EFFECTS OF CAPPARIS SPINOSA L. EXTRACT 323 studying in vivo skin damage after acute UV exposure (5,6,21). For this reason, two gel formulations containing LECS or tocopheryl acetate (TOC), used as reference compound, were applied to the skin immediately after exposure to UVB radiation, and the induced erythema was monitored by reflectance spectrophotometry. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Flower buds of Capparis spinosa (capers) were obtained from the "Consorzio dei Produt- tori di Capperi" (Pantelleria, Trapani, Italy) and were collected in October 1999. Car- bopol 934 was a gift from Biochim (Milan, Italy). Tocopheryl acetate, triethanolamine, DPPH' radical, phosphatidylcholine, rutin, and ethanol were all purchased from Sigma- Aldrich (Milan, Italy). Quercetin and kaempferol were purchased from Extrasynth•se (Genay, France). All the other reagents were of analytical grade. PREPARATION OF LECS The capers (41.24 g) were chopped into small pieces and defatted with hexane (200 ml) and CHC13 (200 ml), and then extracted with MeOH (300 ml) two times. After removal of methanol under vacuum, the solid residue obtained was suspended in water and then lyophilized to give 8.65 g of LECS. For the in vitro tests, LECS was reconstituted in the opportune EtOH/H20 solution (7:3). For the in vivo experiments, LECS was employed in a gel formulation prepared as described below. CHEMICAL ANALYSIS Apparatus. The melting points were uncorrected. UV spectra were obtained with a Perkin-Elmer 550 SE spectrophotometer. A Bruker DRX-600 spectrometer operating at 599.2 MHz for 1H and 150.1 for 13C, using the UXNMR software package, was used for NMR measurements in CD3OD solutions. Chemical shifts were expressed in 8 (ppm), referring to the following solvent peaks: 8 H 3.34 and 8 c 40.0 for CD3OD. DEPT (distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer), tH-1H DQF-COSY (double quan- tum filtered-homonuclear proton correlation spectroscopy), 1D TOCSY (1D homo- nuclear Hartmann Hahn spectroscopy), and HMBC (2D 1H-13C long-range hetero- nuclear correlation) spectra were obtained by employing the conventional pulse se- quences as previously described (22). Electron spray mass spectra (ESIMS) were recorded in the negative ion mode on a Finnigan LCQ Deca ion trap instrument (Thermo Finnigan, San Jos6, CA) equipped with Xcalibur software. Semipreparative HPLC sepa- rations were performed with a Waters 6000A pump equipped with a U6 K injector and a module 401 refractive index detector. Quantitative HPLC analysis was performed with a Shimadzu LC-10AD system equipped with a model SPD-10AV UV-VIS detector and a Rheodyne model 7725 injector (Millipore, Boston), 20 pl loop. Peak areas were calculated with a Shimadzu Chromatopac C-R6A integrator. Isolation and characterization of flavonol compounds I-VIII. LECS (8.64 g) was partitioned between n-BuOH and H20 to afford an n-BuOH-soluble portion (2.86 g), which was chromatographed on a Sephadex LH-20 column (100 x 5 cm) using MeOH as eluent.
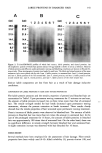
324 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Fractions of 8 ml were collected, checked by TLC (Si gel plates in n-BuOH-HOAc-H20, 60:15:25 and CHCI3-MeOH-H20, 80:18:2) and combined to give five fractions con- taining fiavonol derivatives. These fractions were subjected to RP HPLC separation on a t•-Bondapak C-18 column (30 cmx 7.8 mm id, flow rate 1.5 ml/min) with MeOH- H20 (1:1) as solvent system. This procedure gave pure compounds: (I) (R t -- 13.1 min) (II) (Rt = 16.2 rain) (lid (R• = 26.0 rain) (IV) (R• = 9.5 min) (V) (R t = 20.1 min) (VII) (Rt = 32.5 rain) and (VIII) (R• = 35.3 min) (Figure 1). Quantitative determination oftotalphenols. LECS was analyzed for its total phenolic content according to the Folin-Ciocalteau colorimetric method (23) total phenols were expressed as lag/ml rutin equivalents. Quantitative HPLC analysis offlavonols. To prepare a standard solution containing com- pounds III and V, accurately weighed amounts of the compounds were dissolved in MeOH. Serial dilutions with a concentration range of 2.5-10.0 lag/ml for V and 7.5- 25.00 lag/ml for III were prepared. Quantitative HPLC was conducted using a C-18 la-Bondapack column (150 x 3.9 mm i.d.). The mobil phase was a linear gradient ranging from 40% to 100% of MeOH (solvent B) in 0.01 M phosphate buffer, pH 5.0, (solvent A) over 30 min. The elution gradient was 40-60% of B from 0 to 10 min and 60-100% from 10 to 30 min. The analyses were carried out in triplicate, at a flow-rate 1.0 of ml/min, with the UV detector set at 366 nm. The peak assignments were based on the retention times of each compound. Calibration ! OH R R' R" I Rha (1-6)-[Rha 1-2]-Glu H H II Rha-(1 -2)-Glu H H III Rha-(1-6)-Glu H H IV Rha (1-6)-[Rha 1-2]-Glu OH H V Rha- (1-6)-Glu OH H VI Rha-(1-2)-Glu H OMe VII H OH H VIII H H H Figure 1. Chemical structures of flavonols isolated from LECS
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)