622 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
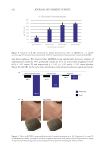
and skin roughness. We observed that pKTSKS-cream significantly decreases volumes of
inflammatory marks by 39%, pockmark volume by 23%, as well as skin roughness by 8%
(all p 0.01 versus T0 and respectively p 0.05, p 0.01 and p 0.01 versus placebo
Figure 9A and 9B). At the same time, the placebo cream showed weak non-significant results.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
Solvent control pKTSKS 6ppm pKTSKS 9ppm pKTSKS 12ppm
Kerag415nocyte treatement
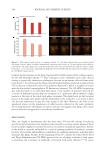
IL-1Ra levels in kerag415nocytes
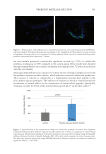
Figure 8. Variation in IL-1Ra production by human keratinocytes effect of pKTSKS (n =5). IL-1Ra
secretion (pg/106 keratinocytes) measured by ELISA in supernatants of keratinocytes treated with pKTKS.
A
B
Figure 9. Effect of pKTSKS-cream and placebo after 2 months treatment (n =18). Variation in %versus T0
of inflammatory marks, pockmark, and skin roughness measured with Antera 3D (A). Representative image
of improved pockmark appearance and example of 3D acquisition modeling by Antera 3D (B).
pg/10^6cells
and skin roughness. We observed that pKTSKS-cream significantly decreases volumes of
inflammatory marks by 39%, pockmark volume by 23%, as well as skin roughness by 8%
(all p 0.01 versus T0 and respectively p 0.05, p 0.01 and p 0.01 versus placebo
Figure 9A and 9B). At the same time, the placebo cream showed weak non-significant results.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
Solvent control pKTSKS 6ppm pKTSKS 9ppm pKTSKS 12ppm
Kerag415nocyte treatement
IL-1Ra levels in kerag415nocytes
Figure 8. Variation in IL-1Ra production by human keratinocytes effect of pKTSKS (n =5). IL-1Ra
secretion (pg/106 keratinocytes) measured by ELISA in supernatants of keratinocytes treated with pKTKS.
A
B
Figure 9. Effect of pKTSKS-cream and placebo after 2 months treatment (n =18). Variation in %versus T0
of inflammatory marks, pockmark, and skin roughness measured with Antera 3D (A). Representative image
of improved pockmark appearance and example of 3D acquisition modeling by Antera 3D (B).
pg/10^6cells