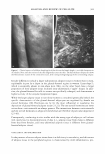
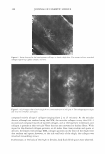
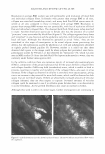
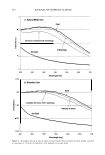
2005 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 463 REDUCING HAIR DAMAGE DURING HAIR LIGHTENING/BLEACHING Ali N. Syed, Ph.D., Narjis A. Askar, Ph.D., Khadijeh Saad and Thomas Ventura Avlon Industries, Inc., Bedford Park, IL Introduction During lightening/bleaching of hair, the melanin pigment is oxidatively removed (Zviak, 1986, p.216). Some of cystine bonds of the hair change to cystic acid residues protein matrix of the keratin is affected, as the pH of the lightening system is around I 0.5 to 11.0 (Robbins, 1979, pp.339-348). Additionally, some of the amide links of the keratin polypeptides undergo hydrolysis (Robbins, 1994, pp. I 33-134 ). The lightened hair fibers show remarkable decrease in elasticity and tensile strength during wet state and are brittle, dry, and rough in feel (Zviak, 1986, p. 228). The decrease in tensile strength is due to the internal damage that has permanently taken place in the cortex region, that is, protein matrix of the hair. Hair fibers show an increase in their porosity (Syed et al, 2002, pp. 57-64). Lightening of excessively curly hair causes even more damage. The excessively curly hair is weaker than the straight Caucasian or Oriental hair (Syed, 1997, pp. 235-259). Permanent coloring and bleaching was not practiced on relaxed hair because of the excessive damage done to the fibers. The purpose of the study is to develop products to reduce damage done to hair due to lightening and double treatments like relaxing and lightening or permanent waving and lightening. Materials and Methods The Lightener containing a mixture of persulfates (Sodium, Potassium and Ammonium) was formulated with special Self-Emulsifying Oils (SEO's) to protect the protein matrix of the hair fibers during lightening. Conventional lighteners which use plant based natural oils with high ACN (Alkane Carbon Number) values and high molecular weight for the purpose of reducing damage are not able to penetrate the hair. The Self Emulsifying Oils because of their polar nature and high HF (hydrophilicity factor) emulsify into very small particles of 0.50 microns and can be easily carried into the structure of the hair. These oils are stable to oxidation unlike natural oils, have excellent spread ability and good absorption in keratin structure. Being light they do not coat the hair unlike natural oils. Two lighteners were formulated with and without these oils in order to study their effect on hair. These oils are a mixture of: 1. Glyceryl Cocoate/Citrate/Lactate 2. Polyoxyethylene (40) Sorbitol Septaoleate 3. Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride A Developer containing Hydrogen Peroxide at 6.00% activity (20 Volume) was formulated to reduce the porosity of hair during lightening. A Method. which can detect even the minutest changes in the elastic behavior of hair fibers, was employed to check the effect ofSEO's. It is known as the intermittent stress relaxation test (ISR) performed using the Dynamic Mechanical Analyzer. In this method hair fibers are studied in the elastic region of0.5 to 1.0 percent strain. The elastic region was used in this study, as it is believed that during most of styling techniques such as combing, brushing, and blow-drying, stretching of hair remains in the elastic region. The intermittent stress relaxation test is useful in providing information on the extent of internal or chemical modification of hair fibers after treatment with hair products such as bleaches, permanent waves, relaxers or hair straighteners, and permanent /semi-permanent hair dyes. In this test single hair fiber (14.82 mm in length) was stretched to 0.5% strain or an elongation of 0.074 mm to a total length of 14.894 mm. This process of imposing the strain and allowing it to recover was repeated for IO times. Hair samples from the before and after treatments were randomly taken, measured and the stress (g/denier) required at 0.5% strain was recorded. The ratio (index) of after to before treatment was used to assess the internal modification of the hair fiber. Higher indices are indicative of stronger fibers. An index of 1.0 means no change in the strength of the fiber, while a value less than 1.0 indicates there was loss in strength to the hair fibers. Pre-cleaned one gram Caucasian hair fibers, 8 inches in length with mixed root to tip / tip to root orientation were divided into the upper and lower portions. The top 4 inches length of the tress was inserted into a plastic tube in order to protect it from any product contamination during treatment and this served as the untreated or before treatment. The remaining lower portion was then treated with the mixture of one part of the test bleach powder and two parts of its corresponding 20- volume developer for 60 minutes (no heat). The specimens were then rinsed for 3 minutes with water and treated with a conditioner for 5 minutes and then rinsed with tepid water for 3 minutes. The last step was the application of a low pH shampoo for 3 minutes, and the fibers were rinsed with tepid water for I min.
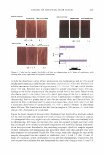
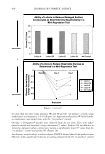
464 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Results and Discussion Results are graphically displayed in figure I and statistical analysis is shown in tables below. Figurel: JSR index of lighteners with and without SEO's Powder Bleaches FN 190-1288 versus FN 190-128D 1.00 : 0.80 "Cl .5 0.60 a:: 0.40 � 0.20 0.00 ..._ _________.____...._____ FN 190-1288 FN 190-128D Powder Bleaches 190-128B was formulated with SEO's and 190-128D was formulated without SEO's Tablet Statistical Analysis of lighteners with and without SEO's Basic Statistics Std. Error N 2 = FN 190-128D Levene's Test for t-test for Equalijy rl C_,_,._, � '35% Interval of Sid. Diflerenc Equal I s;g 12-tailedJ MAAn Difference Sig. ... OiffArflflr. ,�, u-• ISR assume 1 279 .260 4.722 138 .000 .07364 015595 .042805 , .104478 Equal not 4.874 137 40 .000 07364 015109 .043765 .103518 It can be seen from figure l that higher index was obtained on hair fibers treated with Lightener containing self-emulsifying oils (Index = 0.89) whereas the index with lightener without SEO's was 0.787. These indices can be translated into 11 % and 21 % loss in elastic strength. The results show that hair treated with Lightener formulated with self-emulsifying oils showed a low damage. The oils plasticize the protein matrix and protect the elasticity of the matrix. The oils moisturize the hair, as they are able to penetrate the cortex because of their small particle size. They also protect the amino acids of the matrix and prevent their degradation. References Syed, A. N., (1997). Ethnic Hair Care Products. Hair and Hair Care. Pp. 235-259. New York: Marcel Dekker. Inc. Syed, A. N., Ayoub, H., (2002). Correlating Porosity and Tensile Strength of Chemically Modified Hair. Pp. 57-64. Cosmetics and Toiletries magazine., Vol. 117, No. 11. Robbins, C.R., (1971). The Chemical Aspects of Bleaching Human Hair. J. Soc.Cosmet.Chem., 22: 339- 348. Robbins, C.R., (1994). Chemical and Physical behavior of Human Hair. Bleaching Human Hair. New York: Spriger-Verlag. Robbins, C.R., & Kelly, C., (1969). Amino Acid Analysis of Cosmetically Altered Hair. J. Soc.Cosmet.Chem., 20: 555. Zaviak, C., (1986). The Science of Hair Care. P. 229, New York: Mercel Dekker.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)