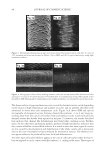
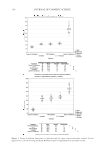
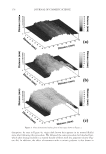
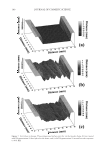
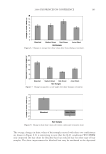
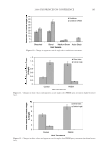
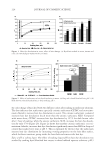
2008 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 147 DETERMINATION OF THE ANTI-BREAKAGE EFFICACY OF COMMERCIAL HAIR CARE PRODUCTS Several shampoos from major brands were tested for their anti-breakage effi cacy. The results of two shampoos from different brands, both containing dimethicone and cat- ionic polymer guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride, are given in Figure 4. Since the producers suggest using fi rst the anti breakage shampoo and then the related anti break- age conditioner from the same product line, this was also tested. It can be seen from Figure 3. Hair breakage of bleached hair at relative different humidities. The result for 40% is signifi cantly different from the data found for 60% and 75% RH ( p0.05). Figure 4. Hair breakage for hair strands treated with benchmark products. All results except for the differ- ence of the last two columns are signifi cantly different (p0.05).
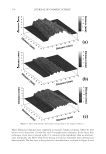
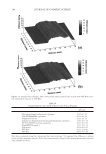
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 148 Figure 4 that both shampoos reduce the amount of broken fi bers signifi cantly by 49% and 69%. These effects are even improved when using both, shampoo and conditioner reaching a nearly 90% hair breakage reduction. Interestingly, the shampoo containing 3% dimethicone was less effective when compared to the other shampoo with only 1.4% dimethicone. DEVELOPMENT OF AN ALTERNATIVE ANTI-BREAKAGE SHAMPOO INGREDIENT In a screening test, several parameters were tested on their infl uence on the deposition of waxes on hair from a shampoo: O Chemistry O Hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity O Particle size O Hair state (virgin/bleached) O Cationic polymer in the shampoo O Concentration of the wax in the shampoo Out of these series, the particle size was found to be the most signifi cant parameter. Therefore, our objective was to develop a wax dispersion with particles smaller than 1 μm. Ether chemistry was chosen to ensure hydrolytic stability over a wide pH range, al- lowing the use in different fi elds like bleaching, perming or hair straightening. Finally, a compound consisting of PEG-4 distearyl ether, distearyl ether and dicaprylyl ether dis- persed in sodium laureth sulfate was developed. The effi cacy of this ingredient was tested in shampoos with increasing concentrations of the wax dispersion combined with guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride. The compo- sition of the shampoos can be found in Table I. In Figure 5 the anti-breakage effi cacy of shampoos containing 1, 2, 3 and 4% dispersions (equal to 0.25–1% active matter of the wax) is compared with the effect of a placebo con- taining a styrene/acrylates copolymer as turbidity ingredient. The shampoo composition is given in Table I. A clear dependence on the dosage was found. By comparing the levels of Table I Tested Shampoo Compositions Placebo Shampoos with active Sodium laureth sulfate 10 10 Cocoamidopropyl betaine 3 3 PEG-4 distearyl ether (and) sodium laureth sulfate (and) distearyl ether (and) dicaprylyl ether 1−4 (equals 0.25 to 1% wax) Styrene/acrylates copolymer (and) cocoglucoside 0.4 (equals 0,12% wax) Guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride 0.2 0.2 Laureth-2 1 1 Citric acid pH adjustment to pH 5 Sodium chloride Viscosity adjustment Perfume 0.3 0.3 Preservative 0.5 0.5 Water Add to 100%
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)