560 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
Examples of prebiotics include fructo-oligosaccharides, galacto-oligosaccharides,
glucomannans, oligosaccharides, inulin, isomalto-oligosaccharides, lactosucrose, lactulose,
palatinose, raffinose, sorbitol, xylitol, and xylo-oligosaccharides.29
In cosmetic formulations, prebiotics can be applied directly to the skin microbiota and
selectively increase the activity and growth of beneficial skin microbiota.29 The major
challenge in a cosmetic formulation containing prebiotics is the correct choice of components
to promote the growth of saprophytic or commensal (good) bacteria, such as S epidermidis,
to the detriment of pathogenic bacteria, such as S aureus.
To provide prebiotic properties, the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution presents a
combination of the polysaccharide inulin and xylitol. Inulin is a polysaccharide, like a
starch, that is available in the form of a white powder with a neutral taste.32 Inulin is used
as a functional ingredient in processed foods due to its primary characteristic: the b-(2,1)
bonds between fructose monomers cannot be digested by human intestinal enzymes. This
characteristic provides important applications in functional foods aimed at controlling type
2 diabetes, obesity, and other health conditions related to blood sugar. When ingested,
inulin passes through the mouth, stomach, and small intestine without being metabolized
until it enters the large intestine, where it is fermented by the colonic microflora. Inulin as
a prebiotic also stimulates the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon, which increases
the absorption of important minerals such as calcium and magnesium and synthesizes
vitamins from the B-complex.32,34
Clinical studies have shown that daily administration of inulin increases the number of
Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli in the colon while also reducing the number of Clostridia,
Bacteroidetes, and other nonspecific aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms.35 Related to
the activity of inulin in the digestive system, studies have shown that this carbohydrate
modulates the immune system, thus influencing the production of natural killer cells,
interleukins, and immunoglobin A.35 However, the scientific literature does not accurately
describe the clear role of topically applied inulin on the skin microbiota.
Xylitol, a naturally occurring five-carbon polyol (sugar alcohol), is used in several products
as a sugar substitute.36 It has beneficial effects for maintaining oral health when present
in chewing gum, including reducing the number of bacteria in saliva without altering
the oral microbial composition, while also providing an inhibitory action on the growth,
metabolism, and production of polysaccharides in Streptococcus mutans, the main causative
agent of dental caries.36
Regarding the topical application of xylitol, studies demonstrated that its association with
farnesol, a natural terpene found in essential oils that is commonly used in cosmetics and
perfumery to enhance sweet floral scents. It is also used as an antibacterial agent37 and has
acted selectively on the skin microbiota of patients with AD to prevent the formation and
dissolving of the biofilm formed by S. aureus, which selectively inhibits its growth,38 thus
indicating a selective action on the pathogen without influence on the resident microflora.39
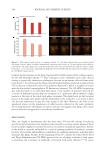
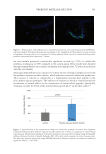
CATHELICIDIN (LL-37) IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE ASSAY
This assay aims to evaluate the positive modulation of cathelicidin (LL-37), the one
exclusively human antimicrobial peptide, that acts as a defense molecule in the skin.40 The
results of the evaluation of cathelicidin protein expression for the test formula prebiotic
aqueous micellar solution are shown in Figures 4 and 5. The images demonstrate that
Examples of prebiotics include fructo-oligosaccharides, galacto-oligosaccharides,
glucomannans, oligosaccharides, inulin, isomalto-oligosaccharides, lactosucrose, lactulose,
palatinose, raffinose, sorbitol, xylitol, and xylo-oligosaccharides.29
In cosmetic formulations, prebiotics can be applied directly to the skin microbiota and
selectively increase the activity and growth of beneficial skin microbiota.29 The major
challenge in a cosmetic formulation containing prebiotics is the correct choice of components
to promote the growth of saprophytic or commensal (good) bacteria, such as S epidermidis,
to the detriment of pathogenic bacteria, such as S aureus.
To provide prebiotic properties, the prebiotic aqueous micellar solution presents a
combination of the polysaccharide inulin and xylitol. Inulin is a polysaccharide, like a
starch, that is available in the form of a white powder with a neutral taste.32 Inulin is used
as a functional ingredient in processed foods due to its primary characteristic: the b-(2,1)
bonds between fructose monomers cannot be digested by human intestinal enzymes. This
characteristic provides important applications in functional foods aimed at controlling type
2 diabetes, obesity, and other health conditions related to blood sugar. When ingested,
inulin passes through the mouth, stomach, and small intestine without being metabolized
until it enters the large intestine, where it is fermented by the colonic microflora. Inulin as
a prebiotic also stimulates the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon, which increases
the absorption of important minerals such as calcium and magnesium and synthesizes
vitamins from the B-complex.32,34
Clinical studies have shown that daily administration of inulin increases the number of
Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli in the colon while also reducing the number of Clostridia,
Bacteroidetes, and other nonspecific aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms.35 Related to
the activity of inulin in the digestive system, studies have shown that this carbohydrate
modulates the immune system, thus influencing the production of natural killer cells,
interleukins, and immunoglobin A.35 However, the scientific literature does not accurately
describe the clear role of topically applied inulin on the skin microbiota.
Xylitol, a naturally occurring five-carbon polyol (sugar alcohol), is used in several products
as a sugar substitute.36 It has beneficial effects for maintaining oral health when present
in chewing gum, including reducing the number of bacteria in saliva without altering
the oral microbial composition, while also providing an inhibitory action on the growth,
metabolism, and production of polysaccharides in Streptococcus mutans, the main causative
agent of dental caries.36
Regarding the topical application of xylitol, studies demonstrated that its association with
farnesol, a natural terpene found in essential oils that is commonly used in cosmetics and
perfumery to enhance sweet floral scents. It is also used as an antibacterial agent37 and has
acted selectively on the skin microbiota of patients with AD to prevent the formation and
dissolving of the biofilm formed by S. aureus, which selectively inhibits its growth,38 thus
indicating a selective action on the pathogen without influence on the resident microflora.39
CATHELICIDIN (LL-37) IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE ASSAY
This assay aims to evaluate the positive modulation of cathelicidin (LL-37), the one
exclusively human antimicrobial peptide, that acts as a defense molecule in the skin.40 The
results of the evaluation of cathelicidin protein expression for the test formula prebiotic
aqueous micellar solution are shown in Figures 4 and 5. The images demonstrate that