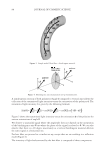
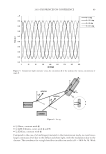
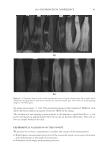
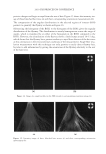
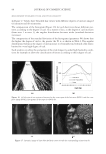
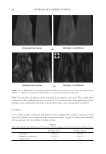
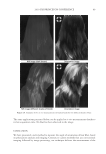
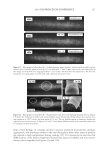
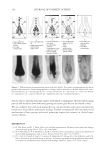
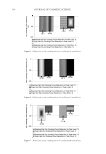
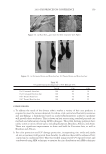
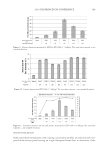
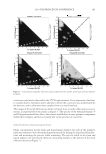
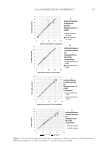
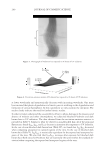
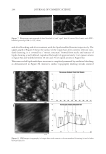
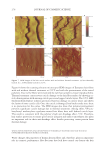
2010 TRI/PRINCETON CONFERENCE 159 CONCLUSIONS a. To address the needs of the diverse ethnic market a variety of hair care products is required to meet the various demands. For shine, style control and humidity resistance and non-fl aking: a formulation based on acrylates/hydroxyesters acrylates copolymer will provide these attributes. This is shown on hair tresses using standard personal care methods and substantiated using AFM techniques. These fi lm forming polymers have utility across a variety of hair types, including European, Brazilian, African, and Asian. There was signifi cant improvement in shine and hold for Caucasian hair, as well as Brazilian and African. b. For color protection and UV damage protection, incorporating zinc oxide and jojoba oil into a treatment will provide these benefi ts. In addition there will be enhanced frizz control and a conditioned feel. This was verifi ed using treated UV exposed tresses and corroborated using SEM techniques to monitor the zinc distribution and AFM techniques Figure 12. (a) Hair fi ber—split end. (b) After treatment with PQ10. Figure 13. (a) Untreated Asian and Brazilian hair. (b) Treated Asian and Brazilian hair. Table VI % Curl Retention after Exposure to 90% RH and 30°C Initial 4 hr 8 hr 13a1 Untreated Asian hair 100 40 10 13a2 Untreated Brazilian hair 100 50 20 13b1 Treated Asian hair 100 70 50 13b2 Treated Brazilian hair 100 80 55
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 160 for cuticle damages. The Zn does not overshadow the treatment. By having a fi ne dis- tribution of zinc oxide across the hair shafts, color protection and damage protection are obtained, without negatively impacting aesthetics. The hairs still feel and look natural as observed by expert panelists. The type of protection and conditioning at- tributes can be specifi cally targeted to curly hair, such as Brazilian and African as well as any color-treated hair. c. By using polyquaternium-10 or 67 into a hair care treatment, there are improvements to the feel, smoothness and antifrizz repair. Using SEM and AFM there is indications of hair repair after treatments. This is critical for tightly curled hair types, including African and Brazilian. d. Overall, many of the needs for this diverse and growing market segment can be met by utilizing a combination of products, with targeted benefi ts depending on the hair type. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors thank Robert Antrim, Kalidah Diamond, Susan Jordan, Kinjal Joshi, Terri Powell, Curtis Schwartz, David Sutton, Rosalind Toth, and Li Zhang of the Dow Chemical Company. REFERENCES (1) M. Starch, Cosmet. Toiletr, 114, 55–60 (1999). (2) C. Reich and C. R. Robbins, J. Soc, Cosmet Chem., 44, 221–234 (1993). (3) I. Reeth, M. Starch, and J. Decaire, Dow Corning Corp. (2000). (4) J. Lim, M. Chang, and M. Park, J. Cosmet. Sci., 57, 475–485 (2006). (5) N. Starostina, M. Brodsky, and S. Prikhodko, J. Cosmet Sci., 59, 225–232 (2008). (6) B. Bhushan, G. Wei, and P. Torgeson, Ultramicroscopy, 105, 248–266, (2005). (7) B. Bhushan and C. LaTorre, Ultramicroscopy, 105, 155–175 (2005). (8) N. Lechocinski and P. Clémenceau, Bossa Nova Technologies, LLC (2007). (9) B. Bhushan, H. Fuchs, and C. LaTorre, Applied Scanning Probe Methods IV, 35–103 (2006).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)