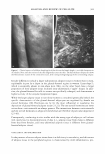
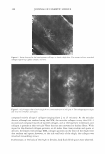
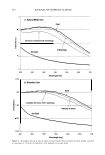
Improvement a 50 45 40 35 Improvement 30 b s en u u,-CD ,:, - ca I. u 0 ti) U-.:t U) 0 I. - CD Improvement ti) C ABILITY OF LOTIONS TO HYDRATE THE SKIN IN A HAND WASH STUDY 120 �------------------ - - 80 -+-LotionH -Lotion GR Lotion W Baseline .. · · .. i;ay O pm · · * · · No Product -40 ··· �············· ·············x.. �o..L_ ____________________x·· ..._J Evaluation The Ability of Lotions to Remove Damaged Surface Corneocytes in a Hand Wash Study Lotion H Lotion GR Lotion W No Product Ability of Lotions to Reduce Dry Skin (Scaling) in a Hand Wash Study 3.5 3 .x·············� .. .. 2.5 . •· �·�·--�·�·_ _____ --Lotion H 2 -Lotion GR 1.5 - - -4 - -.i.- Lotion W :--- .. : 1 · · * · · No Product 0.5 0 Baseline DayO pm Day 1 pm Day2 pm Day3 pm Evaluation Figure 2. Prevention of skin dryness. The ability of lotions to prevent soap-inducing dryness on the backs of the hands. The skin parameters assessed were: (a) Conductance as a measure of skin hydration. (b) Squamometry as a measure of surface corneocyte integrity. (c) Dryness assessed by a trained observer.
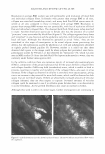
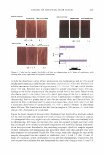
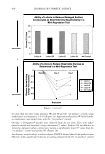
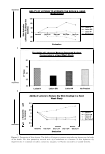
440 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE (Figure 2c). No significant difference between products was detected. In general, it can be concluded from the conductance and the squamometry results that product GR is the most effective moisturizer at reducing or even preventing the drying effects of soap on the skin. BENEFIT: PREVENTION OF PRIMARY IRRITATION-SURFACTANT PATCH TEST Occlusive patching with a 0.5% SLS solution produced a moderate-to-severe level of erythema on the control ("no product") site. For the two sites exposed to the product, the data was averaged. Applying lotion H prior to the SLS solution did little to prevent the induction of erythema in comparison to the "no product" control, whereas lotion GR was able to significantly reduce erythema induction (Figure 3). BENEFIT: REDUCTION IN PRE-EXISTING PRIMARY IRRITATION The two controls used for this procedure were a 1 % hydrocortisone gel and de-ionized water. Hydrocortisone is known to have anti-irritant properties and to significantly reduce observable, soap-induced erythema compared with water. This was found to be the case (Figure 4), and was used to validate the procedure. Lotion GR was shown to be as effective as 1 % hydrocortisone at reducing erythema after 24 hours, and significantly more effective than water, the "no product" control. In contrast, 20% benzocaine, a topical analgesic that has an anesthetic mode of action, did not reduce erythema more than water. VALIDATION: HOME-USE STUDY Tolerability (physician-assessed). All products were well tolerated by all participants, i.e., no panelist dropped out of this study. Improvement 2.5 �--�----------------------�I � 2 • e. 1.5 0 u U) ! 0.5 a+---- Lotion GR Lotion H No Product Figure 3. Prevention of primary dermal irritation. The ability of lotions to prevent surfactant-induced primary irritation was assessed by a trained observer evaluating erythema.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)