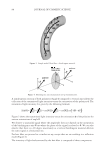
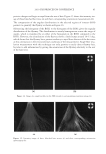
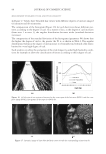
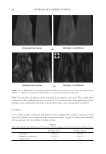
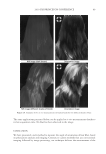
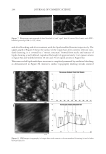
2010 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 213 Table III Titration Data (SLS) Quat Sample Amount of quat solution added to achieve haze point in SLS (g) Viscosity (cps) Notes AMB 9.75 10 Did not form a gel AME 6.28 10 Did not form a gel AEB 14.58 10 Did not form a gel AMM 17.63 10 Did not form a gel DMB 18.33 10 Did not form a gel AEG 29.53 10 Did not form a gel AMG 30.49 10 Did not form a gel Soft Quats Quat Sample Amount of quat solution added to achieve haze point in SLS (g) Viscosity (cps) Notes MMB 15.28 14,000 Formed a gel MMM 21.25 13,400 Formed a gel DMM 23.85 6,000 Formed a gel CaMB 25.72 1,000 Formed a gel MMG 31.02 19,200 Formed a gel DMG 40.25 12,000 Formed a gel Table IV Titration Data (SLES) Quat Sample Amount of quat solution added to achieve haze point in SLS (g) Final pH Viscosity (cps) Notes AMB 18.67 6.6 10 Did not form a gel AME 4.47 7.0 10 Formed a gel AMG 25.04 7.2 1,000 Formed a gel AMM 17.44 7.2 10 Did not form a gel AEB 18.35 7.2 10 Did not form a gel AEG 38.72 7.1 1,000 Formed a gel CaMB 24.31 7.6 1,000 Formed a gel CaMG 46.23 7.3 1,000 Formed a gel DMB 11.09 7.3 10 Did not form a gel DMG 28.37 7.9 6,800 Formed a gel DMM 20.00 7.0 6,200 Formed a gel MMB 25.00 7.1 10 Formed a gel MMG 26.68 7.1 40,000 Formed a gel MMM 20.23 7.3 50,000 Formed a gel
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 214 Table V Titration Data (SLS) Quat Sample Amount of quat solution added to achieve haze point in SLS (g) Viscosity (cps) Notes AMB 18.67 10 Did not form a gel AMM 17.44 10 Did not form a gel AEB 18.35 10 Did not form a gel DMB 11.09 10 Did not form a gel Soft Quats Quat Sample Amount of quat solution added to achieve haze point in SLS (g) Viscosity (cps) Notes AME 4.47 7,000 Formed a gel DMM 20.00 6,200 Formed a gel MMM 20.23 50,000 Formed a gel CaMB 24.31 1,000 Formed a gel AMG 25.04 1,000 Formed a gel MMB 25.00 9,800 Formed a gel MMG 26.68 40,000 Formed a gel DMG 28.37 6,800 Formed a gel AEG 38.72 1,000 Formed a gel CaMG 46.23 1,000 Formed a gel RESULTS The quats that showed the best compatibility and gellation properties with sodium lauryl sulfate were the amido quats. The only exception was the amido quat that contained an aromatic group (DMB). There was improved compatibility with sodium laureth-3-sulfate when compared to sodium lauryl sulfate. This leads to the conclusion that SLES is a softer anionic than SLES. All quat compounds reached a cloud point when titrated into anionic. However, the amount necessary to reach the haze point were different and the nature of the end point were different. The so-called hard quats have very little tolerance for anionic, forming insoluble precipitates with very little addition. Quaternary compounds having inter- mediate hardness show compatibility with anionic surfactants at near stoichiometric amounts, but do eventually haze. Soft quats do not exhibit a haze, but rather show a clear gel. (B) FOAM HEIGHT AND STABILITY It has been generally assumed that a gel made using an anionic and cationic combination would not foam. An evaluation of the gelled system was therefore undertaken to see if this is true.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)