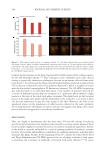
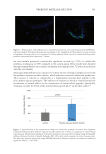
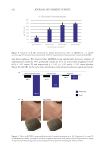
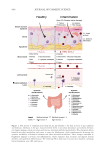
563 Prebiotic Micellar Solution
(2) McCabe R, Sterno I, Priebe S, Barnes R, Byng R. How do healthcare professionals interview patients to
assess suicide risk? BMC Psychiatry. 2017 17(1):122. doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1212-7
(3) Palumbo RV, Marraccini ME, Weyandt LL, et al. Interpersonal autonomic physiology: A systematic
review of the literature. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2017 21(2):99–141. doi:10.1177/1088868316628405
(4) Klatt J, Eimler SC, Krämer NC. Makeup your mind: the impact of styling on perceived competence and
warmth of female leaders. J Soc Psychol. 2016 156(5):483–497. doi:10.1080/00224545.2015.1129303
(5) von Baeyer H, Gahl GM, Riedinger H, Borowzak B, Kessel M. Nutritional behaviour of patients on
continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1981 18:193–198.
(6) Tran D, Andrade H, Durier G, et al. Supplementary Material from “Growth and Behaviour of Blue Mussels, a
Re-emerging Polar Resident, Follow a Strong Annual Rhythm Shaped by the Extreme High Arctic Light Regime”.
Royal Society 2020. doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.c.5144743.v1
(7) Watanabe K, Masuda M, Nakamura K, et al. A new makeup remover prepared with a system comprising
dual continuous channels (bicontinuous phase) of silicone oil and water. Intern J of Cosmetic Sci. Shiseido
Co, Research Center, Hayabuchi. Igarashi-2181 Japan. 2005 27(2):224–8558 Japan, Faculty of Education &
Human Science, Niigata University. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2494.2005.00259_4.x
(8) Skadiņa D, Nokalna I, Balcere A. Assessment of micellar water pH and product claims. Dermato.
2024 4(3):79–85. doi:10.3390/dermato4030009
(9) Lochhead M, Lochhead R, Grabenhofer R. Micellar water history, claims, functions, ingredients and
market relevance. Cosmet Toiletries. March 1, 2022.
(10) Sfriso R, Claypool JT. Microbial reference frames reveal distinct shifts in the skin microbiota after
cleansing. Microorganisms. 2020 8(11):1634. doi:10.3390/microorganisms8111634
(11) Lee HJ, Jeong SE, Lee S, Kim S, Han H, Jeon CO. Effects of cosmetics on the skin microbiome of facial
cheeks with different hydration levels. MicrobiologyOpen. 2018 7(2):e00557. doi:10.1002/mbo3.557
(12) Skin care and microbiome. In: Skin Microbiome Handbook 2021. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-819265-8.00021-8
(13) Henkens T, Kiekens F, Lebeer S, Claes I. Microbiome-Safe Cosmetic Cleaning Compositions 2019.
(14) Callewaert C, Knödlseder N, Karoglan A, Güell M, Paetzold B. Skin microbiome transplantation
and manipulation: current state of the art. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 19:624–631. doi:10.1016/j.
csbj.2021.01.001
(15) Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the
concept of prebiotics. J Nutr. 1995 125(6):1401–1412. doi:10.1093/jn/125.6.1401
(16) Bioestatística VS. Tópicos Avançados – Testes Não Paramétricos, Testes Diagnósticos, Medidas de Associação e
Concordância. Elsevier Brasil. ISBN: 978-85-352-9774-5 2018.
(17) Armitage P, Berry G, Matthews J. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 4th ed 2013. Wiley. ISBN:
9781118712492. https://www.perlego.com/book/1009731/statistical-methods-in-medical-research-pdf
(original work published 2013)
(18) Draelos ZD. The science behind skin care: cleansers. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018 17(1):8–14. doi:10.1111/
jocd.12469
(19) Goyal PS, Aswal VK. Micellar structure and inter-micelle interactions in micellar solutions: results of
small angle neutron scattering studies. Curr Sci. 2001 80:972–974. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92838-2
(20) Rosenthal M, Goldberg D, Aiello A, Larson E, Foxman B. Skin microbiota: microbial community
structure and its potential association with health and disease. Infect Genet Evol. 2011 11(5):839–848.
doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.03.022
(21) Vandegrift R, Bateman AC, Siemens KN, et al. Cleanliness in context: reconciling hygiene with a
modern microbial perspective. Microbiome. 2017 July 14 5(1):76. doi:10.1186/s40168-017-0294-2
(22) Kong HH. Skin microbiome: genomics-based insights into the diversity and role of skin microbes.
