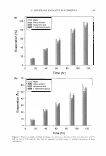
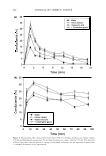
U. DA VIVIANA EXTRACTS IN COSMETICS 357 EXTRACTION AND ISOLATION The air-dried bark of the roots of V lmus davidiana (l kg) were cut into pieces and extracted with distilled water (30 kg) for 24 h at 90°C. After filtration through a 400-mesh filter cloth, it was precipitated into EtOH (22 kg) and filtered with filter paper (Whatman, No. 5 ). White powder (105 g) was obtained. The obtained white powder was then dissolved with water and filtered with 0.45 µm cartridge paper. The filtrate was reprecipitated into EtOH, and white powder (60 g) was again obtained. MEASUREMENT OF WATER LOSS IN A DESICCATOR The preweighed sample (10 g) in a chamber (50 x 20 mm) was placed in a desiccator (240 x 130 x 220 mm) that maintained relative humidity at 15% and 55%, respec tively, using silica gel blue and saturated MgC12 solution at 3 7 ° C, followed by reweigh ing at regular intervals. The water loss was considered to be the ratio between the hydrated and dry weights of the samples. The percentage of an evaporation rate was calculated as:. Evaporation(%) = {(W0 - Wt) / W0 } x 100 where W0 is the initial sample weight of the sample or formulation (g), and W e is the sample weight of the sample or formulation at each hour (g). MOISTURIZING EFFECT ON SKIN USING A CORNEOMETER (11) A skin hydration reading of each sample was recorded using a Corneometer CM820 (Courage Khazaka, West Germany). This equipment consists of a recording device and impedance probe that measures electrical conductivity on the skin surface. Capacitance refers to the quantity of electric changes stored, and thus capacitance is proportional to the amount of water in the skin, a factor that is commonly referred to as skin hydration. Simply put, the higher the level of skin moisture, the stronger the observed conductance signal will be (11). Baseline values of ten female volunteers aged 22-3 7 years were taken using 40-mm-diameter-circle test areas on the right and left forearms. These panelists remained at rest in a room at 20°-25°C and 45-55% relative humidity for the duration of the test. Each designated area was then treated with five different test formulations of 0.05 ml/circle. A conductance % was calculated using the following formula: Conductance % = {(A - B) / A} x 100 where A is the corneometer value before sample treatment, and B is the corneometer value after sample treatment. TEWL MEASUREMENT (12) A group of female volunteers, of ages ranging from 22 to 3 7 years, were recruited. Each of the volunteers was familiarized with the transepidermal water loss (TEWL) technique so as to reduce any emotional stress associated with the test procedure. Additionally, the volunteers were asked to shave 24 h before the test and to avoid intake of foods or drinks containing high levels of stimulatory caffeine. fo an attempt to eliminate any artificial
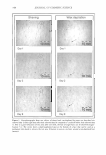
358 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE effects on TEWL due to sweating, the volunteers were treated with an antiperspirant product. Prior to testing, the volunteers were asked to apply the antiperspirant product. TEWL measurements were made in a climate-controlled room with conditions of 20°- 250C under 50 ± 5% relative humidity. The volunteers spent 20 min of the equilibra tion period in the room, relaxing in a prone position with their hands behind their heads, exposing their underarms to the air. The TEWL was measured using a Vapometer (Delfin Technologies Ltd.). TEWL measurements were recorded sequentially at the site of application prior to treatment. These initial measurements served as pretreatment control values. Subse quently, 20 µl of sample was applied over a 4-cm2 area of the volar forearm (2 x 2 cm), followed by measurements at regular intervals for six hours. CYTOTOXICITY ASSAY A Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD) was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of Ulmus davidiana root extract. Five thousand cells (human fibroblast cells) were seeded on a 96-well plate with DMEM + 10% FBS and incubated at 3 7 ° C and humidified with 5% CO 2 until confluency reached ~ 70%. 0 5 2 5 10 15 Retention time (min) 20 Figure 1. Liquid chromatogram of the hydrolysis products of Ulnzus davidiana root extract. Conditions: CarboPac PAl column, PED2 with integrated amperometry detector eluenr: 16 mM NaOH flow rate: 1.0 ml/min. (1) fucose, (2) rhamnose, (3) galactosamine, (4) glucosamine, (5) galactose, and (6) glucose. Table I Constituents of Polysaccharide of U Imus davidiana Root Extract Constituent Rhamnose Galactose Glucose Fucose Galactosamine Glucosamine Content (wt%) 57.37 35.50 4.98 1.13 0.55 0.48
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)