573 COSMETIC INGREDIENTS THAT RESPECT SKIN MICROBIOTA
Phenoxyethanol (1%) was used as a negative control in each test series to validate the
efficacy of the assay.
EVALUATION OF NEUTRAL SUBSTANCES
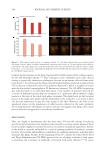
Substances without bactericidal effect were evaluated: Two carbohydrates (glucose and
inulin), two amino acids (glycine and proline) and glycerol. After 8 hours, the bacterial
concentrations were measured and the score of each tested ingredient (sum of LR, Table II)
was calculated according to the method described above (Figure 6).
Glucose and inulin were tested at 0.1% and 1%, as well as 2% for glucose. Even at the
highest concentrations, the LRs were negligible for all bacteria and consequently the scores
were close to zero, indicating an absence of effect of the materials.
Amino acids were tested at 0.1% and 1%. The maximum LR was observed for proline
at 1% on S epidermidis (LR =–2.7). The other LR were close to –1 and overall, scores
were comprised between 0 and –5. The maximum LR for glycerol (1%) was observed for
S epidermidis (–2.1). The maximum score on the consortium was –4.2. The scores obtained
by summing up all the LR indicate that the products had a negligible effect on the
consortium. As expected, glucose, inulin, proline, glycine, and glycerol can be considered
friendly toward the microbiota.
Table II
Logarithmic Reductions (LR) of Each Five Bacterial Species After Contact With Neutral Ingredients
Concentration (%)C acnes S epidermidis S mitis M luteus C xerosis
Glucose 0.1 –0.24 –0.82 –0.13 –0.27 –0.23
1.0 –0.44 –0.82 –0.20 0.03 –0.25
2.0 –0.23 –0.16 –0.27 0.18 0.02
Inulin 0.1 –0.86 –0.59 0.13 –0.05 –0.08
1.0 –1.20 –0.31 0.14 0.37 –0.16
Glycine 0.1 –0.70 –1.23 0.00 0.64 –0.55
1.0 –2.53 –0.75 –2.60 1.19 0.02
Proline 0.1 –1.70 –1.80 –0.30 0.10 –0.10
1.0 –0.80 –2.70 –0.80 0.20 –0.50
Glycerol 0.1 –1.20 –1.10 –0.30 0.10 0.00
1.0 –1.50 –2.10 –0.40 0.20 –0.40
Figure 6. Evaluation of neutral substances on the consortium. The gray hatched histogram represents the
maximum score (maximum LR).
Phenoxyethanol (1%) was used as a negative control in each test series to validate the
efficacy of the assay.
EVALUATION OF NEUTRAL SUBSTANCES
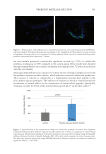
Substances without bactericidal effect were evaluated: Two carbohydrates (glucose and
inulin), two amino acids (glycine and proline) and glycerol. After 8 hours, the bacterial
concentrations were measured and the score of each tested ingredient (sum of LR, Table II)
was calculated according to the method described above (Figure 6).
Glucose and inulin were tested at 0.1% and 1%, as well as 2% for glucose. Even at the
highest concentrations, the LRs were negligible for all bacteria and consequently the scores
were close to zero, indicating an absence of effect of the materials.
Amino acids were tested at 0.1% and 1%. The maximum LR was observed for proline
at 1% on S epidermidis (LR =–2.7). The other LR were close to –1 and overall, scores
were comprised between 0 and –5. The maximum LR for glycerol (1%) was observed for
S epidermidis (–2.1). The maximum score on the consortium was –4.2. The scores obtained
by summing up all the LR indicate that the products had a negligible effect on the
consortium. As expected, glucose, inulin, proline, glycine, and glycerol can be considered
friendly toward the microbiota.
Table II
Logarithmic Reductions (LR) of Each Five Bacterial Species After Contact With Neutral Ingredients
Concentration (%)C acnes S epidermidis S mitis M luteus C xerosis
Glucose 0.1 –0.24 –0.82 –0.13 –0.27 –0.23
1.0 –0.44 –0.82 –0.20 0.03 –0.25
2.0 –0.23 –0.16 –0.27 0.18 0.02
Inulin 0.1 –0.86 –0.59 0.13 –0.05 –0.08
1.0 –1.20 –0.31 0.14 0.37 –0.16
Glycine 0.1 –0.70 –1.23 0.00 0.64 –0.55
1.0 –2.53 –0.75 –2.60 1.19 0.02
Proline 0.1 –1.70 –1.80 –0.30 0.10 –0.10
1.0 –0.80 –2.70 –0.80 0.20 –0.50
Glycerol 0.1 –1.20 –1.10 –0.30 0.10 0.00
1.0 –1.50 –2.10 –0.40 0.20 –0.40
Figure 6. Evaluation of neutral substances on the consortium. The gray hatched histogram represents the
maximum score (maximum LR).