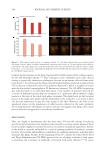
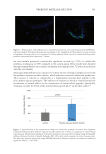
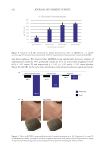
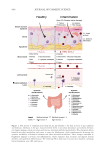
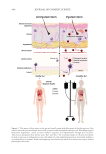
587 Specificities of Microbiota From Sensitive Skin
a tool to import, store, analyze, and graphically display complex phylogenetic sequencing
data that has already been clustered into Operational Taxonomic Units (GitHub, San
Francisco, CA, USA). The Cumulative Sum Scaling was produced by exporting data in
the appropriate format using phyloseq_to_metagenomeSeq function from the phyloseq
package and counts were normalized with MRcounts from metagenomeSeq package. TSS
also called “relative abundance” was used as default method for the subsequent analysis.
CREATION OF A BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM THE NORMAL AND SENSITIVE SKIN SUBJECTS
More than 4,000 isolates were retrieved by DBMT (droplet containing or not bacteria
sorting drop by drop). Amplification of the 16S rRNA gene was performed with the high-
fidelity polymerase (Q5 polymerase) and sequenced using PacBio Sequel II 8M. 16S rRNA
gene sequences allowed for isolate identification (genus, species, and ASVs level). The NS
and SS microbial collections were then constituted by coupling the information from the
bioinformatic analysis regarding prevalence and abundance. Thirty-one isolated species
from NS were selected to create our representative NS collection: 10 Cutibacterium, 17
Staphylococcus, 1 Micrococcus, and 3 Corynebacterium. Likewise, 31 species were selected from
SS for the SS collection: 8 Cutibacterium, 12 Staphylococcus, 1 Micrococcus, 3 Corynebacterium, 2
Kocuria, 2 Streptococcus, 1 Roseomonas, 1 Enhydrobacter, and 1 Bacillus.
ACTIVE INGREDIENT PROFILING ON THE BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM INDIVIDUALS WITH
NORMAL SKIN
Ingredients: Inonotus obliquus (mushroom) extract was tested at concentrations ranging from
0.01–1% and Dendrobium officinale stem extract at concentration from 0.002–0.05% (BASF,
France).
A classical microtiter plate method was performed. Briefly, the species from the NS
collection were grown in 96-well culture plates with triplicates of the ingredients at 4
concentrations or without ingredients, in 200 µL of BHI medium for all species except
for Corynebacterium species that were cultivated in liquid medium (confidential medium).
Plates were incubated at 37°C in a shaking or non-shaking incubator depending on the
strains. Growth was assessed after 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours by optical density
measurement at 600 nm (Spark, Tecan, Switzerland). Results from n =4 and compared to
the untreated. Statistics: Dunnett’s multiple comparison test significant if p 0.05.
IMPACT OF C. ACNES FROM NS OR SS ON KERATINOCYTES
C. acnes coming from four donors were evaluated (namely NS, SS4, SS7, and SS8) on normal
human keratinocytes either through indirect or direct interaction. The representative strain
of NS was first chosen according to its phylotype (IA1, i.e. the more represented on skin)
and a preselection based on the evaluation of lipase activity (the selected NS strain has a
medium range of lipase activity among five other strains, data not shown).
To study indirect interaction, normal human keratinocytes from plastic surgery
(abdominal part, 26 years old) were seeded in 96-well culture plates with 15,000 cells/
cm2 in Keratinocyte Serum-Free Medium (KSFM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 24
a tool to import, store, analyze, and graphically display complex phylogenetic sequencing
data that has already been clustered into Operational Taxonomic Units (GitHub, San
Francisco, CA, USA). The Cumulative Sum Scaling was produced by exporting data in
the appropriate format using phyloseq_to_metagenomeSeq function from the phyloseq
package and counts were normalized with MRcounts from metagenomeSeq package. TSS
also called “relative abundance” was used as default method for the subsequent analysis.
CREATION OF A BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM THE NORMAL AND SENSITIVE SKIN SUBJECTS
More than 4,000 isolates were retrieved by DBMT (droplet containing or not bacteria
sorting drop by drop). Amplification of the 16S rRNA gene was performed with the high-
fidelity polymerase (Q5 polymerase) and sequenced using PacBio Sequel II 8M. 16S rRNA
gene sequences allowed for isolate identification (genus, species, and ASVs level). The NS
and SS microbial collections were then constituted by coupling the information from the
bioinformatic analysis regarding prevalence and abundance. Thirty-one isolated species
from NS were selected to create our representative NS collection: 10 Cutibacterium, 17
Staphylococcus, 1 Micrococcus, and 3 Corynebacterium. Likewise, 31 species were selected from
SS for the SS collection: 8 Cutibacterium, 12 Staphylococcus, 1 Micrococcus, 3 Corynebacterium, 2
Kocuria, 2 Streptococcus, 1 Roseomonas, 1 Enhydrobacter, and 1 Bacillus.
ACTIVE INGREDIENT PROFILING ON THE BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM INDIVIDUALS WITH
NORMAL SKIN
Ingredients: Inonotus obliquus (mushroom) extract was tested at concentrations ranging from
0.01–1% and Dendrobium officinale stem extract at concentration from 0.002–0.05% (BASF,
France).
A classical microtiter plate method was performed. Briefly, the species from the NS
collection were grown in 96-well culture plates with triplicates of the ingredients at 4
concentrations or without ingredients, in 200 µL of BHI medium for all species except
for Corynebacterium species that were cultivated in liquid medium (confidential medium).
Plates were incubated at 37°C in a shaking or non-shaking incubator depending on the
strains. Growth was assessed after 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours by optical density
measurement at 600 nm (Spark, Tecan, Switzerland). Results from n =4 and compared to
the untreated. Statistics: Dunnett’s multiple comparison test significant if p 0.05.
IMPACT OF C. ACNES FROM NS OR SS ON KERATINOCYTES
C. acnes coming from four donors were evaluated (namely NS, SS4, SS7, and SS8) on normal
human keratinocytes either through indirect or direct interaction. The representative strain
of NS was first chosen according to its phylotype (IA1, i.e. the more represented on skin)
and a preselection based on the evaluation of lipase activity (the selected NS strain has a
medium range of lipase activity among five other strains, data not shown).
To study indirect interaction, normal human keratinocytes from plastic surgery
(abdominal part, 26 years old) were seeded in 96-well culture plates with 15,000 cells/
cm2 in Keratinocyte Serum-Free Medium (KSFM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 24