548 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
PA, USA). This assay determines the lowest dilution of the phage cocktail necessary to
diminish biofilms formed by C. acnes.
BLEMISHED THREE-DIMENSIONAL SKIN MODEL
The blemish-prone three-dimensional epidermal skin model was constructed by infusing a
reconstituted human epidermis (RHE, prepared from the foreskin of three Caucasian donors)
with C. acnes (#6919, ThermoFisher Scientific) at levels of approximately 106 colony forming
units (CFU) per milliliter. The bacterial suspensions (diluted in phosphate-buffered saline, PBS)
were topically applied to the RHE and incubated for 72 hours at 37°C. The three individual
C. acnes bacteriophages used in the cocktail were each diluted according to their respective
titers to provide equivalent dosages. The bacteriophage cocktail was incubated on the three-
dimensional RHE for 72 hours after which analyses of tissue toxicity, C. acnes reduction, and
inflammatory factor levels were evaluated relative to an RHE not inoculated with C. acnes.
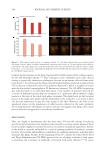
The evaluation of tissue toxicity was conducted via imaging analysis of the tissue
morphology post-staining with hemalun (J.T. Baker®, Phillipsburg, NJ, USA – blue/
purple color that stains nucleic acids) and eosin (Klinipath, Fisher Scientific, Hampton,
NH, USA – pink color that stains basic structures such as proteins). For a non-cytotoxic
negative control, the tissue was treated with PBS. For the cytotoxic positive control, the
tissue was treated with 0.1% SDS. Afterwards, the tissue samples were fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde, dehydrated, and paraffin embedded. The tissue was examined using a
Nikon Ni-E photomicroscope fitted with a Nikon DS-Ri2 camera (Tokyo, Japan).
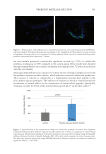
Relative C. acnes levels were assessed by collecting bacteria with swabs soaked in PBS
containing 0.1% Tween-80, which were then inoculated onto brain-heart infusion media
plates and incubated under anaerobic conditions at 37°C for 5 days. The number of CFUs
were counted and the relative reductions were calculated as described.
Changes in the gene expression of various inflammatory factors (IL-8, MIP-1β, and MCP-1) were
evaluated using TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA).
Briefly, RNA was collected and purified from the experimental and control tissue samples,
complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized, and the relative expression was determined via
reverse-transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) using a QuantStudio7
PCR System (Applied Biosystems) using RPLP0 as a housekeeping gene to normalize against.
The relative expression was calculated as =2−(Ct treated condition – Ct reference condition) ,where Ct =Ct
(target gene) – Ct (housekeeping gene) in each cDNA sample.
PILOT CLINICAL STUDY
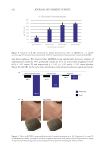
A pilot clinical study was conducted on a group of three female individuals (one Black, one
Caucasian, and one Hispanic/Latino) with mild to moderate blemished skin. Each participant
used a finished formulation containing 1% of the C. acnes targeted triple bacteriophage
cocktail twice daily once in the morning and once in the evening for a total of 7 days. The
participants were examined at baseline, 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days in the 1-week pilot study.
Investigated metrics included sebum levels that were determined using a Sebumeter® SM 815
PC (Courage and Khazaka electronic GmbH, Köln, Germany) and relative coproporphyrin
III fluorescence levels evaluated by porphyrins analysis algorithm on images captured in a
PA, USA). This assay determines the lowest dilution of the phage cocktail necessary to
diminish biofilms formed by C. acnes.
BLEMISHED THREE-DIMENSIONAL SKIN MODEL
The blemish-prone three-dimensional epidermal skin model was constructed by infusing a
reconstituted human epidermis (RHE, prepared from the foreskin of three Caucasian donors)
with C. acnes (#6919, ThermoFisher Scientific) at levels of approximately 106 colony forming
units (CFU) per milliliter. The bacterial suspensions (diluted in phosphate-buffered saline, PBS)
were topically applied to the RHE and incubated for 72 hours at 37°C. The three individual
C. acnes bacteriophages used in the cocktail were each diluted according to their respective
titers to provide equivalent dosages. The bacteriophage cocktail was incubated on the three-
dimensional RHE for 72 hours after which analyses of tissue toxicity, C. acnes reduction, and
inflammatory factor levels were evaluated relative to an RHE not inoculated with C. acnes.
The evaluation of tissue toxicity was conducted via imaging analysis of the tissue
morphology post-staining with hemalun (J.T. Baker®, Phillipsburg, NJ, USA – blue/
purple color that stains nucleic acids) and eosin (Klinipath, Fisher Scientific, Hampton,
NH, USA – pink color that stains basic structures such as proteins). For a non-cytotoxic
negative control, the tissue was treated with PBS. For the cytotoxic positive control, the
tissue was treated with 0.1% SDS. Afterwards, the tissue samples were fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde, dehydrated, and paraffin embedded. The tissue was examined using a
Nikon Ni-E photomicroscope fitted with a Nikon DS-Ri2 camera (Tokyo, Japan).
Relative C. acnes levels were assessed by collecting bacteria with swabs soaked in PBS
containing 0.1% Tween-80, which were then inoculated onto brain-heart infusion media
plates and incubated under anaerobic conditions at 37°C for 5 days. The number of CFUs
were counted and the relative reductions were calculated as described.
Changes in the gene expression of various inflammatory factors (IL-8, MIP-1β, and MCP-1) were
evaluated using TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA).
Briefly, RNA was collected and purified from the experimental and control tissue samples,
complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized, and the relative expression was determined via
reverse-transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) using a QuantStudio7
PCR System (Applied Biosystems) using RPLP0 as a housekeeping gene to normalize against.
The relative expression was calculated as =2−(Ct treated condition – Ct reference condition) ,where Ct =Ct
(target gene) – Ct (housekeeping gene) in each cDNA sample.
PILOT CLINICAL STUDY
A pilot clinical study was conducted on a group of three female individuals (one Black, one
Caucasian, and one Hispanic/Latino) with mild to moderate blemished skin. Each participant
used a finished formulation containing 1% of the C. acnes targeted triple bacteriophage
cocktail twice daily once in the morning and once in the evening for a total of 7 days. The
participants were examined at baseline, 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days in the 1-week pilot study.
Investigated metrics included sebum levels that were determined using a Sebumeter® SM 815
PC (Courage and Khazaka electronic GmbH, Köln, Germany) and relative coproporphyrin
III fluorescence levels evaluated by porphyrins analysis algorithm on images captured in a