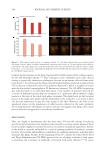
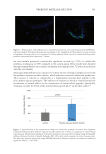
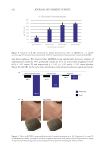
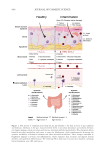
632 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
(26) Martin Patrick Pagac, Stalder M, Remo Campiche. Menopause and facial skin microbiomes: a pilot
study revealing novel insights into their relationship. Frontiers in aging. 2024 5(21). doi:10.3389/fragi
.2024.1353082
(27) Russo E, Leandro Di Gloria, Matteo Cerboneschi, et al. Facial skin microbiome: aging-related
changes and exploratory functional associations with host genetic factors, a pilot study. Biomedicines.
2023 11(3):684–684. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11030684
(28) Huang S, Haiminen N, Carrieri AP, et al. Human skin, oral, and gut microbiomes predict chronological
age. Grice EA, ed. mSystems. 2020 5(1). doi:10.1128/msystems.00630-19
(29) Jugé R, Rouaud-Tinguely P, Breugnot J, et al. Shift in skin microbiota of Western European women
across aging. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2018 125(3):907–916. doi:10.1111/jam.13929
(30) Downing DT, Stewart ME, Strauss JS. Changes in sebum secretion and the sebaceous gland. Clinics
in Geriatric Medicine. 1989 5(1):109–114. Accessed July 29, 2024. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.
gov/2645990/
(31) O’Neill AM, Gallo RL. Host-microbiome interactions and recent progress into understanding the
biology of acne vulgaris. Microbiome. 2018 6(1). doi:10.1186/s40168-018-0558-5
(32) Liavonchanka A, Hornung E, Feussner I, Rudolph MG. Structure and mechanism of the
Propionibacterium acnes polyunsaturated fatty acid isomerase. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences. 2006 103(8):2576–2581. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510144103
(33) Sangseob L, Hye LK, Hae JS, et al. Skin aging-related microbial types separated by Cutibacterium and
α-diversity. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 2023 23(3). doi:10.1111/jocd.16070
(34) Toba T, Virkola R, Westerlund B, et al. A collagen-binding S-layer protein in Lactobacillus crispatus.
Applied and environmental microbiology. 1995 61(7):2467–2471. doi:10.1128/aem.61.7.2467-2471.1995
(35) Antunes LC, Poppleton D, Klingl A, et al. Phylogenomic analysis supports the ancestral presence of
LPS-outer membranes in the Firmicutes. eLife. 2016 5. doi:10.7554/elife.14589
(26) Martin Patrick Pagac, Stalder M, Remo Campiche. Menopause and facial skin microbiomes: a pilot
study revealing novel insights into their relationship. Frontiers in aging. 2024 5(21). doi:10.3389/fragi
.2024.1353082
(27) Russo E, Leandro Di Gloria, Matteo Cerboneschi, et al. Facial skin microbiome: aging-related
changes and exploratory functional associations with host genetic factors, a pilot study. Biomedicines.
2023 11(3):684–684. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11030684
(28) Huang S, Haiminen N, Carrieri AP, et al. Human skin, oral, and gut microbiomes predict chronological
age. Grice EA, ed. mSystems. 2020 5(1). doi:10.1128/msystems.00630-19
(29) Jugé R, Rouaud-Tinguely P, Breugnot J, et al. Shift in skin microbiota of Western European women
across aging. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2018 125(3):907–916. doi:10.1111/jam.13929
(30) Downing DT, Stewart ME, Strauss JS. Changes in sebum secretion and the sebaceous gland. Clinics
in Geriatric Medicine. 1989 5(1):109–114. Accessed July 29, 2024. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.
gov/2645990/
(31) O’Neill AM, Gallo RL. Host-microbiome interactions and recent progress into understanding the
biology of acne vulgaris. Microbiome. 2018 6(1). doi:10.1186/s40168-018-0558-5
(32) Liavonchanka A, Hornung E, Feussner I, Rudolph MG. Structure and mechanism of the
Propionibacterium acnes polyunsaturated fatty acid isomerase. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences. 2006 103(8):2576–2581. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510144103
(33) Sangseob L, Hye LK, Hae JS, et al. Skin aging-related microbial types separated by Cutibacterium and
α-diversity. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 2023 23(3). doi:10.1111/jocd.16070
(34) Toba T, Virkola R, Westerlund B, et al. A collagen-binding S-layer protein in Lactobacillus crispatus.
Applied and environmental microbiology. 1995 61(7):2467–2471. doi:10.1128/aem.61.7.2467-2471.1995
(35) Antunes LC, Poppleton D, Klingl A, et al. Phylogenomic analysis supports the ancestral presence of
LPS-outer membranes in the Firmicutes. eLife. 2016 5. doi:10.7554/elife.14589