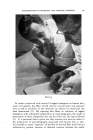
SURVEY OF DR. IRVIN H. BLANK'S SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS 367 philic material from the horny layer. Using the removal of water-soluble constituents as a measure of skin damage, Blank (8) could demonstrate no difference in the extent of damage between synthetic detergents and coco- nut oil soaps. The role of hydration of the stratum comeurn in the control of the surface bacterial flora was pointed out by Blank and co-workers (14). With the method developed in th}s study and with a serial basin dilution technique Blank and colleagues studied the effectiveness of hexachloro- phene (4, 7) and other antibacterial agents (14). Blank and his collab- orators (10) used the same techniques to show that the aluminum salts have antibacterial action in •itro and in •iro. In 1958 (13), Blank made an attempt to explain the antiperspirant action of aluminum salts. He determined the depth of penetration of aluminum (from aqueous solutions) into excised skin. It was shown that very little aluminum reaches the dermal a•ea even if the stratum corneum and the barrier layer are removed mechanically. The mechanism of antiperspirant action, therefore, does not involve a/tera/ion of the physio- logical activity of the sweat glands by aluminum salts. More recently, Blank has begun a study of the permeability of the skin. Together with Griesemer and Gould, Blank (l l) studied the penetration ofsarin (isopropylmethyl phosphonofluoride) into the skin. By autoradi- ography, the pathway of penetration was shown to be transepidermal, not transfollicular (12). Sarin, an anticholinesterase agent, quickly and in small amounts produces extreme physiological effects when placed on the skin of experimental animals. Late in 1958 (15), Blank and co-workers demonstrated that it is possible to determine the amount of percutaneous penetration of satin in live rabbits quantitatively. This assay (of sarin in the blood stream) permits the precise determination of in vivo penetration rates (amount penetrating per unit time per unit area.) The work of a number of outstanding nominees was considered for the 1958 Special Award Committee. Dr. Blank's contribution to the science of cosmetics was so immediate and beneficial that the Committee was pleased to select him as the recipient. SELECTED BIBLIOGRAPHY (1) Blank, I. H., "Action of Soap on Skin," Atrch. DermatoL and SyphiloL, 39, 811 (1939). (2) Lane, C. G., and Blank, I. H., "Cutaneous Detergents," •. Arm. Med. Atssoc., 118, 804 (1942). -. (3) I.ane, C. G., and Blank, I. H., "Action of Soap on the Skin. IV. Action of a Soap Containing Little or No Irauric or Oleic Acid," Atrch. Dermatol. and Syphilol, 56, 419 (1947). (4) Blank, I. H., and Coolidge, M. H., "Degerming the Cutaneous Surface. II. Hexa- chlorophene (G-11)," y. Invest. Dermatol., 15, 257 (1950). (5) Blank, I. H., "Factors Which Influence the Water Content of the Stratum Comeurn," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 18, 43& (1952). (6) Blank, I. H., "Further Observations on Factors Which Influence the Water Content of the Stratum Comeurn," J. Invest. DermatoL, 21, 259 (1953).
368 (7) JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Blank, I. H., and Barker, F. M., "The Action of Hexachlorophene-Detergent Mixtures on the Bacterial Population of the Cutaneous Surface," Proc. Sci. Sect. Toilet Goods •lssoc., No. 19, 50 (1953). (8) Blank, I. H., and Shappirio, E. B., "The Water Content of the Stratum Corneum. III. Effect of Previous Contact with Aqueous Solutions of Soaps and Detergents," 7- Invest. Dermatol., 25, 391 (1955). (9) Blank, I. H., "Mechanism of the Action of Agents Used for the Relief of Dry Skin," Proc. Sci. Sect. Toilet Goods •lssoc., No. 23, 19 (1955). (10) Blank, I. H., Moreland, M., and Dawes, R. K., "The Antibacterial Activity of Aluminum ß Salts," Proc. Sci. Sect. Toilet Goods •lssoc., No. 27, 24 (1957). (11) Blank, I. H., Griesemer, R. D., and Gould, E., "The Penetration of an Anticholinesterase Agent (Satin) into Skin. I. Rate of Penetration into Excised Human Skin," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 29, 299 (1957). (12) Idem, "The Penetration of an Anticholinesterase Agent (Satin) into Skin. II. Auto- radiographic Studies," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 30, 187 (1958). (13) Blank, I. H., Jones, J. L., and Gould, E., "A Study of the Penetration of Aluminum Salts into Excised Human Skin," Proc. Sci. Sect. Toilet Goods •lssoc., No. 29, 32 (1958). (14) Blank, I. H., and Dawes, R. K., "The Water Content of the Stratum Corneum. IV. The Importance of Water in Promoting Bacterial Multiplication on Cornified Epithe- lium," 7. Invest. DermatoL, 31, 141 (1958). (15) Griesemer, R. D., Blank, I. H., and Gould, E., "The Penetration of an Anticholinesterase Agent (Satin) into Skin. III. A Method for Studying the Rate of Penetration into the Skin of the I.iving Rabbit," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 31, 255 (1958). CHICAGO CHAPTER NEWS O•r Justy: 9th Dr. Ernest T. Theimer, Director of Research, van Ameringen-Haebler, Union Beach, N.J., discussed "Instrumental Analysis and Its Role in the Creation of Perfume Materials." Dr. Theimer has been closely associated with the development of instrumental analytical techniques. In addition, he has authored several papers on Friedel- Crafts reactions, the synthesis of aromatic alcohols and various analytical procedures. He has been granted a number of patents as well. Dr. Theime• was educated at the University of Cincinnati (AßB. and M.A. degrees) and at New York University (Ph.D.). Since 1931 he has been in the employ of van Ameringen-Haebler. Besides the Society of Cosmetic Chemists, Dr. Theimer is quite active in the North Jersey Section of the American Chemical Society and is a national alternate councillor.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)