591 Specificities of Microbiota From Sensitive Skin
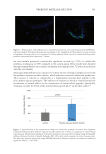
even if less abundant than other Staphylococci, S. aureus was increased by 2.8-fold in the SS
compared to the NS subjects.
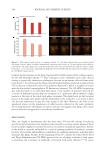
The genus Corynebacterium is another good example of the interest of an analysis at the
species level. At the genus level we observed no variation of abundance between the two
cohorts (Figure 3), but if we look at the species level, we can see a lot of variations between
NS and SS (Figure 5). The most represented Corynebacterium species is Corynebacterium
kroppenstedtii, and this species is 1.6 times more present in SS than in NS. Less represented,
but maybe important in the biology of sensitive skin, Corynebacterium tuberculostearicum,
Corynebacterium coyleae, and Corynebacterium imitans were increased by 3.8, 16.5, and 7.9-fold
respectively in SS. Conversely, the relative abundance of C. accolens decreased by 4-fold in
SS subjects.
In addition, multiple species were only found in one cohort or the other. For instance,
Corynebacterium simulans, Corynebacterium genitalium, Corynebacterium durum, Corynebacterium
pseudogenitalium, Corynebacterium jeikeium, and Corynebacterium amycolatum, were only found
in NS, but Corynebacterium casei, Corynebacterium lipophiloflavum, Corynebacterium massiliense,
Corynebacterium resistens, and Corynebacterium mastitidis were only found in SS.
CREATION OF BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM NORMAL AND SENSITIVE SKIN TO TEST ACTIVE
INGREDIENTS
Using DBMT, we isolated several hundred species and built our bacterial collection, from
which we selected the species representative of SS and NS conditions. For some bacteria,
we decided to select multiple species from a single genus. For the NS, we isolated and
selected 10 Cutibacteria, 17 Staphylococci, 1 Micrococcus, and 3 Corynebacteria species. Then
31 species were isolated and selected from SS with 8 Cutibacteria, 12 Staphylococci, 1
Micrococci, 3 Corynebacteria, 2 Kocuria, 2 Streptococci, 1 Roseomonas, 1 Enhydrobacter, and 1
Bacillus.
5
9
1
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Normal skin Sensitive skin
C.mastitidis
C.resistens
C.massiliense
C.lipophiloflavum
C.casei
C.bovis
C.suicordis
C.urinapleomorphum
C.aurimucosum
C.imitans
C.amycolatum
C.jeikeium
C.pseudogenitalium
C.coyleae
C.durum
C.ureicelerivorans
C.genitalium
C.tuberculostearicum
C.mucifaciens
C.simulans
C.accolens
C.kroppenstedtii
0.5
0.5
Figure 5. Sequencing analysis between normal and sensitive skin. Illustration of Corynebacterium species
abundance relative to the global abundance bacterial species between normal and sensitive skin.
Corynebacterium
abundance
(%)
even if less abundant than other Staphylococci, S. aureus was increased by 2.8-fold in the SS
compared to the NS subjects.
The genus Corynebacterium is another good example of the interest of an analysis at the
species level. At the genus level we observed no variation of abundance between the two
cohorts (Figure 3), but if we look at the species level, we can see a lot of variations between
NS and SS (Figure 5). The most represented Corynebacterium species is Corynebacterium
kroppenstedtii, and this species is 1.6 times more present in SS than in NS. Less represented,
but maybe important in the biology of sensitive skin, Corynebacterium tuberculostearicum,
Corynebacterium coyleae, and Corynebacterium imitans were increased by 3.8, 16.5, and 7.9-fold
respectively in SS. Conversely, the relative abundance of C. accolens decreased by 4-fold in
SS subjects.
In addition, multiple species were only found in one cohort or the other. For instance,
Corynebacterium simulans, Corynebacterium genitalium, Corynebacterium durum, Corynebacterium
pseudogenitalium, Corynebacterium jeikeium, and Corynebacterium amycolatum, were only found
in NS, but Corynebacterium casei, Corynebacterium lipophiloflavum, Corynebacterium massiliense,
Corynebacterium resistens, and Corynebacterium mastitidis were only found in SS.
CREATION OF BACTERIAL COLLECTION FROM NORMAL AND SENSITIVE SKIN TO TEST ACTIVE
INGREDIENTS
Using DBMT, we isolated several hundred species and built our bacterial collection, from
which we selected the species representative of SS and NS conditions. For some bacteria,
we decided to select multiple species from a single genus. For the NS, we isolated and
selected 10 Cutibacteria, 17 Staphylococci, 1 Micrococcus, and 3 Corynebacteria species. Then
31 species were isolated and selected from SS with 8 Cutibacteria, 12 Staphylococci, 1
Micrococci, 3 Corynebacteria, 2 Kocuria, 2 Streptococci, 1 Roseomonas, 1 Enhydrobacter, and 1
Bacillus.
5
9
1
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Normal skin Sensitive skin
C.mastitidis
C.resistens
C.massiliense
C.lipophiloflavum
C.casei
C.bovis
C.suicordis
C.urinapleomorphum
C.aurimucosum
C.imitans
C.amycolatum
C.jeikeium
C.pseudogenitalium
C.coyleae
C.durum
C.ureicelerivorans
C.genitalium
C.tuberculostearicum
C.mucifaciens
C.simulans
C.accolens
C.kroppenstedtii
0.5
0.5
Figure 5. Sequencing analysis between normal and sensitive skin. Illustration of Corynebacterium species
abundance relative to the global abundance bacterial species between normal and sensitive skin.
Corynebacterium
abundance
(%)