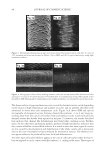
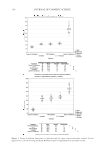
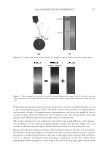
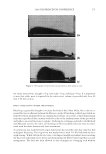
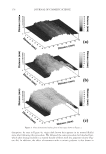
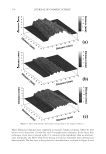
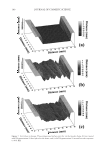
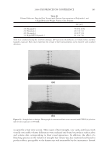
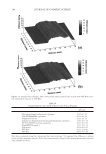
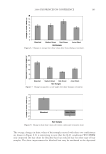
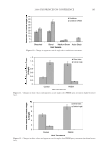
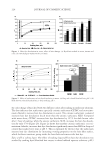
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 238 market need of oxidative hair color fastness from shampooing beyond its other hair care benefi ts such as conditioning and styling. The protective mechanism has been under- stood to be the combination of hydrophobic substitution and cationic nature of the polymer which forms a hydrophobic and substantive barrier fi lm on hair. The effective- ness of the protective benefi t of PQ-55 are substantiated from hair tress and mannequin heads made with human hair and have been quantifi ed with well known measurement techniques such as Hunter L,a,b and digital image analysis. The data from these tech- niques confi rm what is perceivable by the naked eye. In addition, measurements such as contact angle demonstrated the presence of the hydrophobic barrier formed by Poly- quaternium-55 on the hair surface and FTIR image analysis confi rmed the dye molecule retention improvement within the hair fi ber of Polyquaternium-55 treated hair. Multiple washing tests with various treatment regimens with formulas containing PQ-55 indicate that optimal effects are realized by applying a combination of leave-in and shampoo prod- ucts. The understanding of the structure–functionality relationship of PQ-55 opens the ways to the development of new anti-fading systems to meet the new market need of oxidative hair color fastness from shampooing. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank Xiaohong Bi for conducting FTIR image analysis Lynda Conforti-Tobin for conducting the Salon evaluation of mannequin heads Donna Laura and Grisel Tumalle for help in color fading tests Roger L McMullen for conducting digital image analysis and Solomon Wossene for help in Mannequin tests and for provid- ing subjective panel test results. REFERENCES (1) S. Marchioretto, The use of silicones as a color lock aid in rinse-off hair conditioners, J. Cosmet. Sci., 55(1), 130–131 (2004). (2) B. Brewster, Color lock in hair care, Cosmet. Toiletr., 121(3), 28–36 (2006). (3) C. Fox, Caring for color-treated hair, Cosmet. Toiletr., 120(11), 36–43 (2005). (4) G. Wis-Surel, Some challenges in modern hair color formulations, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 21, 37–340 (1999). (5) M. Reisch, Color protection, Chem. Eng. News, 30 (June 9, 2008). (6) A. Schlosser, Silicones used in permanent and semi-permanent hair dyes to reduce the fading and color change process of dyed hair occurred by wash-out or UV radiation, J. Cosmet. Sci., 55(Suppl.), S123– S131 (2004). (7) R. L. McMullen, J. Jachowicz, and Stephen P. Kelty, Correlation of AFM/LFM with combing forces of human hair, IFSCC Magazine, 3(3), 2–8 (2000). (8) C. LaTorre, B. Bhushan, J.-Z. Yang, and P. M. Torgerson, Nanotribological effect of silicone deposition level, and surfactant type on human hair using atomic force microscopy. J. Cosmet. Sci., 57(1) (2006). (9) C. Robbins, C. Reich, and A. Patel, Absorption to keratin surfaces: A continuum between a charge- driven and a hydrophobically driven process, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 45(2), 85–94 (1995).
J. Cosmet. Sci., 60, 239–250 (March/April 2009) 239 Evaluation of novel synthetic conditioning polymers for shampoos S. L. JORDAN, X. ZHANG, J. AMOS, D. FRANK, R. MENON, R. GALLEY, C. DAVIS, T. KALANTAR, and M. LADIKA, Dow Wolff Cellulosics, A Subsidiary of the Dow Chemical Company, 171 River Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854 (S.L.J, X.Z., J.A., D.F., R.M., R.G., C.D., M.L.), and the Dow Chemical Company, Building 1712, Midland, MI 48674.(T. K.). Synopsis Cationic polymers have traditionally been used in shampoo formulations to impart conditioning properties to hair. In this study, commercial synthetic cationic polymers were investigated using coacervate formation, objective wet comb analysis, silicone deposition and panel studies to determine structure function properties with the goal of developing novel conditioning polymers. New polymers were synthesized and, based on criteria determined in the fi rst part of the study, found to have marginal improvement over existing synthetic cationic conditioning polymers. A novel experimental polymer developed for a different industry was also investigated for conditioning properties. This polymer showed signifi cant enhancement of silicone deposition over current commercial polymers, including cationic guar, even at signifi cantly reduced silicone and polymer concentrations. The experimental polymer exhibited parity or improvement over benchmark polymers in panel studies, and similar performance to other synthetic polymers in objective wet comb studies. BACKGROUND For over thirty years cationic conditioning polymers have been used in anionic shampoo formulations to impart improved look, feel comb properties (1,2). These polymers are also used as deposition aids for benefi t agents such as silicone. Two naturally derived cat- ionic polymers, cationic hydroxyethyl cellulose (polyquaternium 10 or PQ10) and guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride (cationic guar) are used extensively in the market to- day. Hydrophobically modifi ed PQ10 (PQ67) was recently introduced as well. Less widely used are various synthetic conditioning polymers including acrylamide and dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride (polyquaternium 7 or, PQ7) and polyvinyl pyrrolidone and dimethyl aminoethylmethacrylate, (polyquaternium 11 or PQ11) (3). In general, cat- ionic conditioning polymers coexist in shampoos with anionic surfactants in a single phase. As the shampoo is diluted during use and the surfactant approaches the critical micelle concentration (CMC), the cationic polymer forms a complex with the surfactant monomers that phase separates from the bulk solution. This phase separation, or coacer- vation, is known as the Lochhead effect (4–7). The gel-like coacervate contains a high concentration of the cationic polymer which is then deposited onto the negatively charged
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)