571 COSMETIC INGREDIENTS THAT RESPECT SKIN MICROBIOTA
Finally, the adequate protocol to grow the five species consortium was at a pH of 6.5, a
temperature of 32°C, under anaerobic atmosphere for 8 hours. The reproducibility of this
method was assessed by proceeding to 13 independent assays. Bacteria concentrations in
the consortium were measured and their proportions were calculated (Figure 4A and B).
In terms of population ratios (%,Figure 4A), the most important variation was observed
on C acnes (CI 95% =31.6–42.8%). The least concentrated bacteria (C xerosis and M luteus)
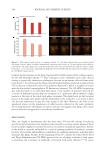
Figure 3. Proportions of bacteria in the consortium containing C acnes (dark blue), S epidermidis (light blue),
S mitis (purple), M luteus (red) and C xerosis (orange) with or without oxygen. Species proportion (%)in the
consortium is the ratio between a species concentration (in CFU/mL) and the concentration of total bacteria
(in CFU/mL) multiplied by 100.
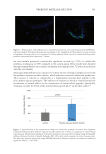
Figure 4. Reproducibility of the consortium in 13 independent assays. (A). Mean species proportions in the
consortium (%,n =13). The whiskers are the confidence intervals (CI 95%). (B). Mean concentrations (log
CFU/mL) of the five bacterial species ±SD (n =13). Marks represent individual values. The coefficients of
variations are indicated above the data. C acnes (dark blue), S epidermidis (light blue), S mitis (purple), M luteus
(red), and C xerosis (orange).
Finally, the adequate protocol to grow the five species consortium was at a pH of 6.5, a
temperature of 32°C, under anaerobic atmosphere for 8 hours. The reproducibility of this
method was assessed by proceeding to 13 independent assays. Bacteria concentrations in
the consortium were measured and their proportions were calculated (Figure 4A and B).
In terms of population ratios (%,Figure 4A), the most important variation was observed
on C acnes (CI 95% =31.6–42.8%). The least concentrated bacteria (C xerosis and M luteus)
Figure 3. Proportions of bacteria in the consortium containing C acnes (dark blue), S epidermidis (light blue),
S mitis (purple), M luteus (red) and C xerosis (orange) with or without oxygen. Species proportion (%)in the
consortium is the ratio between a species concentration (in CFU/mL) and the concentration of total bacteria
(in CFU/mL) multiplied by 100.
Figure 4. Reproducibility of the consortium in 13 independent assays. (A). Mean species proportions in the
consortium (%,n =13). The whiskers are the confidence intervals (CI 95%). (B). Mean concentrations (log
CFU/mL) of the five bacterial species ±SD (n =13). Marks represent individual values. The coefficients of
variations are indicated above the data. C acnes (dark blue), S epidermidis (light blue), S mitis (purple), M luteus
(red), and C xerosis (orange).