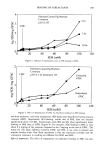
REDUCTION OF HUMAN HAIR 219 the stress-relaxation of the disulfide bonds in the fiber, the reaction rate constant and kinetic behavior may be determined. Ammonium thioglycolate. The effects of reduction by 1M ATG solutions at pH 8.0, 9.0, 9.4, and 9.5, 23øC, were studied by collecting stress-relaxation data (26). Graphs of the ln[(F t - Ff)/(F o - Ff)] vs time were prepared from data that was continuously collected for 20 minutes (a minimum of 120 data points were used to create the logarithm graphs). These graphs indicated that all four ATG solutions exhibited pseudo first-order kinetics. The results of an F-test (p = 0.05) confirmed fit to the pseudo first-order kinetic model. The reaction rate constant, k, for each condition was determined from the slopes of plots of In [(F t - Ff)/(F o - Ff)] vs time, and the mean value for each was calculated (Table I). Data analysis indicated that the reaction rate increased as the pH of the solution was increased. A 1M ATG solution reduces hair more rapidly at pH 9.4-9.5 (which is nearest the pKsi_ x of 10.4) than the same solution at either pH 9.0 or 8.0. Sodium thioglycolate has been observed to exhibit pseudo first-order kinetic be- havior at pHs 10 (1). Ammonium thioglycolate, which differs from sodium thio- glycolate only by the type of cation, also exhibits pseudo first-order kinetic behavior at pHs 10. Cysteamine. Stress-relaxation data were collected for disulfide reduction by 1 M cyste- amine solutions at pH 7.0, 7.6, 8.0, and 8.5, 23øC. Table II contains the results of stress-relaxation measurements fit to the pseudo first-order kinetic model. The fit for the model was confirmed statistically. The results indicated that the rate of reduction of disulfide bonds in human hair by a 1 M cysteamine solution increased as the pH of the solution was increased. Similar to ATG, a 1 M cysteamine solution at pH 8.5 (pKsi_x of 8.6) reduces hair more rapidly than the same solution at pH 7.0-8.0. This pH trend for ATG and cysteamine is in agreement with the previously established concept (21) that the redox potentials of thiol compounds increase with pH and that increasing the pH of the solution also affects the reaction rate constant. AMINO ACID ANALYSIS Ammonium thioglycolate. The effects of reduction by a 1 M ATG solution at pH 9.4 on the percentage of cystine cleaved at increasing time lengths were studied. The solution pH was adjusted to 9.4 in order to have 10% of the active reducing species present in solution (pKsi_ x = 10.4). In this manner, a direct comparison of percent cystine reduced over time by a ATG solution vs a cysteamine solution could be made. Also, a correlation could be determined between kinetic data from the SFTK measurements and amino acid Table I Reaction Rate Constants for Hair Fibers Reduced With 1 M Ammonium Thioglycolate at pH 8.0, 9.0, 9.4, or 9.5, 23øC Treatment k x 103 (s- l) Mean, SD pH 8.0 1.52, 0.35 pH 9.0 4.57, 1.59 pH 9.4 7.44, 1.26 pH 9.5 6.29, 0.46 Nine fibers per treatment.
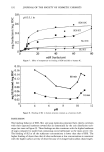
220 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II Reaction Rate Constants for Hair Fibers Reduced With 1 M Cysteamine at pH 7.0, 7.6, 8.0, or 8.5, 23øC Treatment k x 103 (s- l) Mean, SD pH 7.0 2.60, 0.35 pH 7.6 3.29, 0.34 pH 8.0 4.61, 1.56 pH 8.5 4.01, 0.90 Nine fibers per treatment. analyses. The results of amine acid analysis (Figure 2a) indicate that under experimen- tal conditions a maximal degree of reduction was achieved in five minutes. This was equivalent to reduction of 74% of cystine bonds (Figure 3). Further increases in length of reduction time only served to allow the reaction to go to completion (30 minutes = 92% of cystine bonds reduced). Cysteamine. Disulfide bond reduction by a 1 M cysteamine solution at pH 7.6 was studied in order to have 10% of the active reducing species present in solution (pKsH = 8.6). The results of amine acid analysis (Figure 2b) indicate that approximately 62% of the disulfide bonds were reduced in 30 minutes. These results indicate that reduction for 30 minutes by a 1 M cysteamine solution at pH 7.6 produces similar increases in the percent cystine cleaved as 1 M ATG solution at pH 9.4 in five minutes (Figure 3). Comparing the percentage of disulfide bonds reduced by ATG and cysteamine at iden- tical reduction times indicates that a greater percentage of the cystine bonds in the hair fiber were reduced by ATG than by cysteamine. Correlation of SFTK measurement data with amino acid analysis data. In order to compare the effects of reduction by ATG with crysteamine, two conditions were chosen where each solution had an equivalent percentage of active thiel species, RS-, present at the respective pH. These conditions were 1 M ATG solution at pH 9.4 (pKsH = 10.4) and 1 M cysteamine solution at pH 7.6, 23øC (PKsH = 8.6). A logarithm plot of the mean reaction rate constants was prepared, and the half-life (t•/2) for each condition was identified (Figure 4). The half-life was defined as the time required for the concentration of the disulfide bonds remaining to decrease to 1/2 of the original value [S- S] o. For a first-order reaction, the half-life can be determined from the following equation: t•/2 = 0.693/k (6) where k is the reaction rate constant that was experimentally determined. Comparison of the two conditions from the SFTK measurements indicates that the rate of reduction of the stress-supporting bonds in the hair fiber by ATG at pH 9.4 was faster than the rate of reduction by cysteamine at pH 7.6. This trend was supported by comparison of the half-life calculated for each condition. For comparison of the effects of reduction by ATG at pH 9.4 vs cysteamine at pH 7.6, using amine acid analysis, a logarithm plot of the disappearance of the disulfide bond, LN [(C t - Cf)/(C o - Cf)], vs time was prepared (Figure 5). The mean reaction rate constant for each of the two conditions was determined and the half-life for each condition was identified. The results indicate that the rate of reduction of the disulfide
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)