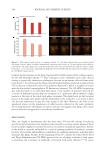
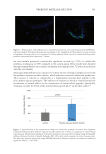
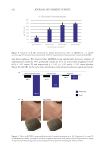
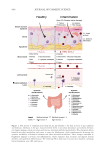
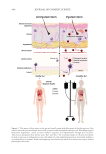
585 Specificities of Microbiota From Sensitive Skin
Twenty microliter reactions were performed in triplicate with the following reactants: 10 µL
PrimeTime™ Gene Expression Master Mix, 0.8 µL of forward primer, 0.8 µL of reverse
primer, 0.4 µL of probe, 6 µL of nuclease-free water, and 2 µL of DNA template. A reaction
was performed with a blank extraction as a DNA template, and another was performed
with nuclease-free water as a DNA template. The reactions were performed in white, low
profile 96-well plates, sealed with thermoresistant optical films. The qPCR was performed
in Agilent Aria Mx machine with the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation
95°C—3 minutes—1 cycle denaturation 95°C—5 seconds annealing/extension 60°C—
40 cycles final extension 60°C for 5 minutes and 1 cycle (Agilent, Les Ulis, France).
PACBIO LIBRARY PREPARATION
The primers used to amplify the full-length 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) gene
were composed of the specific regions 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and
1492R (5′-CGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) combined to asymmetrical barcodes. PCRs
were performed with the following solution mix: 10 µL of Q5 reaction buffer, 1 µL of
10 mM deoxinucleotides triphosphates (dNTPs), 2 µL of forward primer at 10 µM, 2 µL
of reverse primer at 10 µM, 2 µL of DNA template at 10-2 ng/µL, 0.5 µL of Q5 high-
fidelity DNA polymerase, 32.5 µL of nuclease-free water. The cycling conditions were as
follows: initial denaturation 95°C—during 30 seconds for 1 cycle denaturation at 95°C for
5 seconds during 30 cycles annealing at 59°C during 30 cycles extension at 72°C for 45
seconds and final extension at 72°C for 2 minutes during 1 cycle.
Amplifications were checked by electrophoresis on 1% v/v agarose gel for a 30 minute
migration, using 100 mV to assess the success of PCR reactions. Nucleic acid fragments
were separated by their length while moving through the agarose matrix then visualized
under ultraviolet light after adding intercalating agent like ethidium bromide (a band
was expected around 1,500 base pairs). Samples were then purified using AMPure™ PB
beads (PacBio, SanDiego, CA, USA) following manufacturer recommendations. The entire
PCR volume was mixed in equal ratio with AMPure™ XP beads, and two washes were
performed with 80% ethanol. Finally, DNA was eluted in 25 µL of nuclease-free water.
DNA concentration was measured using Qubit™ dsDNA HS assay kit (Thermofisher
Scientific) following manufacturer recommendations. Three µL of eluted DNA was used
for quantification. Samples were pooled in equal amounts to reach a final DNA mass of
1,000 ng. In total, 3 DNA pools were generated to ensure sufficient sample coverage. Pools
were then kept at −20°C until completion of library preparation.
Pools were sent to Maryland Genomics (Baltimore, United States) to perform a PacBio short-
insert library preparation, which included DNA damage repair, end repair/A-tail, ligation,
and AMPure™ PB bead purifications. Each pool was sequenced in a PacBio Sequel II 8M
run, 30-hour movie, to generate circular consensus sequences. Samples were demultiplexed
and exported in FASTQ format. FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a
biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding quality scores.
MOCK COMMUNITY PREPARATION
To assure the quality of the sequencing and bioinformatic workflows, as a positive control
a mock community composed of 14 wild species previously isolated from the skin was
Twenty microliter reactions were performed in triplicate with the following reactants: 10 µL
PrimeTime™ Gene Expression Master Mix, 0.8 µL of forward primer, 0.8 µL of reverse
primer, 0.4 µL of probe, 6 µL of nuclease-free water, and 2 µL of DNA template. A reaction
was performed with a blank extraction as a DNA template, and another was performed
with nuclease-free water as a DNA template. The reactions were performed in white, low
profile 96-well plates, sealed with thermoresistant optical films. The qPCR was performed
in Agilent Aria Mx machine with the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation
95°C—3 minutes—1 cycle denaturation 95°C—5 seconds annealing/extension 60°C—
40 cycles final extension 60°C for 5 minutes and 1 cycle (Agilent, Les Ulis, France).
PACBIO LIBRARY PREPARATION
The primers used to amplify the full-length 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) gene
were composed of the specific regions 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and
1492R (5′-CGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) combined to asymmetrical barcodes. PCRs
were performed with the following solution mix: 10 µL of Q5 reaction buffer, 1 µL of
10 mM deoxinucleotides triphosphates (dNTPs), 2 µL of forward primer at 10 µM, 2 µL
of reverse primer at 10 µM, 2 µL of DNA template at 10-2 ng/µL, 0.5 µL of Q5 high-
fidelity DNA polymerase, 32.5 µL of nuclease-free water. The cycling conditions were as
follows: initial denaturation 95°C—during 30 seconds for 1 cycle denaturation at 95°C for
5 seconds during 30 cycles annealing at 59°C during 30 cycles extension at 72°C for 45
seconds and final extension at 72°C for 2 minutes during 1 cycle.
Amplifications were checked by electrophoresis on 1% v/v agarose gel for a 30 minute
migration, using 100 mV to assess the success of PCR reactions. Nucleic acid fragments
were separated by their length while moving through the agarose matrix then visualized
under ultraviolet light after adding intercalating agent like ethidium bromide (a band
was expected around 1,500 base pairs). Samples were then purified using AMPure™ PB
beads (PacBio, SanDiego, CA, USA) following manufacturer recommendations. The entire
PCR volume was mixed in equal ratio with AMPure™ XP beads, and two washes were
performed with 80% ethanol. Finally, DNA was eluted in 25 µL of nuclease-free water.
DNA concentration was measured using Qubit™ dsDNA HS assay kit (Thermofisher
Scientific) following manufacturer recommendations. Three µL of eluted DNA was used
for quantification. Samples were pooled in equal amounts to reach a final DNA mass of
1,000 ng. In total, 3 DNA pools were generated to ensure sufficient sample coverage. Pools
were then kept at −20°C until completion of library preparation.
Pools were sent to Maryland Genomics (Baltimore, United States) to perform a PacBio short-
insert library preparation, which included DNA damage repair, end repair/A-tail, ligation,
and AMPure™ PB bead purifications. Each pool was sequenced in a PacBio Sequel II 8M
run, 30-hour movie, to generate circular consensus sequences. Samples were demultiplexed
and exported in FASTQ format. FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a
biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding quality scores.
MOCK COMMUNITY PREPARATION
To assure the quality of the sequencing and bioinformatic workflows, as a positive control
a mock community composed of 14 wild species previously isolated from the skin was