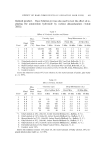
REACTIONS OF OXIDATION DYE INTERMEDIATES 365 with peroxide at pH 9.5 for one hour. Aliquots were diluted in pH 2.3 buffer and their absorption examined in the 380-400 m/• region (Fig. 3 and Table I). Chromatographic Method for BB In a second method, the above oxidation mixtures were spotted on thin-layer chromatographic plates and developed in two dimensions. TLC plates, 500 /• thick, were made using a 1:2 slurry of Silica Gel G and water. Development was effected by using the upper layer of n-BuOH: HOAc: H20 = 40:10:50. The chromatography tank was equilibrated at 38øC before insertion of the thin-layer plate. The solvent was allowed to ascend 10 cm in one dimension, the plate was removed and air-dried (oven-drying caused BB to be immobile in the second dimension), and then developed 10 cm in the second dimension. Approximately 0.1 3' BB is the limit of detection. Spotting load for a reaction solution was 4 X (Table I). Ouinonediimine Synthesis of ODI QDI was prepared by the method of Willstatter (6). It was used immediately. Table I OCCURRENCE OF BANDROWSKI BASE Dye Intermediates Molar TLC Evidence Spectral Is BB Present Ratio of BB Evidence of BB Present PPD + + Yes PPD: Resorcinol 4:1 + + Yes PPD: Resorcinol 1 '. 1 + -- Trace? PPD: Resorcinol 1: 4 -- -- No PPD: Hydroquinone I: 1 -- -- No PPD: Pyrogallol I: 1 -- -- No PPD: p-Arninophenol 1:1 -- -- No PPD: m-Aminophenol 1:1 -- ? Trace? PPD: Picramic acid 1:1 + ? Trace?
366 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS QDI Determination by Ammonia Evolution The hydrolysis of pure QDI or QDI mixtures to give ammonia was done using a modified Folin-Farmer micro-Kjeldahl apparatus. QDI was weighed into the reaction vessel, which contained lg Na2COa/100 ml (pH 9.6) and other reactants as desired. Water or 6% H20•. was added after the system was connected. Reactions were allowed to proceed for one hour (Table II). Table 'n' QUINONEDIIMINE, AMMONIA EVOLUTION % of Theoretical Reactants* Average ñ St, Dev. No, of Expts. QDI (No H202) 17.1 _.+ 6.0 4 QDI (H20•) 18.4 _+ 6.0 5 QDI: PPD 1:1 5.8 --+ 1.8 7 QDI: Resorcinol 1:2 (2 hours) 2.0 +-- 0.9 3 *QDI varied from 0.06-0.3 g. in 50 mi. 1% Na2CO3, pH 9.6 H20• when used, at 3% time I hr. QDI in Oxidation Mixtures/ Ammonia Evolution Various oxidation dye intermediates (PPD, resorcinol, m-amino- phenol), as well as BB, both with and without peroxide, were subjected to hydrolytic conditions as described above and any evolution of am- monia was noted. PPD was used in a 1% solution, and the other com- ponents were used in the proportions indicated in Table III. QDI Determination by Spectral Method A standard absorption spectrum for QDI was established by dissolv- ing a known amount in absolute ether absorption maxima, 255 mu and 265 mu molar extinction coefficient (at 265 mu), 24,000 (Fig. 4). The stability of QDI in aqueous mixtures was determined as follows:
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)