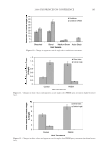
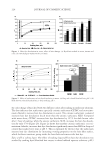
2008 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 221 ingredients such as surfactants. Small aliquots of soaking liquors were sampled after fi xed time period of soaking and the sample aliquots were read for L, a and b values on Hunter- Lab colorimeter (the values at t = 0 were read before adding hair sample into the soaking liquors). Color changes in soaking liquor were determined as ΔE calculated from L, a, b values of the soaking liquors before and after soaking. For testing the surfactant effect on hair color fading in a soaking test, color changes are measured on the hair itself. Because some surfactants such as some anionic surfactants change the color of soaking liquors in which hair dye dissolves, the color changes of soak- ing liquor can not be totally credited to the hair dye dissolution in the soaking liquors. 1% surfactant solutions were made in water. pH was adjusted to the same value around 5.5. Hair dye removal in the presence of surfactants was determined by soaking 0.46 g dyed hair samples in 100 ml of the surfactant solutions. Instead of reading the color change of the soaking liquor during soaking, the soaked hair samples were taken out after a fi xed time, dried then read for L, a and b values (the L, a and b values of hair samples before soaking were read before adding into soaking liquors) and ΔE of the soaked hair samples were calculated. 10× SHAMPOO WASHING & TREATMENT PROCEDURES Washing and treatment procedure Application of pre-shampoo treatment O Add 0.35 g, leave in treatment sample if part of regimen. O Blow dry with cool air from hair blowdryer. Cycling O Add 0.75 g testing shampoo or SLES, rub 1 minute and rinse 1 minute under warm, running tap water. O Add 0.35 g conditioner sample if part of regimen, rub through and rinse 20 second under running water. O Add 0.35 g, leave in treatment again if part of regimen, blow dry. O Or combination of the above to test various regimens on fading. Colorimetric measurements O Taken after 3×, 5×, 8×, and 10× wash cycles to measure color loss. SALON TEST PROCEDURE WITH HUMAN HAIR MANNEQUINS Pre-bleached mannequins with human hair were dyed with commercial permanent hair coloring products. For intense red color, the manneqin was dyed twice in order to increase the intensity of the red color. Dyeing time was 30 minutes and 45 minutes long for the
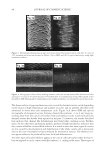
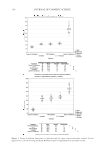
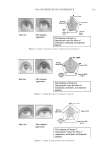
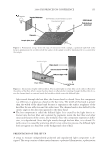
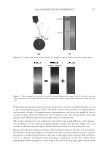
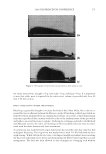
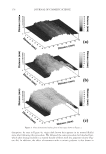
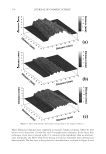
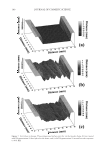
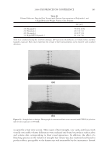
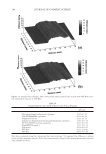
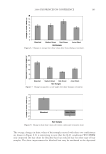
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 222 fi rst and second cycle respectively. For dark brown and dark red color, a one cycle, 45 minute dyeing process was used. The mannequin head was divided into two half sections. The right side of head was treated and washed with a regimen of formulations containing polyquaternium-55 the left side was washed and treated with a commercial color lock product. Ten wash and treatment cycles were conducted on each mannequin test. At the end of 2×, 5× and 10× wash and treatment cycles, digital pictures were taken of the man- nequin head. Pictures consisted of both sides of the head as well as front and back. Hunter L, a, b values were measured on these sections of the head as well. COLOR ANALYSIS METHODS Hunter L, a, b reading. Color changes were measured by using HunterLab Ultra Scan color- imeter. Color readings of Hunter L, a, b parameters were obtained with “specular in- cluded” and D65 light source settings. Hair color changes after washes were determined by dE. dE was calculated using equations 1 and 2 to evaluate color change: -L a - a b -b dE = ((L t o t o t o ) ( ) ( ) )1 /2 2 2 2 + + (1) dC = ( a - a b -b t o t o ( ) ( ) ) . /2 2 2 1 + (2) where Lo, ao, bo and Lt, at, bt are measured Hunter L, a, b color parameters before and after the wash and treatment cycles, respectively. The larger value of dE refl ects a greater change of color. The values of L, a, b readings on each hair tress represent an average of ten measurements, each corresponding to a different site on the hair but within the same area (a 0.39 diameter circle) before and after washes. The result of each test is repeated at least 3 times. The amount of color protection from a treatment is calculated from equa- tion 3: % Color protection = % dE = (dEcontrol – dEtreatment) × 100 dEcontrol (3) where dEtreatment is the total color changes after washes and protective treatment dEcontrol is the total color change after washes without protective treatment and %dE over 15% or a dE values of 1 for red color is generally perceivable by eye. Taking digital pictures. Digital pictures of hair tresses were obtained by scanning the tresses using EPSON Perfection 4990 photo scanner. Digital pictures of mannequin were taken using a professional camera. Image analysis of digital pictures. Digital pictures of a mannequin were cropped into equal areas from both the right side and left side of the picture using Adobe Photoshop soft- ware, CS 3 edition. The cropping was done either from the front or the side areas of the head. Image analysis of digital pictures was performed using Image Pro software. Lumi- nosity histogram analysis of the cropped pictures was obtained. The histogram consists of a plot of pixels versus color scale of luminosity. The number of pixels indicates the color intensity of the hair sample. The darkness of the hair sample was derived from population of darker pixels which was calculated by integrating the area under the curve left to the middle point of the curve.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)