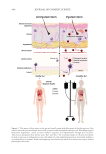
645 Bidirectional Gut-Skin Axis
NUTRICOSMETIC APPLICATIONS
Nutricosmetics are a diverse range of wellness products designed to improve the cosmetic
health of skin, nails and hair through nutritional supplementation.120 Often marketed as
promoting “beauty from within” or as “beauty pills,” these products incorporate nutraceuticals
or food-derived substances that support cosmetic appearance and concerns.121 This category
includes probiotic products, as well as their complementary prebiotics and postbiotics, which
are used to enhance overall health, and other supplements, such as collagen peptides and
omega-3 fatty acids. Other examples beyond the scope of this review include polysaccharides
(e.g., hyaluronic acid), minerals (e.g., zinc, selenium), vitamins (e.g., vitamin E, vitamin
C), secondary metabolites (e.g., carotenoids, astaxanthin, coenzyme Q10) and other plant
extracts (e.g., aloe vera, horsetail).120 Unlike LBPs, which are intended for therapeutic disease
prevention or treatment, nutricosmetics generally enhance general health and well-being.
As previously stated, prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively
stimulate the growth and activity of microorganisms, primarily focusing on promoting
beneficial bacteria.122 These prebiotics may be oral or topical products that serve to nourish
probiotics, which are live microorganisms known for their ability to positively influence
the host organism by modulating the immune response and competing with pathogenic
bacteria.123 The definition of probiotics has evolved in conjunction with advancements in
research, although the term originally comprises the Greek root word meaning “for life,”
coined by Parker in 1974.34 Postbiotics are utilized to enhance the effects of probiotics they
consist of non-viable, active by-products derived from probiotic lysates, including cellular
components and metabolites that exhibit potent immunomodulatory properties. Probiotics
and postbiotics may also be administered orally or topically.97
The use of probiotics to address various cosmetic skin conditions has shown promise.124 While
most research in this field focuses on topical applications, this review will concentrate on oral
supplementation within the context of the gut-skin axis, targeting cosmetic concerns. One
area of interest is skin brightening and whitening, targeting issues like ephelides (freckles)
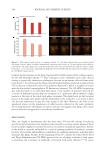
and melasma, wherein melanin is overproduced.125 In a preclinical study, B. adolescentis
culture filtrate was shown to reduce melanin levels in B16F10 murine melanoma cells by
inhibiting tyrosinase activity, a key enzyme in melanogenesis.126 Similarly, Lactobacillus
species, like L. helveticus NS8, have demonstrated the ability to decrease melanin levels and
improve skin pigmentation in B16F10 murine melanoma cells.127 Rhodobacter sphaeroides
(Lysogen™) has also shown an ability to reduce melanin synthesis in B16F10 murine
melanoma cells and zebrafish, in a dose-dependent manner.128
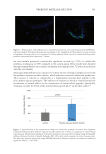
Additionally, research has demonstrated that probiotics may cause alterations in the gut
microbiome that provide a photoprotective effect by modulating the immune response to
UV radiation.129 This effect was investigated in a study where participants consumed the
oral probiotic L. johnsonii daily for 2 months. Following this period, sample sites on their
skin were exposed to short-term UV radiation to assess the impact on skin homeostasis.
The results showed that epidermal cells in the probiotic group recovered significantly faster,
with immune function improving or fully returning by day 4, compared to day 10 in
the placebo group.130 Further research exploring the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
properties of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and lactic acid bacteria, specifically L.
fermentum TKSN041, demonstrated its ability to mitigate skin damage from UV radiation,
potentially offering health benefits in treating age-associated skin conditions.131
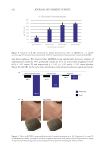
Furthermore, other strains of Lactobacillus have also demonstrated anti-photoaging effects. Oral
probiotic L. plantarum HY7714 demonstrated a reduction in moisture loss and wrinkle depth,
NUTRICOSMETIC APPLICATIONS
Nutricosmetics are a diverse range of wellness products designed to improve the cosmetic
health of skin, nails and hair through nutritional supplementation.120 Often marketed as
promoting “beauty from within” or as “beauty pills,” these products incorporate nutraceuticals
or food-derived substances that support cosmetic appearance and concerns.121 This category
includes probiotic products, as well as their complementary prebiotics and postbiotics, which
are used to enhance overall health, and other supplements, such as collagen peptides and
omega-3 fatty acids. Other examples beyond the scope of this review include polysaccharides
(e.g., hyaluronic acid), minerals (e.g., zinc, selenium), vitamins (e.g., vitamin E, vitamin
C), secondary metabolites (e.g., carotenoids, astaxanthin, coenzyme Q10) and other plant
extracts (e.g., aloe vera, horsetail).120 Unlike LBPs, which are intended for therapeutic disease
prevention or treatment, nutricosmetics generally enhance general health and well-being.
As previously stated, prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively
stimulate the growth and activity of microorganisms, primarily focusing on promoting
beneficial bacteria.122 These prebiotics may be oral or topical products that serve to nourish
probiotics, which are live microorganisms known for their ability to positively influence
the host organism by modulating the immune response and competing with pathogenic
bacteria.123 The definition of probiotics has evolved in conjunction with advancements in
research, although the term originally comprises the Greek root word meaning “for life,”
coined by Parker in 1974.34 Postbiotics are utilized to enhance the effects of probiotics they
consist of non-viable, active by-products derived from probiotic lysates, including cellular
components and metabolites that exhibit potent immunomodulatory properties. Probiotics
and postbiotics may also be administered orally or topically.97
The use of probiotics to address various cosmetic skin conditions has shown promise.124 While
most research in this field focuses on topical applications, this review will concentrate on oral
supplementation within the context of the gut-skin axis, targeting cosmetic concerns. One
area of interest is skin brightening and whitening, targeting issues like ephelides (freckles)
and melasma, wherein melanin is overproduced.125 In a preclinical study, B. adolescentis
culture filtrate was shown to reduce melanin levels in B16F10 murine melanoma cells by
inhibiting tyrosinase activity, a key enzyme in melanogenesis.126 Similarly, Lactobacillus
species, like L. helveticus NS8, have demonstrated the ability to decrease melanin levels and
improve skin pigmentation in B16F10 murine melanoma cells.127 Rhodobacter sphaeroides
(Lysogen™) has also shown an ability to reduce melanin synthesis in B16F10 murine
melanoma cells and zebrafish, in a dose-dependent manner.128
Additionally, research has demonstrated that probiotics may cause alterations in the gut
microbiome that provide a photoprotective effect by modulating the immune response to
UV radiation.129 This effect was investigated in a study where participants consumed the
oral probiotic L. johnsonii daily for 2 months. Following this period, sample sites on their
skin were exposed to short-term UV radiation to assess the impact on skin homeostasis.
The results showed that epidermal cells in the probiotic group recovered significantly faster,
with immune function improving or fully returning by day 4, compared to day 10 in
the placebo group.130 Further research exploring the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
properties of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and lactic acid bacteria, specifically L.
fermentum TKSN041, demonstrated its ability to mitigate skin damage from UV radiation,
potentially offering health benefits in treating age-associated skin conditions.131
Furthermore, other strains of Lactobacillus have also demonstrated anti-photoaging effects. Oral
probiotic L. plantarum HY7714 demonstrated a reduction in moisture loss and wrinkle depth,