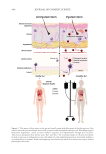
651 Bidirectional Gut-Skin Axis
(2) Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 9(4):244–253. doi:10.1038/
nrmicro2537
(3) De Pessemier B, Grine L, Debaere M, Maes A, Paetzold B, Callewaert C. Gut-skin axis: current
knowledge of the interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms.
February 2021 9(2). doi:10.3390/microorganisms9020353
(4) Mahmud MR, Akter S, Tamanna SK, et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis
observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes. July 2022 14(1):2096995. doi
:10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995
(5) den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud D-J, Bakker BM. The role of short-
chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res.
2013 54(9):2325–2340. doi:10.1194/jlr.R036012
(6) Dokoshi T, Chen Y, Cavagnero KJ, et al. Dermal injury drives a skin to gut axis that disrupts the
intestinal microbiome and intestinal immune homeostasis in mice. Nat Commun. April 2024 15(1):3009.
doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47072-3
(7) Hiergeist A, Gläsner J, Reischl U, Gessner A. Analyses of intestinal microbiota: culture versus
sequencing. ILAR J. 2015 56(2):228–240. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilv017
(8) Aguiar-Pulido V, Huang W, Suarez-Ulloa V, Cickovski T, Mathee K, Narasimhan G. Metagenomics,
metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics approaches for microbiome analysis. Evol Bioinform Online.
2016 12(suppl 1):5–16. doi:10.4137/EBO.S36436
(9) Handelsman J, Rondon MR, Brady SF, Clardy J, Goodman RM. Molecular biological access to the
chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem Biol. 1998 5(10):
R245–R249. doi:10.1016/s1074-5521(98)90108-9
(10) Ursell LK, Metcalf JL, Parfrey LW, Knight R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr Rev. 2012 70(suppl
1):S38–S44. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00493.x
(11) Martín R, Miquel S, Langella P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG. The role of metagenomics in understanding
the human microbiome in health and disease. Virulence. 2014 5(3):413–423. doi:10.4161/viru.27864
(12) Payne M, Azana R, Hoang LMN. Review of 16S and ITS direct sequencing results for clinical specimens
submitted to a reference laboratory. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2016 (March 2016) 2016:4210129.
doi:10.1155/2016/4210129
(13) Thomas T, Gilbert J, Meyer F. Metagenomics – a guide from sampling to data analysis. Microb Inform
Exp. February 2012 2(1):3. doi:10.1186/2042-5783-2-3
(14) Logsdon GA, Vollger MR, Eichler EE. Long-read human genome sequencing and its applications. Nat
Rev Genet. 2020 21(10):597–614. doi:10.1038/s41576-020-0236-x
(15) Grundy BS, Parikh H, Jacob S, et al. Pathogen detection using metagenomic next-generation sequencing
of plasma samples from patients with sepsis in Uganda. Microbiol Spectr. January 2023 11(1):e0431222.
doi:10.1128/spectrum.04312-22
(16) Pan S, Chen R. Metaproteomic analysis of human gut microbiome in digestive and metabolic diseases.
Adv Clin Chem. 2020 97:1–12. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2019.12.002
(17) Al-Amrani S, Al-Jabri Z, Al-Zaabi A, Alshekaili J, Al-Khabori M. Proteomics: concepts and applications
in human medicine. World J Biol Chem. 2021 12(5):57–69. doi:10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.57
(18) Han X, Gross RW. The foundations and development of lipidomics. J Lipid Res. February 2022 63(2):
100164. doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100164
(19) Chetty A, Blekhman R. Multi-omic approaches for host-microbiome data integration. Gut Microbes.
2024 16(1):2297860. doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2297860
(20) Bharti R, Grimm DG. Current challenges and best-practice protocols for microbiome analysis. Brief
Bioinform. 2021 22(1):178–193. doi:10.1093/bib/bbz155
(21) Huang H, Ren Z, Gao X, et al. Integrated analysis of microbiome and host transcriptome reveals
correlations between gut microbiota and clinical outcomes in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Genome Med. November 2020 12(1):102. doi:10.1186/s13073-020-00796-5
(2) Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 9(4):244–253. doi:10.1038/
nrmicro2537
(3) De Pessemier B, Grine L, Debaere M, Maes A, Paetzold B, Callewaert C. Gut-skin axis: current
knowledge of the interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms.
