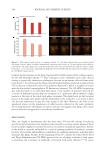
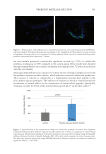
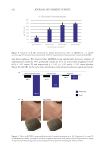
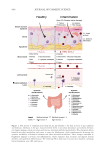
584 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RECRUITMENT OF PARTICIPANTS AND SAMPLING PROTOCOL
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (statement of
ethical principles applicable to medical research involving human beings, including research
on human biological material and identifiable data) and informed consent was obtained
from all subjects involved in the study. Seventy-eight volunteers assessed by dermatologists
were found to have healthy skin (free of eczema, psoriasis, wounds, and inflammatory
scaring) and were enrolled in this study. We recruited males and females, aged 18–77 years
old, and having the skin phototype ranging from 1–5. Among the 73 volunteers on which
the analysis was completed, 30 reported having thin and sensitive skin, and were tested
for their hypersensitivity to heat prior to sampling. More precisely, recruited panelists of
the sensitive skin cohort had an electrodermal response evaluated at 155% after a heating
stimulation on the cheeks versus before (using skin conductance response rate measured
with a Galvanic Skin Response electrode).
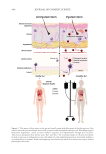
The skin site investigated in this study was the face. Participants were asked not to wash
their face 24 for hours prior to sample collection, as well as not to apply any cosmetics
during this time frame. A cotton swab immersed in 1.5 mL of skin sampling buffer (10%
glycerol, 0.1% Tween80 in 1× phosphate buffer saline) was used for sampling. An area of
4 cm2 on the cheek was vigorously rubbed with the cotton swab for 30 seconds. Swabs
were then vortexed for 30 seconds at maximum speed in a 1.5 mL microtube to resuspend
biological matter in solution. They were squeezed to maximize the volume of SSB (Single-
Stranded Binding buffer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, United States) in the
microtube by centrifugation. The samples were concentrated in 400 microliters (µL) of 1×
phosphate buffer saline and stored at −80°C until DNA extraction.
DNA EXTRACTION
DNA was extracted using the kit Zymo BIOMICS™ DNA miniprep (D4300, Zymo
Research, Irvine, CA, USA) following manufacturer recommendations including a
mechanical lysis step with BashingBead™ Lysis tube. Blank extractions without swab
samples were also performed to check for potential contamination. The final DNA was
eluted in 50 µL of nuclease-free water. DNA samples were kept at −80°C until bacterial
quantification.
DNA QUANTIFICATION
These TaqMan™ probe-based quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to measure the bacterial concentration of the samples.
The TaqMan™ probes have a 5′ fluorescent reporter dye and a 3′ quencher dye. These
probes are target-specific, and only bind to the DNA sequence of interest downstream
of one of the primers during the annealing step. A culture of Escherichia coli (E. coli) was
grown overnight at 37°C in brain heart infusion (BHI) medium, which was followed by
a DNA extraction. The eluted DNA was quantified using Qubit™ dsDNA HS assay kit
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) following manufacturer recommendations using 5 µL of E. coli
DNA solution to generate standard curves.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RECRUITMENT OF PARTICIPANTS AND SAMPLING PROTOCOL
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (statement of
ethical principles applicable to medical research involving human beings, including research
on human biological material and identifiable data) and informed consent was obtained
from all subjects involved in the study. Seventy-eight volunteers assessed by dermatologists
were found to have healthy skin (free of eczema, psoriasis, wounds, and inflammatory
scaring) and were enrolled in this study. We recruited males and females, aged 18–77 years
old, and having the skin phototype ranging from 1–5. Among the 73 volunteers on which
the analysis was completed, 30 reported having thin and sensitive skin, and were tested
for their hypersensitivity to heat prior to sampling. More precisely, recruited panelists of
the sensitive skin cohort had an electrodermal response evaluated at 155% after a heating
stimulation on the cheeks versus before (using skin conductance response rate measured
with a Galvanic Skin Response electrode).
The skin site investigated in this study was the face. Participants were asked not to wash
their face 24 for hours prior to sample collection, as well as not to apply any cosmetics
during this time frame. A cotton swab immersed in 1.5 mL of skin sampling buffer (10%
glycerol, 0.1% Tween80 in 1× phosphate buffer saline) was used for sampling. An area of
4 cm2 on the cheek was vigorously rubbed with the cotton swab for 30 seconds. Swabs
were then vortexed for 30 seconds at maximum speed in a 1.5 mL microtube to resuspend
biological matter in solution. They were squeezed to maximize the volume of SSB (Single-
Stranded Binding buffer Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, United States) in the
microtube by centrifugation. The samples were concentrated in 400 microliters (µL) of 1×
phosphate buffer saline and stored at −80°C until DNA extraction.
DNA EXTRACTION
DNA was extracted using the kit Zymo BIOMICS™ DNA miniprep (D4300, Zymo
Research, Irvine, CA, USA) following manufacturer recommendations including a
mechanical lysis step with BashingBead™ Lysis tube. Blank extractions without swab
samples were also performed to check for potential contamination. The final DNA was
eluted in 50 µL of nuclease-free water. DNA samples were kept at −80°C until bacterial
quantification.
DNA QUANTIFICATION
These TaqMan™ probe-based quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to measure the bacterial concentration of the samples.
The TaqMan™ probes have a 5′ fluorescent reporter dye and a 3′ quencher dye. These
probes are target-specific, and only bind to the DNA sequence of interest downstream
of one of the primers during the annealing step. A culture of Escherichia coli (E. coli) was
grown overnight at 37°C in brain heart infusion (BHI) medium, which was followed by
a DNA extraction. The eluted DNA was quantified using Qubit™ dsDNA HS assay kit
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) following manufacturer recommendations using 5 µL of E. coli
DNA solution to generate standard curves.