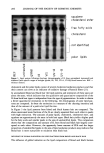
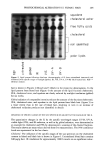
PREPRINTS OF THE 1996 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 275 number of irritants, and absence of cutaneous sensory or vasodilatory stimulants. Sen- sitive-skin products can minimize potential problems by including anti-inflammatory agents, improving barrier function, and creating an exogenous barrier. REFERENCES (1) F. A. Simion and A. H. Rau, Sensitive skin, Cosmet. Toiletr., 109, 43-50 (1994). (2) S. Amin and H. I. Maibach, Cosmetic intolerance syndrome: Pathophysiology and management. Cosmet. Dermatol., 9, 34-42 (1996). (3) A. Fisher, Cosmetic actions and reactions: Therapeutic, irritant, and allergic, Cutis, 26(1), 22-29 (1980). Stability of dihydroxyacetone in self-tanning cosmetic products ASIRA OSTROVSKAYA, ANTHONY D. ROSALIA, PETER A. LANDA, and DANIEL MAES, Estee Lauder Inc., Research and Development Center, 125 Pinelawn Road, Melville, NY 11747. INTRODUCTION Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is commonly used as a self-tanning agent in cosmetic prod- ucts. We have found that during its shelf life, DHA may release trace amounts of substances that can cause skin irritation or dermatitis (1). For this reason, DHA deg- radation has become a great concern to us and the industry as a whole. We have found that under certain uncontrolled conditions DHA can degrade, with the subsequent formation of formaldehyde, formic acid, and acetic acid. The levels of these three can be indicative of the extent of DHA's degradation. To determine and quantitate the possible degradation products of DHA, we at Estee Lauder developed modern analytical techniques and used them further to prevent and control DHA degradation. METHODS FORMALDEHYDE When applicable classical methods employing derivatizing agents such as Nash's reagent (2,3) or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (4) are used for the determination of free formal- dehyde in the presence of dihydroxyacetone, erroneous results are obtained. Therefore,
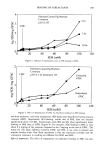
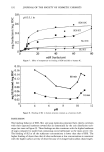
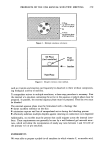
276 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS we developed a method that utilizes the unique approach of derivatizing formaldehyde with acetylacetone at room temperature, in the presence of ammonium acetate, to form the derivative 3,5-diacetyl-1,4-dihydrolutidine directly in the sample. The derivatiza- tion process is completed in 90 minutes at room temperature. The derivative is then subsequently quantitated via high-performance liquid chromatography using a reverse- phase C 18 column with water/acetonitrile (80:20) as a mobile phase. Detection is at 414 nm (5). FORMIC ACID AND ACETIC ACID Both formic and acetic acids are assayed by high-performance liquid chromatography using a polymeric polystyrene divinylbenzene sulfonate column. The mobile phase is 0.001 N aqueous sulfuric acid solution, and the UV/VIS programmable detector is set at 210 nm (6,7). PROTOCOL We investigated the kinetics of DHA in reference to pH, time, and temperature. We studied the influence of certain types of cosmetic ingredients and chemical classes of raw materials to inhibit or stabilize degradation of DHA in cosmetic products. RESULTS The analysis of 5% aqueous DHA solutions stored at room temperature showed in- creased levels of formaldehyde, formic acid, and acetic acid over time (Figure 1). If samples are stored at 45øC, increased levels of these by-products are observed, indicating a greater degradation of DHA. We also found that changes in the initial pH of aqueous solutions of DHA from acidic to alkaline lead to higher levels of formaldehyde, formic acid, and acetic acid over time. The influence of certain raw materials was also investigated in 5 % DHA solutions. We found that raw materials can affect DHA by increasing, decreasing, or having no effect on the formation of by-products and, therefore, on the degradation of DHA (Figure 2). We also applied our acquired knowledge of the interactions between DHA and certain o Figure 1. Time study of DHA degradation.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)