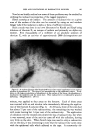
346 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS calculate with analytical data, that esterification of all the acids with all the alcohols will leave an excess of hydroxyl groups. Those esters which have a free hydroxyl group are known as hydroxyesters. They may be formed from the reaction of normal and iso acids with dihydric alcohols, or of hydroxyacids with either type of alcohol (monohydric or dihydric). Hydroxyesters are responsible for the major part of the hydroxyl number of lanolin and comprise a substantial percentage of the total esters. ACETYLATED DERIVATIVES With this as a background, the synthesis of those derivatives of the hy- droxyesters of lanolin which could theoretically be expected to have inter- esting characteristics was investigated in our laboratory. These deriva- tives were prepared by acylation of the hydroxyestdrs, resulting in replace- ment of the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group with an acyl radical. The de- rivatives possess new properties of interest to many industries. They are rapidly becoming important cosmetic and pharmaceutical ingredients. Figure 2 illustrates the esterification reactions which are of interest in this study. Figure 2.--Formation and acetylation of hydroxyesters 1. Formation of an ester from an acid and an alcohol RCOOH q- R'OH -• RCOOR' q- H,•O 2. Formation of a hydroxyester H H R--C--COOH q- R'OH -• R--C--COOR' q- H,•O I OH OH 3. Acetylation of cholesteryl a-hydroxypalmitate H I CH•--(CH,)•--C--COO(C,.7H45) H O•H• q- OCH•C -,- CHa--(CH=)•--C--COO(C,.7H45) q- I 0 I CH•CO0 I I CHaCOOH I OCH•C •, The first type is a simple ester of a fatty acid with an alcohol. A typical example would be cholesteryl stearate. The second type, of which cholesteryl hydroxypalmitate is an example, is an ester in which a free hydroxyl remains on the fatty acid portion of the compound.
ACETYLATED LANOLIN DERIVATIVES 347 The third reaction described is typical of the procedure we have developed to modify lanolin by acylation of hydroxyesters. An acetyl radical re- places the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group resulting in an acetylated droxyester which, in this case, might be called the acetate of cholesteryl a hydroxy-palmitate. It is interesting to note that the hydrophilic proper- ties of the lanolin hydroxyesters are lost as a result of this reaction. The acyl radical need not be limited to acetic since we have successfully used propionic, benzoic and related acid radicals. This presentation, however, is limited mainly to a discussion of the acetylated derivatives. Acetates are widely distributed in nature both as salts and as esters. They have been identified as constituents of perspiration. They are used both internally and externally in such varied products as aspirin and desoxy- corticosterone acetate U.S.P. In addition, there is abundant evidence that acetic acid is metabolized and serves as a food (8). Acetates have been used for years in antiperspirants, deodorants, perfumes and flavors. Greenberg and Lester in their book entitled "Handbook of Cosmetic Mate- rials" (9) state that there is no evidence of allergic responses (to acetic acid) on theoretical grounds there should be none." It has been well established that acetates are basic building blocks from which compounds such as cholesterol, certain hormones, and vitamins are biosynthesized. Table 2 presents data comparing a typical U.S.P. lanolin to its acetylated derix ative.* TABLE 2--COMPARATIVE DATA ON LANOLIN AND ACETYLATED LANOLIN* Lanolin U.S.P. Acetylated Lanolin* Ester no. 95 110 Acid no. Approx. 1 Approx. 1 Iodine no. 27 27 Hydroxyl no. 32 2 Water sol. acids (U.S.P.) Neutral to litmus Neutral to litmus Melting point (U.S.P.) 39øC. 36øC. Specific gravity 0.935 at 25øC. 0.935 at 25øC. Color Pale yellow Pale yellow Odor Typical Practically odorless Mineral oil solubility 0.5% 10% Emulsification w/o None "Feel" on the skin Tacky Waxy * Modulan. T.M. It will be noted that, as a result of the acetylation, the hydroxyl number drops from 32 to 2. Other changes are: an increase in the ester number from 95 to 110 and a decrease in the melting point by about 3øC. The loss of free hydroxyls in acetylated lanolin renders the product hydrophobic, and its physical properties are affected accordingly. The modified product * Modulan--Trade Mark of American Cholesterol Products, Inc.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)