602 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
MINIMUM INHIBITORY CONCENTRATION ANALYSIS
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is another effective tool used to access a
microbiome environment. This method was developed in response to issues pertaining to
the inefficiency of medical therapies to cure bacterial infections. MIC measures the in vitro
susceptibility or resistance of bacteria strains to an antibiotic, which is crucial for selecting
a therapeutic strategy to directly influence the success of infection treatment.13 MICs go a
step further than the above metagenomic sequencing. While metagenomic sequencing is
valuable for assessing the entire microbial environment, MIC testing provides a solution to
the infectious problem. With the current research of correlating certain bacteria overgrowth
on the skin to certain skin conditions, an MIC reading will provide an effective treatment
plan to restore the skin’s microbiome.
There are a few different MIC methods, including dilution (in agar or in a liquid medium)
or gradient methods (strips impregnated with a predetermined concentration gradient of
an antibiotic).13 Whichever media is chosen, within 30 minutes of preparation, the bacteria
should be added in a way that cell density is maintained. The incubation is conducted in
aerobic conditions between 18 to 24 hours. After this time, the medium is observed for any
growth of bacterial colonies. The report then states the lowest concentration of an antibiotic
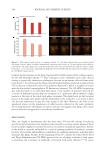
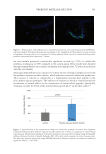
in which there is no bacterial growth, the MIC.13 Figure 2 below displays an example of the
agar dilution method, one of the most used and accepted.14
Usually, multiple antibiotics are evaluated on the same bacteria to gather data at which
would be the most effective. The data is split into quantitative data (the MIC value) and
qualitative data (susceptible, intermediate, or resistant). Table I below is an example of MIC
data collected to assess the susceptibility against Klebsiella pneumoniae, a type of Gram-
negative bacteria that typically causes nosocomial infections, or infections commonly
acquired in a hospital setting.13
It is important to highlight that an alternative model was recently required due to the
growing body of evidence indicating that problematic bacterial species on the skin
frequently form biofilms. To address this, antimicrobial efficacy must be evaluated within
the context of biofilm formation, necessitating the use of a Minimum Biofilm Eradication
Figure 2. Redrawn from Giuliano.14 A quantified concentration of microorganisms on an agar plate. The
MIC is determined by identifying the lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth. This
example shows an MIC of 32 mcg/mL.14
MINIMUM INHIBITORY CONCENTRATION ANALYSIS
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is another effective tool used to access a
microbiome environment. This method was developed in response to issues pertaining to
the inefficiency of medical therapies to cure bacterial infections. MIC measures the in vitro
susceptibility or resistance of bacteria strains to an antibiotic, which is crucial for selecting
a therapeutic strategy to directly influence the success of infection treatment.13 MICs go a
step further than the above metagenomic sequencing. While metagenomic sequencing is
valuable for assessing the entire microbial environment, MIC testing provides a solution to
the infectious problem. With the current research of correlating certain bacteria overgrowth
on the skin to certain skin conditions, an MIC reading will provide an effective treatment
plan to restore the skin’s microbiome.
There are a few different MIC methods, including dilution (in agar or in a liquid medium)
or gradient methods (strips impregnated with a predetermined concentration gradient of
an antibiotic).13 Whichever media is chosen, within 30 minutes of preparation, the bacteria
should be added in a way that cell density is maintained. The incubation is conducted in
aerobic conditions between 18 to 24 hours. After this time, the medium is observed for any
growth of bacterial colonies. The report then states the lowest concentration of an antibiotic
in which there is no bacterial growth, the MIC.13 Figure 2 below displays an example of the
agar dilution method, one of the most used and accepted.14
Usually, multiple antibiotics are evaluated on the same bacteria to gather data at which
would be the most effective. The data is split into quantitative data (the MIC value) and
qualitative data (susceptible, intermediate, or resistant). Table I below is an example of MIC
data collected to assess the susceptibility against Klebsiella pneumoniae, a type of Gram-
negative bacteria that typically causes nosocomial infections, or infections commonly
acquired in a hospital setting.13
It is important to highlight that an alternative model was recently required due to the
growing body of evidence indicating that problematic bacterial species on the skin
frequently form biofilms. To address this, antimicrobial efficacy must be evaluated within
the context of biofilm formation, necessitating the use of a Minimum Biofilm Eradication
Figure 2. Redrawn from Giuliano.14 A quantified concentration of microorganisms on an agar plate. The
MIC is determined by identifying the lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits bacterial growth. This
example shows an MIC of 32 mcg/mL.14