in the itchy and hyperkeratotic phenotype of the stratum corneum chymotryptic (SCCE) transgenic mouse model, which is over-expressing a serine protease. Developing inhibitors to these neuropeptides and mediators may be an attractive strategy for anti-itch treatment. The significant progress made in development of moisturizers may have an additional benefit in reducing the itch associated with dry skin. Formulating * These abstracts appear as they were originally published. They have not been edited by the Journal of Cosmetic Science. 311
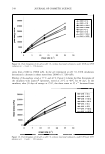
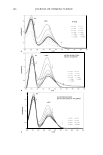
312 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE topical combination therapies containing moisturizers and anti-pruritics can significantly reduce the itch associated to dry skin. This paper will review the current clinical knowledge on the association between dry skin and itch and the recent advances in understanding the pathophysiology of this problem. Moisturizing Potentials Of Ascorbyl Palmitate and Calcium Ascorbate In Various Topical Formulations D. Goniillii, G. Y ener , M. Dner and T. Incegiil Istanbul University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology , 34119 istanbul, Turkey The aim of this study was to use two of Vitamin C derivatives, lipophilic ascorbyl palmitate and hydrophilic calcium ascorbate to determine their skin hydrating effects for the first time. For this purpose, anhydrous cream, gel and w/o emulsion were prepared and applied to the volunteers' inner forearms. A commercial topical preparation containing a known moisturizer, Vitamin E was also chosen and used for comparison. Moisture contents of the skin were measured by using comeometer. Rheological Characterization of Hair Shampoo in The Presence of Dead Sea Salt Basim Abu-Jdayil, Hazim A Mohameed, Maha Sa'id and Tamara Snobar Department of Chemical Engineering, Jordan University of Science and Technology P.O. Box: 3030, 22110 Irbid, Jordan In Jordan, a growing industry has been established to produce different types of Dead Sea (DS) cosmetics that have Dead Sea salt ( contains mainly NaC/,KC/,MgC/ 2 ) in their formulas. In this work, the effect of DS salt on the rheology of hair shampoo containing the sodium lauryl ether sulfate as a main active matter was studied. The effects of DS salt and active matter concentration, and the temperature and time of salt mixing on the rheological properties of hair shampoo were investigated. The salt-free shampoo showed a Newtonian behavior at 'low active matter' (LAM) and shear thinning at 'high active matter' (HAM). The presence of DS salt changed the rheological behavior of LAM shampoo from Newtonian (for the salt-free shampoo) to shear thinning. On the other hand, at the behavior of HAM shampoo switched from shear thinning to Newtonian behavior in the presence of high concentration of DS salt. The addition of DS salt increased the apparent viscosity of shampoo to reach a maximum value that corresponded to a salt concentration of 1.5 wt%. Further addition of DS salt led to a decrease in the shampoo viscosity to reach a value less than that of the salt free sample at high salt concentration. Changing the mixing temperature (25 45 °C) and mixing time (15 - 120 min) of DS salt with shampoo has no significant influence on the rheological behavior. However, the mixing process increased the apparent viscosity of salt free shampoo. The power law model fitted well the flow curves of hair shampoo with and without DS salt. Detection and Quantitation of Apocrine Secreted Odor Binding Protein on Intact Human Axillary Skin Ronald B. Jacoby, John C. Brahms, Shamim A Ansari, Jairajh Mattai Colgate-Palmolive, Co. Personal Care Products Division, Piscataway, NJ, USA A proposed mechanism of axillary malodor formation is bacterial interaction with secreted odor carrier proteins leading to the release of volatile odor molecules. One primary volatile odor molecule, 3- methyl-2-hexenoic acid, is secreted into the apocrine glandular lumen bound to two carrier proteins known as Apocrine Secretion Odor-Binding proteins (ASOBI and ASOB2). The objective of this study was to develop a biological method to detect and quantify ASOB2 in-vitro and on intact axillary skin. The proteins present in pure apocrine secretion were separated via SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electro-blotted, and reacted with antibodies to detect ASOB2. The results of this study demonstrate that ASOB2 shares immunologically homologous epitopes with the human serum protein, apolipoprotein-D (apo D). Axillary secretions and baseline microflora were collected from two groups of panelists 6 hours after showering with a non-antibacterial soap. The extracts were fractionated by SOS-PAGE. ASOB2 was detected selectively by Western blot using a monoclonal mouse-anti-human apolipoprotein-D antibody and quantified on human axillary skin using the presented methods. Axillary ASOB2 concentration varied among individuals (0.1 - 4.1 µg cm" 2 ) with significant differences (p0.05, ANOV A) seen between those of Chinese descent and non-Chinese descent. Panelists of Chinese ancestry did not show significantly lower baseline microflora levels when compared to non-Chinese panelists.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)