561 Prebiotic Micellar Solution
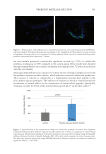
the test formula promoted a statistically significant increase (p 0.01) in cathelicidin
synthesis, reaching up to 98% compared to the control group. These results were obtained
through immunofluorescence analysis on human skin explants after 72 hours of incubation
with the test formula.
Analyzing immunofluorescence images reveal more intense coloring in samples treated with
the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution, which indicates increased cathelicidin production.
This increase is relevant as cathelicidin is a fundamental antimicrobial peptide in the
skin’s defense against pathogens. The influence of cleansers on the skin extends beyond the
microbiome to include effects on the composition of antimicrobial peptides. Specifically,
cleansing can alter the levels of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on the skin surface.41
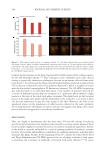
Figure 4. Evaluation by immunofluorescence anticathelicidin (green) and counterstaining with DAPI (blue,
cell nuclei marker). The figure shows microscope images at 40× magnification. Histological sections of 10 µm
in fragments of human skin (ex vivo) incubated in culture medium (basal control) or treated with the product
prebiotic aqueous micellar solution for 72 hours.
Figure 5. Quantification of the representative images of cathelicidin synthesis in human skin fragments
incubated with the product prebiotic aqueous micellar solution for 72 hours in comparison to control (basal
control) group. The mean pixel intensity of the green channel was measured for each image using the ImageJ®
software (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), with results expressed in units of square pixels.
The data were analyzed statistically using ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test and were considered
significant when p 0.05 (95%).
the test formula promoted a statistically significant increase (p 0.01) in cathelicidin
synthesis, reaching up to 98% compared to the control group. These results were obtained
through immunofluorescence analysis on human skin explants after 72 hours of incubation
with the test formula.
Analyzing immunofluorescence images reveal more intense coloring in samples treated with
the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution, which indicates increased cathelicidin production.
This increase is relevant as cathelicidin is a fundamental antimicrobial peptide in the
skin’s defense against pathogens. The influence of cleansers on the skin extends beyond the
microbiome to include effects on the composition of antimicrobial peptides. Specifically,
cleansing can alter the levels of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on the skin surface.41
Figure 4. Evaluation by immunofluorescence anticathelicidin (green) and counterstaining with DAPI (blue,
cell nuclei marker). The figure shows microscope images at 40× magnification. Histological sections of 10 µm
in fragments of human skin (ex vivo) incubated in culture medium (basal control) or treated with the product
prebiotic aqueous micellar solution for 72 hours.
Figure 5. Quantification of the representative images of cathelicidin synthesis in human skin fragments
incubated with the product prebiotic aqueous micellar solution for 72 hours in comparison to control (basal
control) group. The mean pixel intensity of the green channel was measured for each image using the ImageJ®
software (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), with results expressed in units of square pixels.
The data were analyzed statistically using ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test and were considered
significant when p 0.05 (95%).