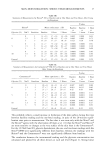
54 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE OH CH. ,.,, _,-- o OH 0 --0 --0 0 0 b [ I • I I Jn Scheme lb. Generic structure of cationic guar. relevant connections to shine and combing properties of human hair treated with cat- ionic polymers. EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS AND FILM PREPARATIONS Polyquaternium-10 and cationic guar samples were obtained from Amerchol Corpora- tion and Rhodia, respectively. The samples used in this study are listed in Table I. The polymers from the same chemical class are categorized as H, M, and L (high, medium, and low) for both molecular weight and cationic substitution. For example, guar (L/H) denotes relative low molecular weight and high cationic charge. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was purchased from ACROS/Fisher Scientific (99%). All chemicals were used as received without further purification. Polyquaternium-10 and guar (L/H) were dissolved at 6% by weight in double de-ionized water. The only exception to this was guar (H/H), which was prepared at 1.5% because it gelled at higher concentrations. The polymer/surfactant coacervate gels were prepared by adding SDS slowly to a 1% polymer solution under agitation until the maximum viscosity was Table I Polyquaternium-10 and Cationic Guar Samples Sample Cationic reference Polymer INCI name Molecular weight substitution PQ-10 (L/H) UCARE JR125 Polyquaternium-10 Low High PQ-10 (M/H) UCARE JR400 Polyquaternium-10 Medium High PQ- 10 (M/M) UCARE LR400 Polyquaternium- 10 Medium Medium PQ- 10 (M/L) UCARE LK400 Polyquaternium- 10 Medium Low Guar (H/H) Jaguar C17 Guar hydroxytrimonium High High chloride Guar (L/H) Jaguar C2000 Hydroxypropyl guar Low High hydroxylpropyl trimonium chloride
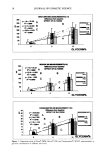
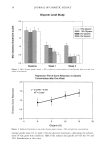
CATIONIC POLYMERS 5 5 obtained. A Brookfield KU-1 viscometer was employed to monitor viscosity and to provide constant mixing. The amount of the SDS required to gel 100 grams of 1% polymer solution is recorded in Table II. The coacervate gel in this study is slightly surfactant-deficient because the charge-neutral polymer-surfactant complex would pre- cipitate out of solution. Polymer solutions and the complex gels were drawn down on Form 3B Leneta opacity charts using a 3-mil Leneta multi-purpose drawdown bar (both from the Leneta Com- pany). The films were dried in a controlled-temperature and controlled-humidity room at 72øF and 50% relative humidity. The thickness of the dried films was relatively uniform at approximately 0.5 rail as measured by a Randall & Stickney gauge. TEST METHODS Gloss. The specular gloss observed from a sample is the relative luminous reflectance factor in the mirror direction. The test method is expressed in Equation 1. It involves measuring the ratio of the intensity of a reflected/specular beam of light (I r) from a polymer film to the intensity of the incident beam (Ii) and comparing this value with that of a standard black surface of known reflective index (12,13). (I/Ii)polymer (I•)po•ymer G= x 100- x 100 (1) (I•/Ii),tanda•d The specular gloss of polymer films on the black section of 3B Leneta charts was measured with a BYK-Gardner micro-TRI-gloss meter (model GB-4520) at 20 ø, 60 ø and 85 ø incident angles. The measuring fields for 20 ø, 60 ø, and 85 ø angles were 9 x 9 mm, 9 x 18 mm, and 7 x 42 mm, respectively. The multi-angle glossmeter was calibrated with a black gloss standard (GB-4522 20ø: 92 60ø: 95 85ø: 99) built in the holder. For each angle, the averaged gloss and standard deviation of six readings were recorded. Good reproducibility was obtained for polyquaternium-10 and cationic guar films, as the standard deviation was typically within +2 gloss units. The black section of the same 3B Leneta chart served as the control. Opacity, Opacity is the power of a polymer film to hide what is behind it. The contrast ratio method for the opacity measurement is described in several published test methods (ASTM D2805-80, TAPPI T425). This test measures the ratio of the reflectance of a dry film over a white backing to that of the sample applied over a black backing (14). A Hunter Tristimulus colorimeter (ColorQuest 45/0) and 3B Leneta opacity charts were used in our study. The opacity was measured as the ratio of the Y value (whiteness) of Table II Coacervate Formation by Addition of SDS to 100 Grams of 1% Polymer Solution Polymer % Polymer SDS KU [SDS]/[N +] PQlO (L/H) 1.01 0.1934 104 0.538 PQlO (M/H) 1.00 0.2004 110 0.571 PQ10 (M/M) 1.00 0.1380 87 0.704 PQlO (M/L) 1.00 0.1088 63 1.02 Guar (H/H) 1.00 0.1243 58 -- Guar (L/H) 1.00 0.0814 101 --
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)