Trends Mol Med. 2011 17(6):320–328. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2011.01.013
(23) Cogen AL, Nizet V. Skin microbiota: a source of disease or defense? Br J Dermatol. 2008.
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08437.x/full
(2) McCabe R, Sterno I, Priebe S, Barnes R, Byng R. How do healthcare professionals interview patients to
assess suicide risk? BMC Psychiatry. 2017 17(1):122. doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1212-7
(3) Palumbo RV, Marraccini ME, Weyandt LL, et al. Interpersonal autonomic physiology: A systematic
review of the literature. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2017 21(2):99–141. doi:10.1177/1088868316628405
(4) Klatt J, Eimler SC, Krämer NC. Makeup your mind: the impact of styling on perceived competence and
warmth of female leaders. J Soc Psychol. 2016 156(5):483–497. doi:10.1080/00224545.2015.1129303
(5) von Baeyer H, Gahl GM, Riedinger H, Borowzak B, Kessel M. Nutritional behaviour of patients on
continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1981 18:193–198.
(6) Tran D, Andrade H, Durier G, et al. Supplementary Material from “Growth and Behaviour of Blue Mussels, a
Re-emerging Polar Resident, Follow a Strong Annual Rhythm Shaped by the Extreme High Arctic Light Regime”.
Royal Society 2020. doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.c.5144743.v1
(7) Watanabe K, Masuda M, Nakamura K, et al. A new makeup remover prepared with a system comprising
dual continuous channels (bicontinuous phase) of silicone oil and water. Intern J of Cosmetic Sci. Shiseido
Co, Research Center, Hayabuchi. Igarashi-2181 Japan. 2005 27(2):224–8558 Japan, Faculty of Education &
Human Science, Niigata University. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2494.2005.00259_4.x
(8) Skadiņa D, Nokalna I, Balcere A. Assessment of micellar water pH and product claims. Dermato.
2024 4(3):79–85. doi:10.3390/dermato4030009
(9) Lochhead M, Lochhead R, Grabenhofer R. Micellar water history, claims, functions, ingredients and
market relevance. Cosmet Toiletries. March 1, 2022.
(10) Sfriso R, Claypool JT. Microbial reference frames reveal distinct shifts in the skin microbiota after
cleansing. Microorganisms. 2020 8(11):1634. doi:10.3390/microorganisms8111634
(11) Lee HJ, Jeong SE, Lee S, Kim S, Han H, Jeon CO. Effects of cosmetics on the skin microbiome of facial
cheeks with different hydration levels. MicrobiologyOpen. 2018 7(2):e00557. doi:10.1002/mbo3.557
(12) Skin care and microbiome. In: Skin Microbiome Handbook 2021. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-819265-8.00021-8
(13) Henkens T, Kiekens F, Lebeer S, Claes I. Microbiome-Safe Cosmetic Cleaning Compositions 2019.
(14) Callewaert C, Knödlseder N, Karoglan A, Güell M, Paetzold B. Skin microbiome transplantation
and manipulation: current state of the art. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 19:624–631. doi:10.1016/j.
csbj.2021.01.001
(15) Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the
concept of prebiotics. J Nutr. 1995 125(6):1401–1412. doi:10.1093/jn/125.6.1401
(16) Bioestatística VS. Tópicos Avançados – Testes Não Paramétricos, Testes Diagnósticos, Medidas de Associação e
Concordância. Elsevier Brasil. ISBN: 978-85-352-9774-5 2018.
(17) Armitage P, Berry G, Matthews J. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 4th ed 2013. Wiley. ISBN:
9781118712492. https://www.perlego.com/book/1009731/statistical-methods-in-medical-research-pdf
(original work published 2013)
(18) Draelos ZD. The science behind skin care: cleansers. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018 17(1):8–14. doi:10.1111/
jocd.12469
(19) Goyal PS, Aswal VK. Micellar structure and inter-micelle interactions in micellar solutions: results of
small angle neutron scattering studies. Curr Sci. 2001 80:972–974. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92838-2
(20) Rosenthal M, Goldberg D, Aiello A, Larson E, Foxman B. Skin microbiota: microbial community
structure and its potential association with health and disease. Infect Genet Evol. 2011 11(5):839–848.
doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.03.022
(21) Vandegrift R, Bateman AC, Siemens KN, et al. Cleanliness in context: reconciling hygiene with a
modern microbial perspective. Microbiome. 2017 July 14 5(1):76. doi:10.1186/s40168-017-0294-2
(22) Kong HH. Skin microbiome: genomics-based insights into the diversity and role of skin microbes.
Trends Mol Med. 2011 17(6):320–328. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2011.01.013
(23) Cogen AL, Nizet V. Skin microbiota: a source of disease or defense? Br J Dermatol. 2008.
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08437.x/full