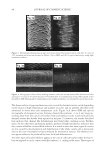
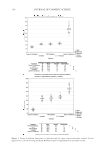
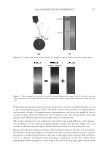
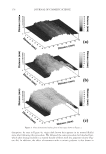
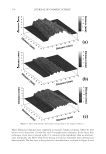
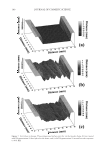
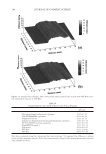
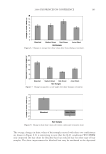
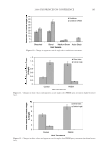
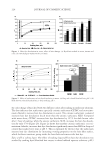
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 226 comparison, are shown in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows the anti-fading test results of the four polymers in a leave-in treatment at 2% level using bleached hair tresses. The results demonstrate that Polyquaternium 55 (VP/DMAPA/C12-MAPTAC copolymer) leave-in treatment provides the highest color protection with 38% higher color improvement at the end of 10× washes over the control and the effect is well perceivable by eye as shown in the picture. VP/DMAPA acrylates copolymer which has a similar structure to Poly- quaternium 55 (PQ-55) but missing a hydrophobic chain and a quaternary group is less effective than PQ-55, with 17% color protection. Moreover, Polyquaternium-28 (VP/ MAPTAC), the quaternized analogue of VP/DMAPA acrylates copolymer without a hy- drophobic chain, is not effective on hair color protection. Therefore, the color fading test results of these three polymers demonstrate the synergistic effect of hydrophobicity and quaternary moiety on PQ-55. Consistently, the data in Figure 5 also shows that the hy- drophobically modifi ed anionic polymer, VP/acrylates/lauryl methacrylate copolymer provides negligible anti-fading effect due to lack of the cationic unit. Therefore this re- sult supports further a synergistic effect of hydrophobicity and quaternization of PQ-55 on hair color protection. The anti-fading effect of hydrophobically modifi ed quaternary salt of hydroxyl ethyl cel- lulose along with other HEC derivatives such as quaternary HEC and alky HEC were tested in a 10× wash color fading test. The results in Figure 6 show that alkyl substituted quaternary HEC provides higher color protection effect than the other two HEC deriva- tives which have no alky substitution or quaternary unit. These results demonstrate again the synergistic effect of hydrophobic and quaternary moieties of a polymer on hair color protection. The results in Figure 6 also show that PQ-55 is much more effective on hair color protection than the alkyl quaternary HEC tested. The higher color protection ben- efi t provided from PQ-55 might be partly attributed to the additional substantivity ef- fect provided by the DMAPA unit on PQ-55. Color fastness test results of PQ-55 tested in treatment regimens Pre-shampoo leave-in treatment with PQ-55. Dyed bleached hair was treated with PQ-55 leave in gel formulation (Table II) then dried before the fi rst shampoo wash. In a control test, the hair tress was treated with the same formula to which 2% PQ-55 was not added. 12% SLES was used as a washing agent for both tresses. The treatment, drying, shampoo washing cycle was repeated for 10 times. Figure 7a shows the total color changes of hair tresses determined as dE values after multiple treatments and wash cycles. The data shows that PQ-55 leave-in gel treatment provides 38% color protection after 10× washes over the control. Figure 7b shows the subjective panel test results of hair tresses after 10× wash and treatment from the test shown in Figure 7a. The 18 panelists agree that the hair tress treated with 2% PQ-55 leave in gel is signifi cantly darker than the hair tress treated Table II Anti-Fading Leave-In Treatment Gel Containing Polyquaternium-55 Ingredients %w/w Supplier Water 87.00 Hydroxpropyl guar (Jaquar HP-60) 1.50 Rhodia Polyquaternim-55 (20% active) 10.00 ISP Propylene glycol (and) diazoklidinyl urea (and) iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (Liquid Germall® Plus) 0.50 ISP Glycerin 1.00 1.00
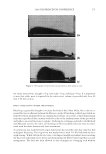
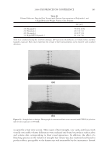
2008 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 227 without PQ-55. The color difference of the two tresses determined by the panel test is within the range from slight to moderate under the three light source used. Therefore, the color protection effect of PQ-55 leave-in treatments is perceivable by the naked eye. Rinse-off treatment with PQ-55 shampoo and conditioner products. The effect of PQ-55 on hair color protection was evaluated in a rinse-off shampoo (Table III) and conditioner formula. The formula for the conditioner is based on a blend of hydroxyethyl cetearami- dopropyldimonium chloride and stearamido propyl dimethylamine as conditioning agents in cream base thickened with fatty alcohols and nonionic surfactants. Figure 8a shows the color fading test results of dyed bleached hair samples washed with a shampoo containing 0.5% PQ-55 against the control, 12% SLES. The result indicates that 0.5% PQ-55 in the shampoo formula provides 21% color retention over the SLES control after 10× washes and the effect is visible by eyes. Figure 8b shows the color fading Figure 4. Chemical structures of selected polymers with/without hydrophobic chain and/or quaternization. Figure 5. Pictures and color loss of dyed hair samples after 10× SLES washes and leave-in treatment of 2% polymers, intense red colored hair, dyed bleached dark brown hair.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)