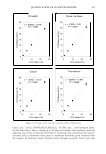
380 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE CEM) for 15 min at 400 W. The digested solutions were analyzed with ICP-AES (OPTIMA 3300DV). The following operational conditions were set for ICP-AES: inci dent power 2000 W cross flow nebulizer plasma gas flow rate 13 1/min auxiliary gas flow rate 0.5 1/min nebulizer gas flow rate 0.5 1/min sample uptake rate 1.8 m/1/min wavelength 323.45 nm. RES UL TS AND DISCUSSION Titanium has two different oxidation states, titanium(III) and titanium(IV). The redox reaction between them is the basis of the quatitation of titanium dioxide in our inves tigation. After calcification of other organic ingredients in the cosmetics, titanium dioxide was dissolved by hot concentrated H2S04 (the boiling points of H2S04 can be elevated by ammonium sulfate up to 500°C). The dissolved titanium(IV) was reduced to titanium (III) by aluminum. Solid zinc amalgam or chromium(II) chloride solution can also be used as reducing agent for titanium(IV) (7). The reduced titanium(III) was titrated against a standard oxidizing agent, Fe(III) (ammonium iron(III) sulfate), with potassium thiocyanate as an indicator. Cosmetics are very complex products. Frequently, more than 20 kinds of organic and inorganic materials are combined together. Although organic ingredients are eliminated by calcination, any remaining inorganic materials could create matrix interferences. In addition, many kinds of inorganic metallic oxides, such as zinc oxide, silica, talc, and iron oxides, remain after calcination. In order to test the accuracy and applicability of the proposed method in the presence of other cosmetic ingredients, we quantified known amounts of titanium dioxide from 1 % to 25% in four types of sunscreen cosmetics. Since the SCCNFP (Scientific Committee on Cosmetic Products and Non-Food Products) proposed the maximum concentration of titanium dioxide as 25%, we did not test over 25%. As shown in Figure 2, R 2 values were acceptable. It appears that linearity was established in the test range. Accuracy was evaluated via percent recovery. The value (i.e., the accuracy) of percent recovery was calculated as follows: Recovery (%) = [Measured amounts (%) / added amounts (%)} x 100 The results are summarized in Table I. The percent recoveries of the four types of formulation were in the range between 96% and 105%. These results reflect that the accuracy of the developed method was also good. We also analyzed seven commercial cosmetics labeled as containing titanium dioxide. We made a comparison between the proposed method and ICP-AES, one of the most powerful atomic analysis tools. The results, given in Table II, show that the titrated amounts accord well with the data from ICP-AES. It appears that the method proposed and studied in this article is adequate for quantifying titanium dioxide in diverse commercial cosmetics. There are many other analytical methods used for the quantitative determination of titanium, but few of them can be applied to cosmetics. A good example of an inappli cable method is colorimetric measurement using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer. A min eral acid solution of Ti(IV) produces yellow-orange-colored acidic cationic species, "per-
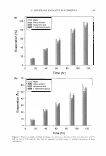
QUANTITATION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE 381 Powder Make-Up Base 30 30 y = 0.9633x + 02491 y = 1.0332x - 0.08 25 R2 = 0.9993 25 R2 = 0.9997 I. ,♦ � 20 * 20 lJ lJ � Q) ::, :5 15 U) 15 U) CCI CCI Q) Q) � � C\J 10 t' C\J 10 • 0 0 i= i= 5 • 5 .. 0 • 0 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 TiO2 Added (%) TiO2 Added (%) Cream Foundation 30 30 y = 1.0443x - 03137 y = 0.9578x + 0.1897 25 R2 = 0.9991 J 25 R2 = 0.9996 I * 20 � 20 lJ lJ � Q) ::, :5 U) 15 U) 15 CCI CCI Q) Q) � � N 10 ,I: N 10 I[ 0 0 i= i= 5 • 5 � • 0 0 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 TiO2 Added (%) TiO2 Added (%) Fi g ure 2. R 2 values of the tit rations in diverse cosmetic formulations. titanic acid," such as [Ti(OHMH2O2)(H 2 O 2 )h + or (TiO 2 .aq) 2 +, with hydrogen perox ide (8). Since Beer's Law is obeyed up to 50 ppm of titanium, this method is good for analyzing trace levels of titanium (9). However, chromium that originates from cosmetic colorants such as chromium oxide green or chromium hydroxide green interferes with the analysis by forming colored material with hydrogen peroxide. Ferric ions that
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)