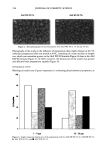
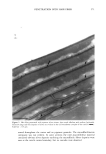
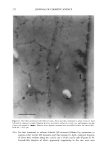
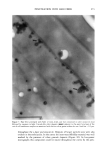
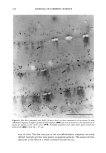
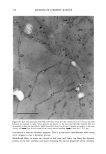
290 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE bonding of polymer to hair and may explain the observed higher stiffness values for treatments comprising water as a solvent. Another piece of evidence supporting such a role for water can be obtained by studying omega-loop bending at high deformations of about 25% (corresponding to 4 mm distance). At such high strains, the bonds between polymer and hair typically break if the polymer is in the glassy state below glass transition temperature. This is illustrated in Figure 7, presenting a plot of force as a function of distance for the first and several consecutive deformations. It shows that above 2 mm of deformation the stress levels off, then decreases, and becomes unstable as reflected by the jagged line depicting the dependence of force as a function of distance. The maximum force probably depends on the mechanical properties of a polymer and its adhesion to the hair. Table I shows the average parameters calculated from data similar to those in Figure 7 for 100% VOC, 80% VOC, and 55% VOC formulations containing 5.71% w/w of vinyl caprolactam/ PVP/dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer. The data in Table I show higher values of F• for formulations with an increasing proportion of water. This is in agreement with a similar increase in stiffness ratios (equal to force (1 mm, polymer-treated hair)/force (1 mm, untreated hair) discussed above and demonstrated in Figure 6. It should be mentioned that the data shown in Figure 6 and Table I were obtained in two different experiments that employed different commercial samples of vinyl caprolactam/PVP/dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer, which probably explains small differences in the numerical values of stiffness reported in the figure and the table. It should be also added that the flexibility parameters in Table I show a very slight change in the direction of greater flexibility for the 55 % VOC system. EFFECT OF POLYMER BLEND COMPOSITION Blends of polymers are frequently employed in commercial fixative compositions. The Force [G] Force [G] Force [G] Distance Distance Distance 100% VOC 80% VOC 55% VOC Figure 7. Force vs distance plots for hair treated with vinyl caprolactam/PVP/dimethylaminoethyl meth- acrylate copolymer at 5.71% w/w 100%, 80%, and 55% VOC formulations.
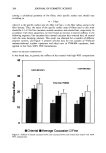
DYNAMIC HAIRSPRAY ANALYSIS 291 Table I Average Parameters Stiffness Sample F• ratio F• o/F• E•o/E • Hn/H • 100% VOC 501 _+ 9 25.4 0.72 0.30 0.92 80% VOC 670 _+ 20 30.3 0.72 0.30 0.92 55% VOC 794 -+ 2 30.4 0.82 0.33 0.88 purpose of using a multi-component system is to adjust the final properties of a product in terms of feel, resistance to humidity, stiffness, or tackiness. Mixed resins are fre- quently employed to lower the cost of a product. The behavior of the main polymeric component can be also modified by the addition of low-molecular-weight compounds such as oils or surfactants. For example, nonionic surfactants can be employed as plas- ticizing agents, which impart a softer feel to a stiff hairspray polymer. On the other hand, rosin gum, which is a complex polymeric material, is employed as an additive to increase stiffness or to produce a perception of "harsher feel." In this work, we have investigated the blend of ethyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer with poly(methylvinylether) (PMVE). The components of this mixture have widely disparate physical properties. Ethyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer forms stiff, hydrophobic, and water-insoluble films under use conditions, i.e., at low neutralization degrees of 10- 20%. In contrast to this, PMVE is a water-soluble, hydrophilic polymer, which forms 40 500 35 3O o 25 n,, 20 • 15 10 f i I I 400 300 •_ 200 100 0 20 40 60 80 100 % PMVE ß Stiffness ----Glass Transition Figure 8. Stiffness of a hairset and theoretically calculated temperatures of glass transition as a function of the blend of PMVE and ethyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer. Stiffness measurements carried out on hair treated with 80% VOC compositions.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)