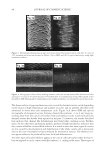
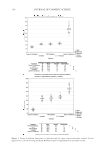
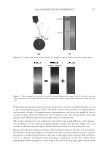
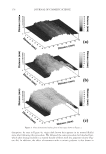
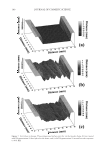
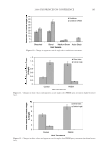
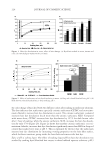
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 234 higher pixel number and less shift to the left indicates the color protective effects of the PQ-55 system. Figure 15 shows the pictures of mannequin Dephne dyed with ruby red color before and after 10× wash and treatment cycles with PQ-55 3-step anti-fading system (right side) and a commercial 3-step anti-fading system (left side). The picture of mannequin Dephne demonstrates that the PQ-55 3-step anti-fading system is superior to the commercial 3-step anti-fading system tested in preventing hair color fading from shampoo stripping. Table V lists the color changes of mannequin Daphne on both sides of the head as mea- sured by L, a, b parameters and calculated as dE values at the end of 10× wash cycle. The color protection % (%dE) by PQ-55 anti-fading system is 33.8% higher than the 3-step commercial anti-fading system. Figure 16 is the image analysis results of the digital pictures of mannequin Daphne after 10× washes and treatments. The color darkness (area under the curve with L 116, darker pixels) of PQ-55 treated side of the hair (right side of mannequin) is 13,321, while that of the commercial 3-step system treated side of the hair (left side of manne- quin) is 9,758. This refl ects a 35.6% higher color protection from the treatment with the PQ-55 system than the commercial 3-step system, consistent with the %dE improve- ment listed in Table V. The luminosity curve of the commercial system treated side of hair also shifts to the right side, the lighter direction, relative to that of the PQ-55 sys- tem treated side. SURFACE PROPERTY CHANGES AFTER POLYMER TREATMENT AND PROPOSED COLOR PROTECTION MECHANISM OF PQ-55 It has been reported that cationic polymers and conditioners tends to bind to the cuticle edges and around the pores (7,8). The cuticle edges and pore perimeters are more dam- aged therefore more charged than other portion of hair, which attract more cationic charged polymers or conditioners. Figure 14. Image analysis of color intensity of mannequin Gabrielle dyed in intense red after 10 cycle washes and treatments with PQ-55 anti-fading system (right side) and commercial color lock system (left side).
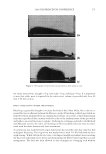
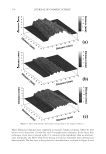
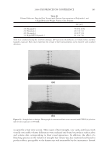
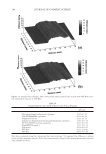
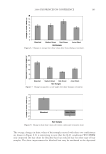
2008 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 235 Table V Total Color Loss of Mannequin Gabrielle Measured by dE, Ruby Red Color PQ-55 3-step anti-fading system Commercial 3-step anti-fading system dE 7.09 10.7 %dE improvement by PQ-55 system over commercial system 33.8% Figure 15. Pictures of mannequin Daphne dyed in red after 10 cycle washes and treatments with PQ-55 anti-fading system (right side) and commercial color lock system (left side). Dyed pre-bleached Asian hair. It is believed that hydrophobically modifi ed cationic polymers such as PQ-55 are able to form a hydrophobic and substantive barrier on hair surface especially on cuticle edges and around the pores, which effectively reduces washing out of hair dye. In order to prove the effect of wash resistant and hydrophobic barrier provided by PQ-55 treatment, water contact angles of dyed hair fi bers were measured after 10× SLES washes and with and without treatment of 2% PQ-55 leave in gel. The difference in water contact angles of treated and untreated hair surface is an indication of hair fi ber surface hydrophobicity changes. Figure 17a is the result of water contact angle measurement of hair fi bers after 10× SLES washes and with or without 10× treatment with 2% PQ-55 leave-in gel. It should be noticed that the treated and untreated hair tresses were the two split halves of a same hair tress before treatment and washes therefore the treated and untreated hair tresses have the same average contact angle before treatment and washes. The results in Figure 17a indicate that the average water contact angles of hair fi ber surface from the treatment with PQ-55 leave-in gel is 60.4° after 10× SLES washes, while the contact an- gle of hair fi bers treated with the gel without PQ-55 after the same washes is 50.4°. These results demonstrate that the hair surface after treatment with 2% PQ-55 leave-in gel is more hydrophobic than the control. The corresponding color protection effect of PQ-55 leave-in treatment is 38% (Figure 5), which is attributed to the increased hydro- phobicity and barrier function of the hair surface. Figure 17b is the water contact angles of hair fi bers after 10× treatment and wash with PQ-55 3 step anti-fading system
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)