February 2021 9(2). doi:10.3390/microorganisms9020353
(4) Mahmud MR, Akter S, Tamanna SK, et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis
observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes. July 2022 14(1):2096995. doi
:10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995
(5) den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud D-J, Bakker BM. The role of short-
chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res.
2013 54(9):2325–2340. doi:10.1194/jlr.R036012
(6) Dokoshi T, Chen Y, Cavagnero KJ, et al. Dermal injury drives a skin to gut axis that disrupts the
intestinal microbiome and intestinal immune homeostasis in mice. Nat Commun. April 2024 15(1):3009.
doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47072-3
(7) Hiergeist A, Gläsner J, Reischl U, Gessner A. Analyses of intestinal microbiota: culture versus
sequencing. ILAR J. 2015 56(2):228–240. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilv017
(8) Aguiar-Pulido V, Huang W, Suarez-Ulloa V, Cickovski T, Mathee K, Narasimhan G. Metagenomics,
metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics approaches for microbiome analysis. Evol Bioinform Online.
2016 12(suppl 1):5–16. doi:10.4137/EBO.S36436
(9) Handelsman J, Rondon MR, Brady SF, Clardy J, Goodman RM. Molecular biological access to the
chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem Biol. 1998 5(10):
R245–R249. doi:10.1016/s1074-5521(98)90108-9
(10) Ursell LK, Metcalf JL, Parfrey LW, Knight R. Defining the human microbiome. Nutr Rev. 2012 70(suppl
1):S38–S44. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00493.x
(11) Martín R, Miquel S, Langella P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG. The role of metagenomics in understanding
the human microbiome in health and disease. Virulence. 2014 5(3):413–423. doi:10.4161/viru.27864
(12) Payne M, Azana R, Hoang LMN. Review of 16S and ITS direct sequencing results for clinical specimens
submitted to a reference laboratory. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2016 (March 2016) 2016:4210129.
doi:10.1155/2016/4210129
(13) Thomas T, Gilbert J, Meyer F. Metagenomics – a guide from sampling to data analysis. Microb Inform
Exp. February 2012 2(1):3. doi:10.1186/2042-5783-2-3
(14) Logsdon GA, Vollger MR, Eichler EE. Long-read human genome sequencing and its applications. Nat
Rev Genet. 2020 21(10):597–614. doi:10.1038/s41576-020-0236-x
(15) Grundy BS, Parikh H, Jacob S, et al. Pathogen detection using metagenomic next-generation sequencing
of plasma samples from patients with sepsis in Uganda. Microbiol Spectr. January 2023 11(1):e0431222.
doi:10.1128/spectrum.04312-22
(16) Pan S, Chen R. Metaproteomic analysis of human gut microbiome in digestive and metabolic diseases.
Adv Clin Chem. 2020 97:1–12. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2019.12.002
(17) Al-Amrani S, Al-Jabri Z, Al-Zaabi A, Alshekaili J, Al-Khabori M. Proteomics: concepts and applications
in human medicine. World J Biol Chem. 2021 12(5):57–69. doi:10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.57
(18) Han X, Gross RW. The foundations and development of lipidomics. J Lipid Res. February 2022 63(2):
100164. doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100164
(19) Chetty A, Blekhman R. Multi-omic approaches for host-microbiome data integration. Gut Microbes.
2024 16(1):2297860. doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2297860
(20) Bharti R, Grimm DG. Current challenges and best-practice protocols for microbiome analysis. Brief
Bioinform. 2021 22(1):178–193. doi:10.1093/bib/bbz155
(21) Huang H, Ren Z, Gao X, et al. Integrated analysis of microbiome and host transcriptome reveals
correlations between gut microbiota and clinical outcomes in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Genome Med. November 2020 12(1):102. doi:10.1186/s13073-020-00796-5