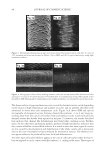
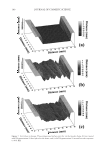
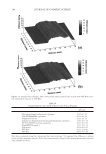
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 220 Cocamide MEA, dilinoleic acid, linolamidopropyl dimethylamine dimer dilinoleate, Streareth-21, ammonium hydroxide, behentrimonium chloride, Polyquaternium-22, so- dium sulfi te, sodium metasilicate, 4-amino-2-hydroxytoluene, P-phenylenediamine, P- aminophenol, N,N-Bis(2-hydroxytoluene), P-phenylenediamine sulfate, mica, iron oxides, 1-hydroxyethyl 4,5-diamino pyrazole sulfate, titanium dioxide. COMMERCIAL COLOR LOCK PRODUCTS Two commercial color lock products were used as benchmarks. The fi rst was a two step system consisting of a shampoo and conditioner. The ingredient labels are: aqua/water, sodium laureth sulfate, disodium cocoamphodiacetate, glycol distearate, cocamide MIPA, sodium chloride, hexylene glycol, disodium ricinoleamide, MEA-sulfosuccinate, parfum/ fragrance, carbomer, disodium EDTA, methylparaben, Polyquaternium-10, DMDM hy- dantoin, benzophenone-3, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, hexyl cinnamal, benzyl salicy- late, glycine soja/soybean oil, tocopherol, isopropanolamine, butylphenyl methylpropional, linalool, amyl cinnamal, hydroxycitronellal, limonene water, cetearyl alcohol, behentri- monium chloride, cetyl esters, amodimethicone, fragrance, methylparaben, trideceth-5, benzophenone-3, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, soybean oil, tocopherol, hexyl cinnamal, Trideceth-10, benzyl salicylate, citric acid, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, butylphenyl methylpropional, linalool, amyl cinnamal hydroxycitronellal. The second commercial color lock system was a three step system and consisted of a leave in treatment cream, shampoo and conditioner. The ingredient labels for the shampoo and conditioner are: water (aqua), sodium laureth sulfate, cocamidopropyl betaine, disodium cocamphodipropionate, phosphoric acid, phenoxyethanol, PPG 5 Ceteth 10 phosphate, fragrance, sodium chloride, methylparaben, ethylparaben, disodium EDTA, arginine HCl, taurine, Polyquaternium 10, hydroxypropyl hydrolyzed soy protein, wheat amino acids, Oleth 10, lecithin, trehalose, tocopherol, octyl salicylate water (aqua), cetearyl al- cohol, dimethicone, propylene glycol, Ceteth 3 acetate, behentrimonium chloride, hy- droxyethyl cellulose, phenoxyethanol, fragrance (parfum), disodium EDTA, sodium citrate, arginine HCl, taurine, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, PPG 5 Ceteth 20, wheat amino acids, hydrolyzed soy protein, Oleth 10, disodium cocoamphodipropionate, leci- thin, hydroxypropyl trimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein, phosphoric acid, trehalose, tocopherol, ethylhexyl salicylate. The ingredient label for the leave-in the treatment is: water, Quaternium-87, stearyl alcohol, potato starch modifi ed, behetrimonium chloride, amodimethicone, phenoxyethanol, 2-oleamido-1,3-octadecanediol, parfum/fragrance, Polysorbate 20, C11-15 pareth-7, methylparaben, C12-16 parath-9, glycerin, Tride- ceth-12, glycine, SOJA/soybean oil, tocopherol, taurine, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, trisodium HEDTA, citric acid, pentasodium pentetate, limonene, butylphenyl methyl- propional, hexyl cinnamal, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, PPG-5-ceteth-20, linalool, Oleth-10, disodium cocoamphodipropionate, citronellol, lecithin, ethylparaben, phos- phoric acid, trehalose, ethyl-hexyl salicylate. SOAKING TEST OF DYED HAIR Hair dye dissolution in water was determined by soaking known amount of dyed hair samples (typically 0.4 to 0.8 g) in 100 ml of the aqueous solution which may contain testing
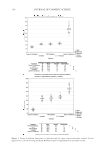
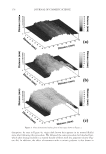
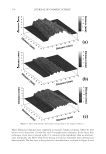
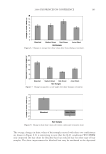
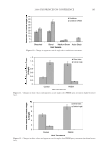
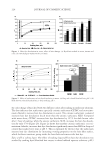
2008 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 221 ingredients such as surfactants. Small aliquots of soaking liquors were sampled after fi xed time period of soaking and the sample aliquots were read for L, a and b values on Hunter- Lab colorimeter (the values at t = 0 were read before adding hair sample into the soaking liquors). Color changes in soaking liquor were determined as ΔE calculated from L, a, b values of the soaking liquors before and after soaking. For testing the surfactant effect on hair color fading in a soaking test, color changes are measured on the hair itself. Because some surfactants such as some anionic surfactants change the color of soaking liquors in which hair dye dissolves, the color changes of soak- ing liquor can not be totally credited to the hair dye dissolution in the soaking liquors. 1% surfactant solutions were made in water. pH was adjusted to the same value around 5.5. Hair dye removal in the presence of surfactants was determined by soaking 0.46 g dyed hair samples in 100 ml of the surfactant solutions. Instead of reading the color change of the soaking liquor during soaking, the soaked hair samples were taken out after a fi xed time, dried then read for L, a and b values (the L, a and b values of hair samples before soaking were read before adding into soaking liquors) and ΔE of the soaked hair samples were calculated. 10× SHAMPOO WASHING & TREATMENT PROCEDURES Washing and treatment procedure Application of pre-shampoo treatment O Add 0.35 g, leave in treatment sample if part of regimen. O Blow dry with cool air from hair blowdryer. Cycling O Add 0.75 g testing shampoo or SLES, rub 1 minute and rinse 1 minute under warm, running tap water. O Add 0.35 g conditioner sample if part of regimen, rub through and rinse 20 second under running water. O Add 0.35 g, leave in treatment again if part of regimen, blow dry. O Or combination of the above to test various regimens on fading. Colorimetric measurements O Taken after 3×, 5×, 8×, and 10× wash cycles to measure color loss. SALON TEST PROCEDURE WITH HUMAN HAIR MANNEQUINS Pre-bleached mannequins with human hair were dyed with commercial permanent hair coloring products. For intense red color, the manneqin was dyed twice in order to increase the intensity of the red color. Dyeing time was 30 minutes and 45 minutes long for the
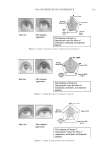
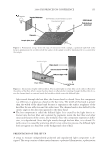
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)