616 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
RESULTS
From a preliminary screening of peptides performed on both NHK, NHF, and C. acnes,
we selected the pKTSKS peptide which modulated pre-inflammatory mediators release,
reduced the growth of C. acnes cells and improved extracellular matrix protein synthesis
without any observed cytotoxicity.
EFFECT OF PKTSKS AND ITS COMPOUNDS ON C. ACNES AND S. EPIDERMIDIS GROWTH
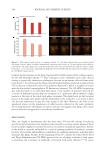
Growth of C. acnes with pKTSKS. C. acnes RT-1 cells grew regularly from 21–53 hours in
their cell culture medium with 0.1% DMSO (control). The presence of 0.1% DMSO had
no impact on C. acnes growth. On the other hand, pKTSKS (6–12 ppm) strongly reduced
C. acnes growth (Figure 2) with a dose-dependent effect. When treated with 6 ppm,
9 ppm and 12 ppm of peptide, C. acnes reached an OD
600nm
of 0.5 at respectively 52 hours,
77 hours, and 96 hours. All these values were significant compared to solvent control
(p 0.01). The peptide slows down the growth of this bacterium, limits its ability to reach
its quorum and to potentially acquire a more virulent phenotype.
In a second set of assays, RT-4, and RT-5 strains of C. acnes were tested in the same way
as RT-1. RT-5 and RT-4 strains required 3X and 2X more time respectively than RT-1 to
reach an OD
600nm
of 0.5 (data not shown). Therefore, it appears that, in vitro, the effects of
pKTSKS differ according to the strain used.
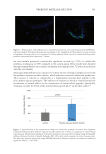
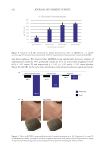
The in vitro activity was validated via a clinical trial. Analysis demonstrated that C. acnes
population of the pKTSKS treated zones of the face was reduced by 18.5% versus the zones
treated with the placebo cream (p =0.067), hence confirming the in vitro results.
Growth of C. acnes with KTSKS and/or palmitic acid. To further validate the interest of the
peptide pKTSKS, C. acnes RT-1 cells were put in contact with either the palmitic acid
alone (4 ppm), the “naked” peptide (8 ppm KTSKS), the association of 4 ppm palmitic acid
+8 ppm KTSKS (note that in the latter, palmitic acid and KTSKS do not form a single
INCI Placebo cream Active cream
%%
Water Qsp 100 Qsp 100
Squalane 3.00 3.00
C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate 2.00 2.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00
Polysorbate 20 1.00 1.00
Phenoxyethanol 0.80 0.80
Caprylyl Glycol 0.50 0.50
Sodium Hydroxide 0.50 0.50
carbomer 0.45 0.45
Acrylates/C10-30
Alkyl Acrylate
Crosspolymer
0.20 0.20
Potassium Sorbate 0.15 0.15
Fragrance 0.10 0.10
pKTSKS 0.00 0.0012
Figure 1. Formulation composition of the placebo and active creams used for the two clinical studies.
RESULTS
From a preliminary screening of peptides performed on both NHK, NHF, and C. acnes,
we selected the pKTSKS peptide which modulated pre-inflammatory mediators release,
reduced the growth of C. acnes cells and improved extracellular matrix protein synthesis
without any observed cytotoxicity.
EFFECT OF PKTSKS AND ITS COMPOUNDS ON C. ACNES AND S. EPIDERMIDIS GROWTH
Growth of C. acnes with pKTSKS. C. acnes RT-1 cells grew regularly from 21–53 hours in
their cell culture medium with 0.1% DMSO (control). The presence of 0.1% DMSO had
no impact on C. acnes growth. On the other hand, pKTSKS (6–12 ppm) strongly reduced
C. acnes growth (Figure 2) with a dose-dependent effect. When treated with 6 ppm,
9 ppm and 12 ppm of peptide, C. acnes reached an OD
600nm
of 0.5 at respectively 52 hours,
77 hours, and 96 hours. All these values were significant compared to solvent control
(p 0.01). The peptide slows down the growth of this bacterium, limits its ability to reach
its quorum and to potentially acquire a more virulent phenotype.
In a second set of assays, RT-4, and RT-5 strains of C. acnes were tested in the same way
as RT-1. RT-5 and RT-4 strains required 3X and 2X more time respectively than RT-1 to
reach an OD
600nm
of 0.5 (data not shown). Therefore, it appears that, in vitro, the effects of
pKTSKS differ according to the strain used.
The in vitro activity was validated via a clinical trial. Analysis demonstrated that C. acnes
population of the pKTSKS treated zones of the face was reduced by 18.5% versus the zones
treated with the placebo cream (p =0.067), hence confirming the in vitro results.
Growth of C. acnes with KTSKS and/or palmitic acid. To further validate the interest of the
peptide pKTSKS, C. acnes RT-1 cells were put in contact with either the palmitic acid
alone (4 ppm), the “naked” peptide (8 ppm KTSKS), the association of 4 ppm palmitic acid
+8 ppm KTSKS (note that in the latter, palmitic acid and KTSKS do not form a single
INCI Placebo cream Active cream
%%
Water Qsp 100 Qsp 100
Squalane 3.00 3.00
C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate 2.00 2.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00
Polysorbate 20 1.00 1.00
Phenoxyethanol 0.80 0.80
Caprylyl Glycol 0.50 0.50
Sodium Hydroxide 0.50 0.50
carbomer 0.45 0.45
Acrylates/C10-30
Alkyl Acrylate
Crosspolymer
0.20 0.20
Potassium Sorbate 0.15 0.15
Fragrance 0.10 0.10
pKTSKS 0.00 0.0012
Figure 1. Formulation composition of the placebo and active creams used for the two clinical studies.