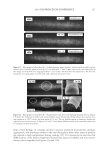
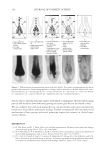
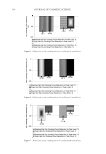
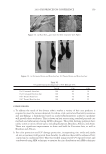
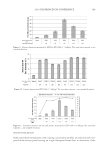
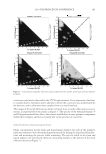
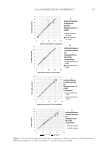
2010 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 215 PURPOSE Determine the height and stability of foam produced from aqueous solutions of anionic surfactant containing quaternium compounds (Tables VI–VIII). PROCEDURE Quat solutions: Titrated quat solutions Controls: INCI: Polyquaternium-10 Sodium lauryl sulfate Sodium laureth sulfate Name ARL-4-84A ARL-4-84B ARL-4-84C ARL-4-84D Polyquaternium 10 1.00% 1.00% — — Deionized water 91.00% 91.00% 92.00% 92.00% Sodium lauryl sulfate 8.00% — 8.00% — Sodium laureth sulfate — 8.00% 8.00% (1) Prepare ARL-4-84A and B by mixing polyquaternium 10 and deionized water with a prop mixer set on low speed until uniform (1-5 min, 20°-25°C). (2) Add surfactant and mix with medium agitation until uniform (1-2 min 20°–25°C). (3) Prepare ARL-4-84C and D by combining deionized water and surfactant. Mix with medium agitation until uniform (1-2 min 20°-25°C). Table VI Foam Heights of SLS Titrations Quat Sample Foam heightmax (ml) Foam heightinital (ml) Foam heightfi nal (ml) Foam stability (min) AMB — — — Does not foam AME 190 90 140 30.0 AMG 500 400 300 30.0 AMM 600 500 350 15.0 AEB 300 200 200 40.5 AEG 200 100 150 40.0 CaMB 250 150 175 95.0 CaMG 200 100 150 79.0 DMB 400 300 250 14.0 DMG 300 200 200 8.0 DMM 250 150 150 13.0 MMB 400 300 250 29.0 MMG 400 300 250 97.0 MMM 400 300 250 1440.0
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 216 RESULTS Quat solutions titrated with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) produced higher levels of foam than those titrated with sodium laureth sulfate (SLES). However, the quat solutions that were titrated with SLES exhibited greater foam stability than those titrated with SLS. In some cases the quats titrated with SLES had a half-life greater than 24 hours (1440 mi- nutes), including the control. After running all controls, it can be concluded that the addition of quaternium compound had a negative effect on the foaming capabilities of SLS and SLES. Stock SLS produced a foam height of 600 ml, while the average foam height produced from quat/SLS was around 250 ml. Quat AMB (SLS) produced no foam. Unlike all the other quats that were titrated with SLS, which formed translucent, cloudy, gels at their respective cloud points, quat AMB produced a white, opaque paste. This is evidence that a complex is forming between this quat and SLS. This did not occur when quat AMB was titrated with SLES. Controls for this experiment produced expected results. ARL-4-84A, which contained 1% polyquaternium 10, produced a higher foam height than ARL-4-84B, which also contained 1% polyquaternium 10, but in SLES. This also proved true for ARL-4-84C and Table VII Foam Heights of SLES Titrations Quat Sample Foam heightmax (ml) Foam heightinital (ml) Foam heightfi nal (ml) Foam stability (min) AMB 150 50 100 141.0 AME 250 150 175 1440.0 AMG 350 250 225 240.0 AMM 200 100 150 1440.0 AEB 200 100 150 47.0 AEG 300 200 200 1440.0 CaMB 150 50 125 8.50 CaMG 150 50 125 6.0 DMB 150 50 125 5.5 DMG 200 100 150 75.0 DMM 150 50 125 9.0 MMB 200 100 150 1440.0 MMG 250 150 175 146.5 MMM 300 200 200 1440.0 Table VIII Foam Heights of Controls Control Foam heightmax (ml) Foam heightinital (ml) Foam heightfi nal (ml) Foam stability (min) ARL-4-84A 200 100 100 31.0 ARL-4-84B 200 100 150 1440.0 ARL-4-84C 600 500 350 25.0 ARL-4-84D 450 350 275 180.0
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)