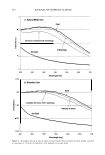
2005 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR Putting them all together there are 144 ester groups. Some recent ester developments include I). Hydrolysis resistant esters 455 Products in this class exhibit extraordinary resistance to hydrolysis both on the acidic and alkaline pH values. This is most easily seen when one attempts to run a saponification value. Saponification value is an analytical technique which allows one to determine the molecular weight of an ester, by breaking down the ester with base (KOH). In standard esters, the amount of KOH consumed in the analysis is measured and is stoichiometric with the molecular weight of the ester. Surprisingly, the esters of the present invention do not have the expected saponification value. They have, in fact, essentially no saponification value, since the ester must hydrolyze to provide the saponification value. Typical of these esters is the following: Hydrolytically stable esters are indicated for use in depilatories, hair relaxers, and as scalp protective barriers during the hair relaxing process. These esters will also provide hair conditioning and manageability. Other applications suggest further use in high pH hair dye emulsions as well as in non-transfer lipstick where they also contribute a high degree of gloss. 2). High humectany esters such as Glyceryl Citrate. These can be clear gels to clear liquids. These materials are anticipated to be humectants and will find application in lipstick products as well as in skin products. 3). Lanolin replacement esters such as Dipentaerythrityl Tetrabehenate/Polyhydroxystearatc. This product has the same consistency as lanolin however, unlike lanolin it has no odor and no taste. Additionally, the product can hold up to 3 times its weight in water. Application in lipstick when humectancy and transfer resistance arc desirable and in substantive skin humectant product are indicated.
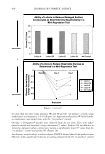
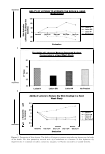
456 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE CATIONIC SURFACTANTS Tony O'Lenick Si/tech LLC, Dacula, GA Fatty quaternaries (quats) have been known for many years. Because of their fatty nature and positive charge, these compounds find application in a variety of areas including as conditioners for hair. Anyone that has added stearylalkonium chloride to sodium lauryl sulfate and observed the white sticky solid that results knows anionic and cationic surfactants can be incompatible. Anionic and cationic materials that produce a white gunky solid when mixed together are referred to as hard complexes. As the expression imp I ies the cationic and anionic compound possess properties which when added together form insoluble complexes (salts). We set out to determine if there are cationic materials having different structures which could be more soluble in the presence of anionic surfactants. The terms used here for quats and anionic materials are an adaptation of the work of Pearson used to describe acids and bases. Pearson proposed that "hard acids bind strongly to hard bases and soft acids bind softly to soft bases" 2 , the anionic and cationic interactions are exactly analogous. (Pearson R.G. Pearson, J Am Chem Soc, 85, 335 (I 963) The structural changes that can be made to cationic molecules can "soften" them, making them more compatible with anionic systems. The compatibility of specific quats with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and sodium laureth-3-sulfate (SLES), the foam properties of the combinations with SLS and SLES and the substantivity of these combinations with SLS and SLES are key factors in understanding the function of conditioners.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)