j. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 47, 241-298 (July/August 1996) Preprints of the 1996 Annual Scientific Meeting December 12-13, 1996 New York Hilton and Towers Hotel New York, NY 241
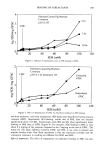
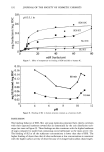
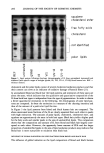
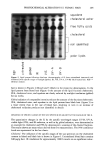
242 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS In vitro percutaneous absorption of an alpha hydroxy acid (glycolic acid) in human skin MARGARET E. K. KRAELING and ROBERT L. BRONAUGH, Office of Cosmetics and Colors, Food & Drug Administration, Washington, D. C. INTRODUCTION Glycolic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) commonly used in cosmetic products. Its activity on skin is likely influenced by its ability to be absorbed into the different layers of skin. The absorption of glycolic acid into and through human skin was therefore measured by using in vitro diffusion cell techniques. The absorption of glycolic acid should be sensitive to pH changes in formulations due to ionization. Its absorption was therefore measured from two emulsions containing different surfactants, each adjusted to pH 3.0 and 7.0. METHODS Skin absorption was measured through freshly obtained human skin dermatomed to a thickness of approximately 200 Ix and assembled in flow-through diffusion cells. Skin was obtained from at least three donors (four replicates per donor) for each measurement, and barrier integrity was assessed by determining 3H-water absorption prior to each study (20-min test). Skin viability was maintained during the 24-hour studies by using a HEPES-buffered Hank's balanced salt solution as the receptor fluid. •4C-glycolic acid was applied in an emulsion vehicle at a 5% concentration. At the end of the study, unabsorbed compound was washed from the skin with soap and water, and the radio- labeled material recovered in the stratum corneum, viable epidermis, papillary dermis, and receptor fluid was determined. Absorption was expressed as the percent of the applied dose absorbed in the 24-hour study. Two oil-in-water emulsions were prepared by using different surfactants. Formulation A contained the non-ionic emulsifying agents PEG 100 stearate and PEG 4 lauryl ether. In Formulation B, the ionic surfactant ammonium laureth sulfate was added in place of the PEG 4 lauryl ether. Barrier integrity of hairless guinea pig skin (dermatomed to 200 ix), after 24-hour exposure to various formulations, was assessed by measuring the steady-state rate of penetration of 3H-water and then calculating a permeability constant (Kp). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Glycolic acid was absorbed into all skin locations and the receptor fluid during the 24 hours after its application in Formulation A (Table I). Greater glycolic acid levels were
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)