562 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
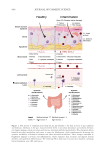
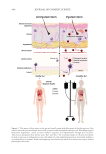
The host skin’s defense mechanisms are facilitated by a “chemical barrier” composed
of various defense molecules produced by epithelial cells. These molecules are either
consistently present or produced in response to external stimuli in different areas of the
epidermis including antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), proteases, and chemokines, such as
cytokines. These elements can directly hinder microbial growth or act as triggers and
facilitators of both innate and adaptive immune reactions.42
AMPs are typically small, amphipathic, and positively charged molecules that work by
disrupting microbial membranes and regulating cellular inflammatory processes. The
synthesis of AMPs by epithelial cells offers an additional layer of protection for immune
defense. Various families of AMPs have been investigated these include cathelicidins and
defensins. While over 30 cathelicidins have been identified in mammals, only LL-37 is
present in humans.42
Cathelicidins are activated in keratinocytes during inflammation34 and are the only
AMPs that act as defensive and signaling molecules. There are two separate pathways
through which cathelicidins operate: they exert direct antimicrobial properties against a
broad spectrum of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and they also trigger a sequence of cellular
reactions. These reactions include the release of cytokines, prostaglandins (PGD2) during
inflammation, chemokines, and adhesion molecules. Additionally, cathelicidins are crucial
for wound healing and tissue regeneration, which aid in skin re-epithelialization and wound
neovascularization.43
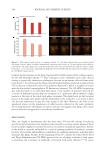
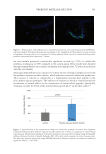
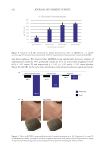
The results presented in this study indicate that the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution was
effective in removing various types of makeup without compromising the skin microbiome.
On the contrary, the solution increased the levels of commensal populations and reduced
the population of pathogenic bacteria. The formulation containing prebiotic agents may at
least partially explain the observed results.
CONCLUSION
A prebiotic micellar solution has shown efficacy in removing makeup and promoting skin
microbiome balance. By enhancing the presence of S epidermidis while decreasing S aureus
levels, this solution not only cleanses the skin but also provides protection against harmful
pathogens, all while preserving the beneficial microbiota. The incorporation of prebiotics
like inulin and xylitol can enhance the skin barrier, as evidenced by the upregulation
of cathelicidin expression. These findings underscore the potential of prebiotic micellar
solutions as a secure and efficient option for makeup removal, which offer additional
advantages for skin well-being.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financed by Chemyunion Ltda.
REFERENCES
(1) Korichi R, Pelle-de-Queral D, Gazano G, Aubert A. Why women use makeup: implication of
psychological traits in makeup functions. J Cosmet Sci. 2008 59(2):127–137.
The host skin’s defense mechanisms are facilitated by a “chemical barrier” composed
of various defense molecules produced by epithelial cells. These molecules are either
consistently present or produced in response to external stimuli in different areas of the
epidermis including antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), proteases, and chemokines, such as
cytokines. These elements can directly hinder microbial growth or act as triggers and
facilitators of both innate and adaptive immune reactions.42
AMPs are typically small, amphipathic, and positively charged molecules that work by
disrupting microbial membranes and regulating cellular inflammatory processes. The
synthesis of AMPs by epithelial cells offers an additional layer of protection for immune
defense. Various families of AMPs have been investigated these include cathelicidins and
defensins. While over 30 cathelicidins have been identified in mammals, only LL-37 is
present in humans.42
Cathelicidins are activated in keratinocytes during inflammation34 and are the only
AMPs that act as defensive and signaling molecules. There are two separate pathways
through which cathelicidins operate: they exert direct antimicrobial properties against a
broad spectrum of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and they also trigger a sequence of cellular
reactions. These reactions include the release of cytokines, prostaglandins (PGD2) during
inflammation, chemokines, and adhesion molecules. Additionally, cathelicidins are crucial
for wound healing and tissue regeneration, which aid in skin re-epithelialization and wound
neovascularization.43
The results presented in this study indicate that the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution was
effective in removing various types of makeup without compromising the skin microbiome.
On the contrary, the solution increased the levels of commensal populations and reduced
the population of pathogenic bacteria. The formulation containing prebiotic agents may at
least partially explain the observed results.
CONCLUSION
A prebiotic micellar solution has shown efficacy in removing makeup and promoting skin
microbiome balance. By enhancing the presence of S epidermidis while decreasing S aureus
levels, this solution not only cleanses the skin but also provides protection against harmful
pathogens, all while preserving the beneficial microbiota. The incorporation of prebiotics
like inulin and xylitol can enhance the skin barrier, as evidenced by the upregulation
of cathelicidin expression. These findings underscore the potential of prebiotic micellar
solutions as a secure and efficient option for makeup removal, which offer additional
advantages for skin well-being.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financed by Chemyunion Ltda.
REFERENCES
(1) Korichi R, Pelle-de-Queral D, Gazano G, Aubert A. Why women use makeup: implication of
psychological traits in makeup functions. J Cosmet Sci. 2008 59(2):127–137.