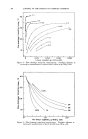
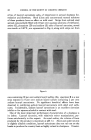
328 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS found that the sedimentation velocities showed a wide range, with a main group with S -- 1.3-1.6 sveds. From the diffusion coefficient, a molecular weight of 60,000 for this main group ofprote, ins was calculated. A frictional ratio of 3.5 was found which indicates a highly asymmetric molecule. Carruthers, Woernley, Baumler and Kress have studied by electrophore- sis some of the properties of the fibrous and non-fibrous proteins of the epi- dermis of beef snout and the mouse (24). The procedures employed for the extraction of these proteins were essentially those of Rudall. The following results were obtained: The mobilities of the fibrous and non- fibrous proteins isolated from a 6 M urea extract of epidermis at 0øC., were lower than those obtained for these proteins extracted with the same solu- tion at 28øC., or with a 10 M urea solution at the same temperature. An insoluble protein of isoelectric point of pH 6.3 was also isolated from the 6 M and 10 M urea extracts of beef snout epidermis. This protein was cleaved further by 6 M urea solution to yield proteins of isoelectric points of pH 4.5 and 5.5. Solutions of several detergents also extracted from the epidermis proteins which were unrelated to those isolated from the concen- trated urea extracts of this tissue. Binding of the fibrous and non-fibrous proteins with the detergent, sodium lauryl sulfate, to form several distinct protein detergent complexes was demonstrated by electrophoresis. In this report investigations were undertaken to determine the effect of dilute and concentrated urea solutions on the extractability of the fibrous and non-fibrous proteins from epidermis. This approach was pursued in order to ascertain whether some of the properties of the keratin precursors was a function of the concentration of urea employed for the extraction of these proteins. METHODS The procedures employed for the extraction of the structural proteins from epidermis with 6 M urea solutions were those of Rudall (17) with some modifications (24). Further experiments were undertaken to obtain more information on the effect of single and repeated extractions of isolated epi- dermis (25) with dilute and concentrated urea solutions on the yields and electrophoretic mobilities of the fibrous and non-fibrous proteins. A typi- cal extraction of beef snout epidermis with a 6 M urea solution is shown in Chart I. The supernatant fraction from the dialyzed extract after acidifi- cation with hydrochloric acid gave a small amount of protein at pH 6.3. The fibrous protein of isoelectric point ofpH 5.5 was purified as previously described (17, 24) and in addition by centrifugation at 130,050 X gravity for five hours in a Spinco Ultracentrifuge. This procedure gave rise to a small amount of a gel-like mass and a slightly yellowish supernatant frac- tion. The former in solution at pH 7.0 and the latter flocculated at pH 5.5 upon the addition of hydrochloric acid. Further treatment of the clot
PROTEINS OF EPIDERMIS, RELATION TO AGING SKIN 329
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)