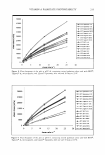
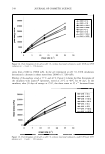
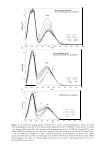
HAIR ANALYSIS BY ToF-SIMS 275 12000 10000 8000 6000 □ 4000 2000 • + 0 300 350 400 450 m/z Figure 9. Positive-ion ToF-SIMS spectrum of cleaned, unbleached hair treated with 2% IB 18-MEA solution. Treatment was repeated three times, with rinsing of the treated hair in water after each treatment. *, C22 derivative. +, C2 1 derivative. D, C20 derivative. •, C 18 derivative. data was further examined. Previous ToF-SIMS studies have successfully monitored the relative surface concentration changes on a number of organic systems using the formula IA/I TO TAL where I A is the peak area of the ion A and ! TOTAL is the total spectral ion intensity (14-16). However, in this study the original hair sample, as previously indi cated, had already been exposed to a range of surfactant products and its "processing history" was therefore uncertain. Nevertheless, some trends are still evident. Examina tion of the spectral intensities of the control "clean" and bleached samples shows the negligible "baseline" intensity of the m/z = 340+ and 368+ signals assigned to the conditioner (Table IV). Application of the IB 18-MEA conditioner to the cleaned and bleached hair shows strong adsorption of the conventional C20 and C22 quaternary derivatives, with the conditioner spectral intensity greater on the bleached hair in comparison to the relatively undamaged hair, probably reflecting the increased substan tivity of the cationic conditioner on the negatively charged bleached hair surface. The intermediate washing with the SLES solution also appears to reduce the surface concen tration and buildup of the conditioner, relative to just water in rinsing, although the adsorption is still clear. From our fiber and film studies, the standard deviation of ToF-SIMS ratio values for components in "flat" films and "clean" wool fibers is typically about ± 10%, while for the hair samples in this study, the standard deviation is about ± 30-35%. Therefore, it is evident that it is important to use "clean" hair, with a well-defined history, as a base material for hair processing and subsequent ToF-SIMS analysis if more accurate quan tification is required. Examination of the higher mass range indicates the presence of the C21 derivative adsorbed onto the hair fiber surface (Figure 10). However, although it is likely that the
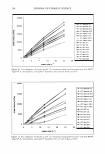
276 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table IV Positive-ion ToF-SIMS Spectral Intensities of Cationic Conditioners on Hair Fiber Treated With Incroquat Behenyl 18-MEA (IB 18-MEA) Hair sample Untreated hair (as received) SLES-cleaned hair Hydrogen peroxide bleached hair 1B 18-MEA film SLES-cleaned hair washed in 2% 1B 18-MEA x 3 rinsed in water x 3 SLES-cleaned hair washed in 2% 1B 18-MEA x 3 SLES-washed x 3 rinsed x 3 Bleached hair washed in 2% 1B 18-MEA x 3 rinsed in water x 3 Bleached hair washed in 2% 1B 18-MEA x 3 SLES-washed x 3 rinsed x 3 (I A/ITOTAL)* 340+ !TOTAL 0.1 0.1 0 10.4 12.7 8.7 18.9 11.9 100+--__.______..___..___,____,__--"'---..L--_...____.___ 0 90 80 70 60 50 40 □ 30 + 20 10 410 420 430 440 450 460 470 480 490 500 mfZ 368+ ITOTAL 0.1 0 0 22.4 30.0 20.4 61.0 30.9 Figure 10. Positive-ion ToF-SIMS spectrum of cleaned, unbleached hair treated with 2% 1B 18-MEA solution. Treatment was repeated three times, with rinsing of the treated hair in water after each treatment. +, C21 derivative. D, C20 derivative. O, C19 derivative. C 21 derivative is adsorbing onto the hair, it is in competition with the predominant softener component, the Incroquat Behenyl-type softener, and residual conditioner con taminants may also contribute. Therefore, further work was undertaken to establish adsorption of the alkylamidopropyl ethyl dimonium ethosulfate species derived from 18-MEA.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)